微网站自己怎么做的手游推广赚佣金的平台
文章目录
- 前言
- Hello World程序
- 运行
- 总结
前言
对于学习任何一种新的编程语言,我们都会从编写一个简单的Hello World程序开始。这是一个传统,也是一个开始。在这篇文章中,我们将一起学习如何在Rust中编写你的第一个程序:Hello World。
Hello World程序
fn main() {println!("Hello, world!");
}
这段Rust代码非常简单,但是每一部分都有其特定的含义。让我们逐一解析:
-
fn main() {}:这是Rust程序的主函数。当你运行一个Rust程序时,main函数是第一个被执行的函数。所有的Rust程序都需要有一个main函数作为程序的入口点。fn关键字用于声明一个新的函数。 -
{}:这是函数体的开始和结束。所有在这两个大括号之间的代码都是main函数的一部分。 -
println!():这是一个Rust的宏,用于在控制台上打印一行文本。注意,它后面有一个感叹号,这是因为在Rust中,宏和函数是不同的。如果你看到一个名字后面有感叹号,那么它就是一个宏。 -
"Hello, world!":这是被打印的字符串。在Rust中,字符串需要被包含在双引号中。
运行
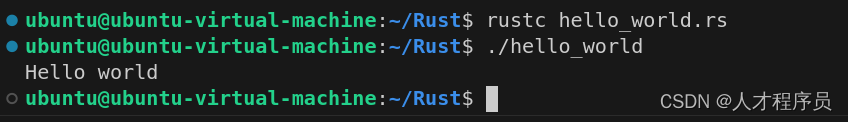
使用rustc 你的rust文件即可生成可执行文件,然后使用./hello_world即可运行
总结
恭喜你,你已经成功编写并运行了你的第一个Rust程序!这只是开始,Rust的世界还有很多等待你去探索和学习。虽然Hello World程序非常简单,但它是你学习Rust的第一步。通过这个程序,你已经学会了如何在Rust中定义函数,以及如何在控制台上打印消息。希望你能继续学习和探索Rust,发现它的强大和美丽。祝你学习愉快!
