免费开源建站教学网站大数据智能营销系统
性能测试报告深度解析:从冰冷数据到火热洞察
本文将通过一份真实的JMeter测试报告,带你一步步解读数据背后的故事,并利用可视化图表将性能问题直观地呈现出来。
一、 报告概览:第一印象
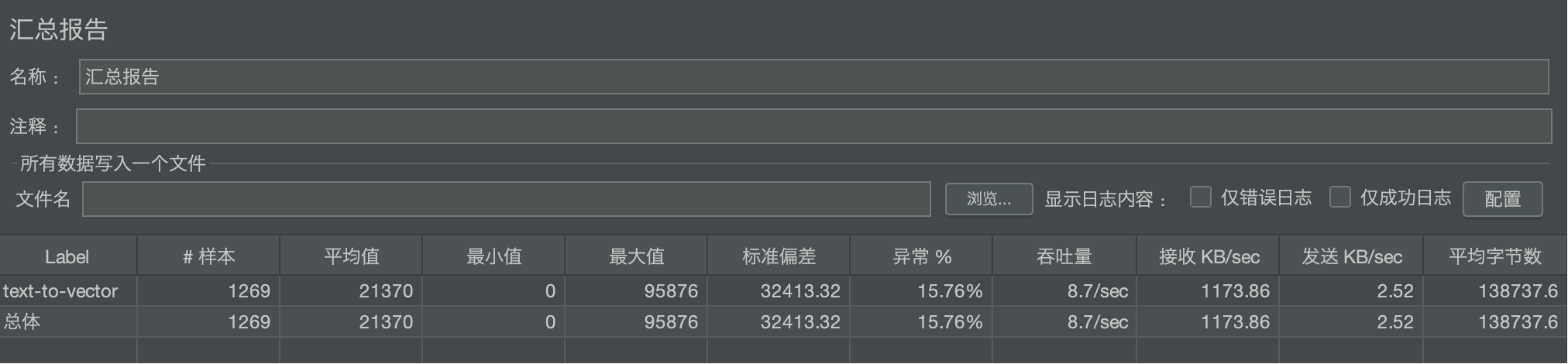
我们测试的对象是一个名为 text-to-vector 的API接口。在测试期间,总共发起了 1269 次请求。
核心摘要(Key Takeaways):
- 性能堪忧:平均响应时间高达 21.4 秒,用户体验极差。
- 稳定性不足:错误率(异常率)高达 15.76%,意味着每6-7个请求中就有一个失败。
- 吞吐量低:系统处理能力仅为 8.7 请求/秒,并发能力严重不足。
- 响应时间分布极度倾斜:大部分请求在12秒内完成,但少数请求极慢,最慢接近100秒,拖累了整体表现。
二、 数据可视化:让问题一目了然
单纯看数字是枯燥的。下面我们通过一组图表来直观感受性能状况。
1. 响应时间分布对比图
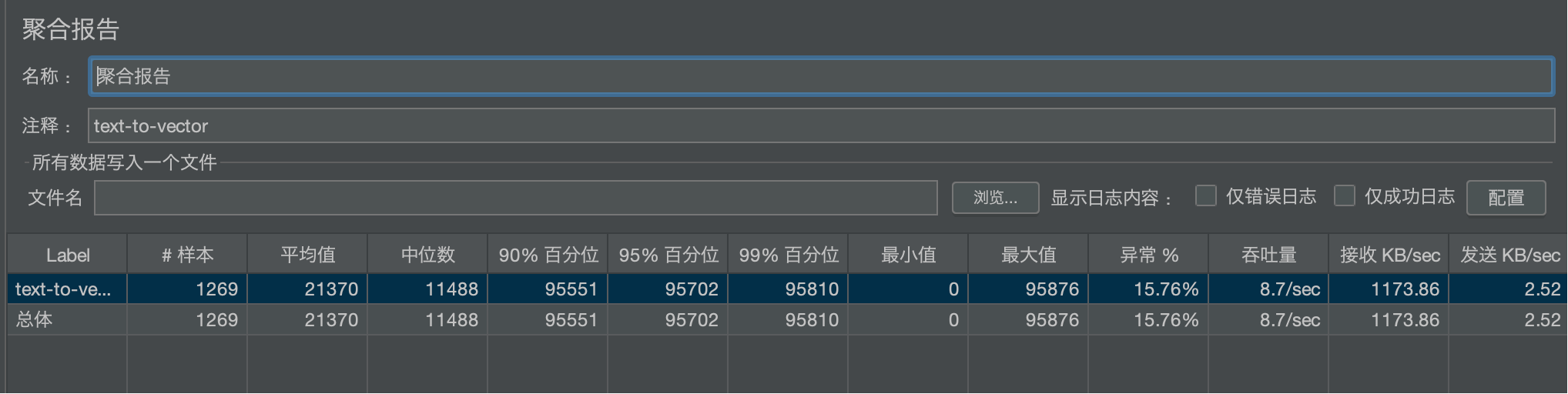
此图表揭示了平均值指标的“欺骗性”。中位数(代表典型用户体验)远低于平均值,说明系统表现非常不稳定,存在严重的“长尾问题”。
xychart-betatitle "响应时间关键指标对比 (单位: ms)"x-axis ["平均值", "中位数", "90%百分位", "95%百分位", "99%百分位", "最大值"]y-axis "响应时间 (ms)" 0 --> 100000bar [21370, 11488, 95551, 95702, 95810, 95876]
- 洞察:你必须关注 90% 或 95% 分位值,因为它们代表了绝大多数用户的体验。本项目中95%的用户等待了超过95秒,这是不可接受的。
2. 请求结果分布饼图
一个成功的系统,错误率应该接近于0。15.76%的错误率是重大警报。
- 洞察:在分析性能之前,必须优先排查并修复这些错误。高错误率会使其他性能数据(如平均响应时间)失真。
3. 系统吞吐量仪表盘
吞吐量是系统处理能力的直接体现。8.7/sec的吞吐量非常低。
- 洞察:低吞吐量和高响应时间通常指向同一问题:系统资源(CPU、内存、数据库、外部API调用)已成为瓶颈,无法有效处理并发请求。
三、 聚合报告 vs. 汇总报告:深度解析
为什么我们需要两种报告?因为它们提供了不同维度的视角。
| 特性 | 汇总报告 (Summary Report) | 聚合报告 (Aggregate Report) |
|---|---|---|
| 角色 | 巡逻警官 | 刑侦专家 |
| 目的 | 快速提供整体性能概况,发现明显问题。 | 进行深度分析,定位问题根源,评估用户体验。 |
| 核心差异 | 提供标准偏差 | 提供中位数、90/95/99%百分位 |
| 优点 | 简洁,一目了然。标准偏差能反映数据的波动性。 | 详细,通过百分位值能清晰描绘响应时间分布,精准定位“长尾”问题。 |
| 如何选择 | 日常监控、快速回归测试。 | 深入性能调优、瓶颈分析、生成正式测试报告。 |
关于“标准偏差”与“百分位”:
- 标准偏差 (32,413.32):这个值非常大(甚至比平均值还高),这本身就是一个强烈的信号,表明数据非常分散,响应时间极不稳定。但它无法告诉你具体有多少用户受到了影响。
- 百分位:它直接告诉你“有多少比例的用户经历了低于某个延迟”。例如,95%百分位为95.7秒,这是一个行动指标,意味着“我们必须优化系统,保证95%的用户响应时间在X秒以内”。
四、 综合分析与优化建议
基于所有数据和图表,我们可以形成一套完整的分析结论和建议。
根因分析假设:
- 资源瓶颈:最可能的原因是数据库查询缓慢、内存不足导致频繁GC,或CPU被某个进程占满。
- 同步阻塞:代码可能存在同步锁竞争,或是在单线程处理耗时任务,导致请求排队。
- 外部依赖:所调用的文本转向量服务(
text-to-vector)本身可能性能很差或不稳定,导致大量超时(这可能是高错误率的直接原因)。 - 网络或配置:不合理的超时设置、网络抖动等。
优化建议:
- 紧急:
- 优先排查15.76%的错误:查看应用日志,确定错误类型(超时、5XX错误、4XX错误?)。这通常是解决性能问题的最快路径。
- 监控系统资源:在测试期间,使用监控工具(如APM、Prometheus+Grafana)实时监控服务器的CPU、内存、磁盘I/O和网络使用情况。
- 高优先级:
- 分析慢请求:聚焦于那最慢的1% 的请求(99%百分位以上)。使用链路追踪(如SkyWalking, Zipkin)定位是在数据库、缓存还是外部API调用上耗时过长。
- 优化数据库:检查慢查询日志,为常用查询添加索引,优化SQL语句。
- 中长期:
- 引入异步处理:如果业务允许,可将耗时操作改为异步方式,先响应客户端“请求已接收”,再后台处理。
- 扩容与负载均衡:评估是否需要增加服务器实例,并通过负载均衡分散压力。
- 代码优化:优化算法、避免重复计算、引入缓存(如Redis)减少对底层资源的重复请求。
结论
一份性能测试报告不仅仅是一张填满数字的表格。通过聚合报告中的百分位数据深入理解用户体验,利用汇总报告快速抓住整体问题,再结合可视化图表进行直观传达,你就能将冰冷的数据转化为火热的、可行动的洞察。
记住,性能优化的目标不是让平均值看起来漂亮,而是让绝大多数用户的感受变得流畅和愉快。本报告中的系统目前处于严重不健康状态,需要立即投入资源进行排查和优化。
