沧州做网站价格爱站网站排行榜
目录
1、v-on事件
2、按键修饰符
3、显示和隐藏v-show
4、条件渲染v-if
1、v-on事件
创建button按钮有以下两种方式:
<button v-on:click="edit">修改</button><button @click="edit">修改</button>完整示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title>
</head>
<body><div id="app"><!-- 插值表达式 -->{{ msg }}<h1>{{web.title}}</h1><h2>{{web.url}}</h2><h1>{{number}}</h1><button v-on:click="edit">修改</button></div><script type="module">import {createApp, reactive, ref} from './vue.esm-browser.js'// const {createApp, reactive} = VuecreateApp({// setup选项,用于设置响应式数据和方法等setup(){const number = ref(10)number.value = 20const web = reactive({title:"开始学习vue啦",url:"vue.com"})const edit = () =>{web.url = "hhahaha"}return{msg:"sucess",web,number,edit}}}).mount("#app")// mount为挂载</script>
</body>
</html>
另:=>是es6中的语法。
举例说明:
(x)=> x + 6
相当于
function(x){return x+6;
}2、按键修饰符
回车:
回车 <input type="text" @keyup.enter="add(20,50)"> <br>空格:
空格 <input type="text" @keyup.space="add(10,80)"> <br>Tab键:
Tab <input type="text" @keydown.tab="add(5,32)"> <br>按键盘w键:
w <input type="text" @keyup.w="add(8,3)"> <br>组合键:
Ctrl+Enter <input type="text" @keyup.ctrl.enter="add(20,50)"> <br>
Ctrl+A <input type="text" @keyup.ctrl.a="add(20,50)"> <br>完整示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><!-- <script src="vue.global.js"></script> -->
</head>
<body><div id="app"><!-- 插值表达式 -->{{ msg }}<h1>{{web.title}}</h1><h2>{{web.url}}</h2> <h2>{{web.user}}</h2>回车 <input type="text" @keyup.enter="add(20,50)"> <br>空格 <input type="text" @keyup.space="add(10,80)"> <br>Tab <input type="text" @keydown.tab="add(5,32)"> <br>w <input type="text" @keyup.w="add(8,3)"> <br><!-- 组合键 -->Ctrl+Enter <input type="text" @keyup.ctrl.enter="add(20,50)"> <br>Ctrl+A <input type="text" @keyup.ctrl.a="add(20,50)"> <br></div><script type="module">import {createApp, reactive} from './vue.esm-browser.js'// const {createApp, reactive} = VuecreateApp({// setup选项,用于设置响应式数据和方法等setup(){const web = reactive({title:"开始学习vue啦",url:"vue.com",user:0})const add = (a,b) =>{web.user += a+b}return{msg:"sucess",web,add}}}).mount("#app")// mount为挂载</script>
</body>
</html>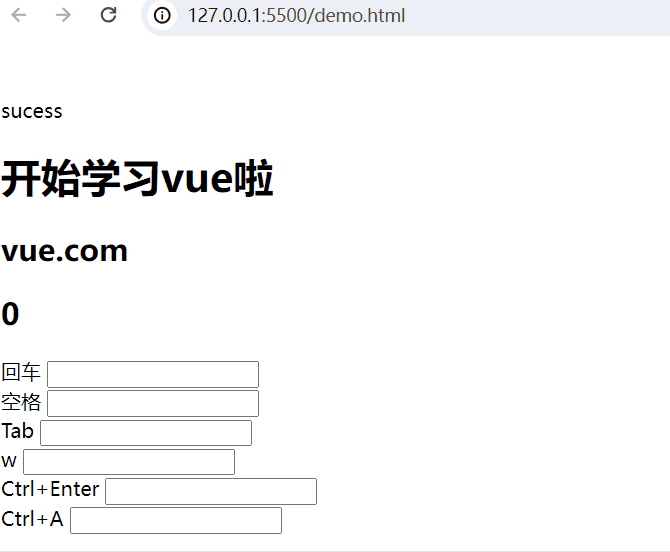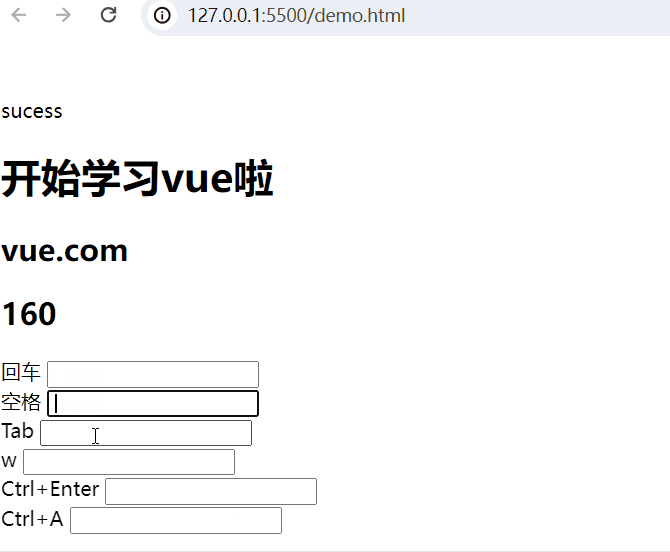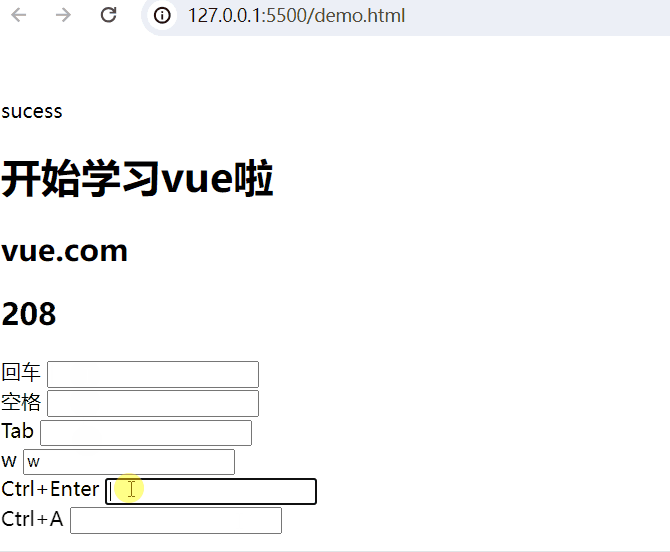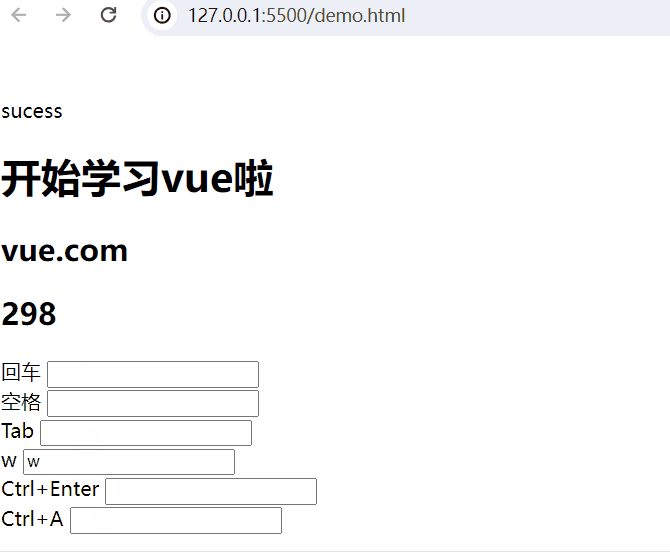
3、显示和隐藏v-show
实现的功能:当web.title为False,隐藏内容;当为True,显示内容。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><!-- <script src="vue.global.js"></script> -->
</head>
<body><div id="app"><!-- 插值表达式 --><h1>{{web.title}}</h1><p v-show="web.title">显示的内容</p><button @click="show">切换显示状态</button></div><script type="module">import {createApp, reactive} from './vue.esm-browser.js'// const {createApp, reactive} = VuecreateApp({// setup选项,用于设置响应式数据和方法等setup(){ const web = reactive({title:false})const show = () => {web.title = !web.title}return{web,show}}}).mount("#app")// mount为挂载</script>
</body>
</html> 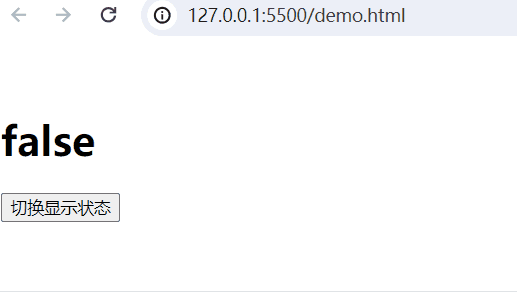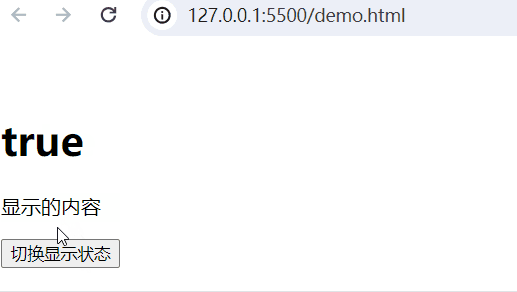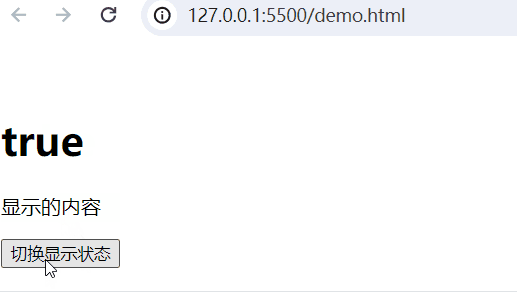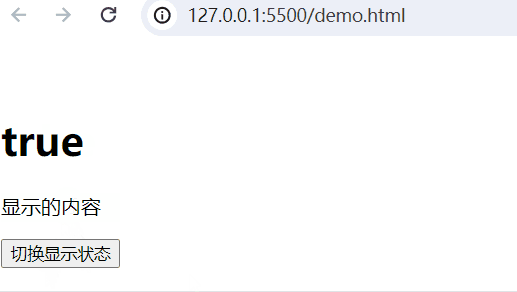
4、条件渲染v-if
通过v-if也可实现上述功能,当v-if为True,显示内容,当为False,则不显示,只需在上述代码添加以下一行代码即可。
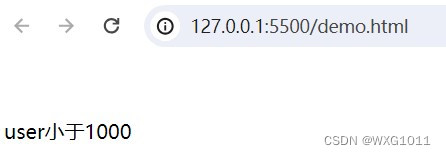
<p v-if="web.title">v-if显示的内容</p>实现的功能:当web.user在不同数值段,显示不同的内容。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><!-- <script src="vue.global.js"></script> -->
</head>
<body><div id="app"><!-- 插值表达式 --><p v-if="web.user < 1000">user小于1000</p><p v-else-if="web.user > 1000 && web.user < 2000">user小于2000</p><p v-else>user大于2000</p></div><script type="module">import {createApp, reactive} from './vue.esm-browser.js'// const {createApp, reactive} = VuecreateApp({// setup选项,用于设置响应式数据和方法等setup(){ const web = reactive({user:500})return{web }}}).mount("#app")// mount为挂载</script>
</body>
</html>