北京门户网站有哪些网站建设主要推广方式
鸿蒙HarmonyOS开发实战往期文章必看:
HarmonyOS NEXT应用开发性能实践总结
最新版!“非常详细的” 鸿蒙HarmonyOS Next应用开发学习路线!(从零基础入门到精通)
非常详细的” 鸿蒙HarmonyOS Next应用开发学习路线!(从零基础入门到精通)
介绍
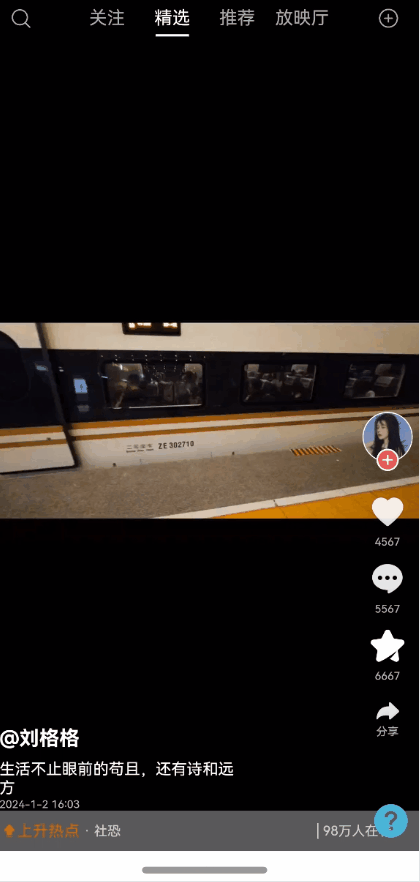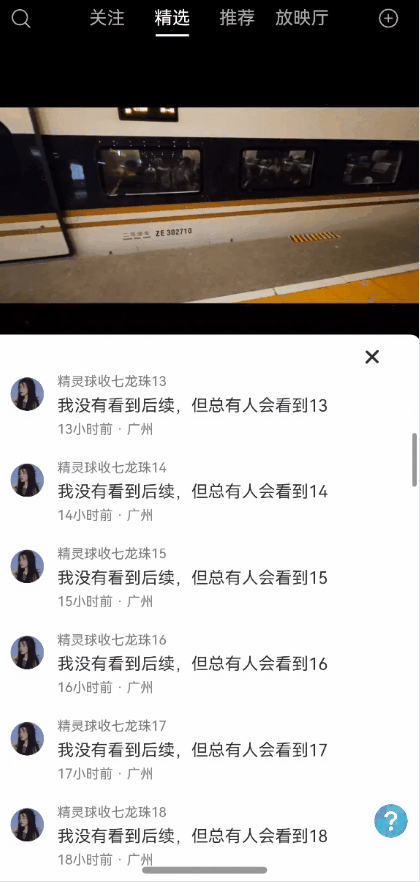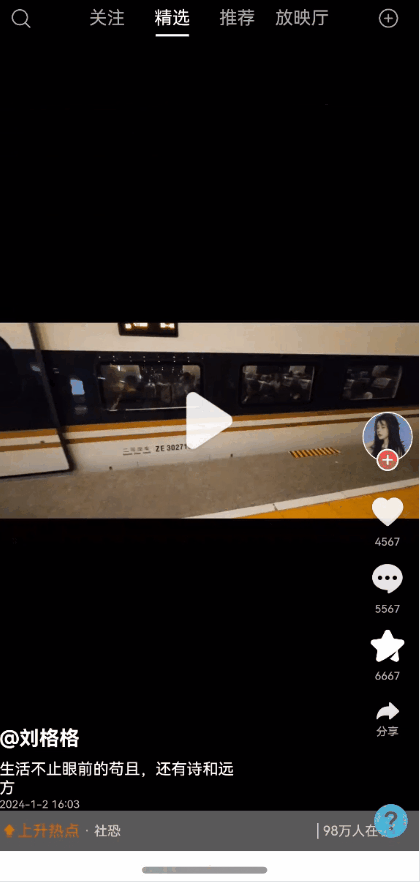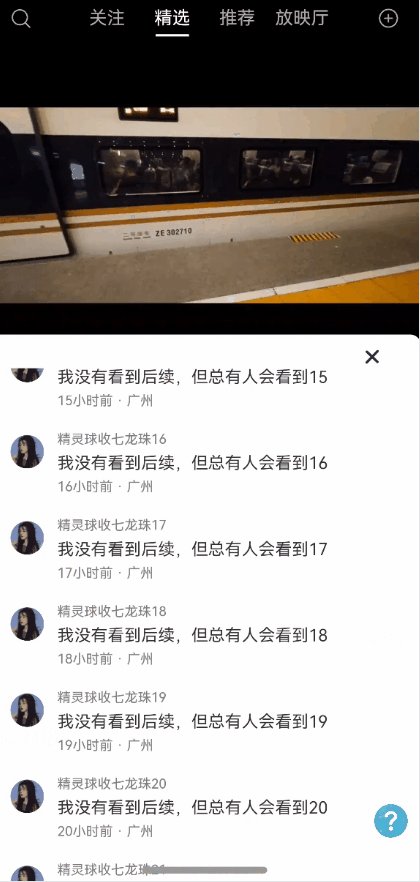
全局状态保留能力弹窗一种很常见的能力,能够保持状态,且支持全局控制显隐状态以及自定义布局。使用效果参考评论组件
效果图预览
使用说明
使用案例参考短视频案例
- 首先程序入口页对全局弹窗初始化,使用GlobalStateDialogManager.getGlobalStateDialogNodeController().setUIContext(this.getUIContext())。
- 在全局入口页设置弹窗位置GlobalStateDialog()。
- 在需要使用弹窗的页面引入GlobalStateDialogManager,使用operateGlobalStateDialog函数对弹窗显隐及内容布局进行配置,配置项参考GlobalStateDialogConfig。
实现思路
- 使用显隐控制来实现弹窗的状态保留能力,使用NodeContainer来动态操作弹窗的布局以及内容。源码参考GlobalStateDialog.ets。
/*** 全局状态保留能力弹窗组件*/
@Component
export struct GlobalStateDialog {@StorageProp('isShowGlobalStateDialog') isShowGlobalStateDialog: boolean = false;build() {Column() {、、、// 弹窗的布局与内容,使用NodeContainer提前占位NodeContainer(GlobalStateDialogManager.getGlobalStateDialogNodeController())}.visibility(this.isShowGlobalStateDialog ? Visibility.Visible : Visibility.Hidden).backgroundColor($r('app.color.ohos_global_state_dialog_background_color')).height($r('app.string.ohos_global_state_dialog_sixty_percent')).borderRadius({topLeft: $r('app.integer.ohos_global_state_dialog_number_10'),topRight: $r('app.integer.ohos_global_state_dialog_number_10')}).width($r('app.string.ohos_global_state_dialog_hundred_percent'))}
}/*** 全局状态保留能力弹窗控制器,对外提供fillGlobalStateDialog函数来操作弹窗的布局与内容*/
export class GlobalStateDialogNodeController extends NodeController {private uiContext: UIContext | null = null;private rootNode: BuilderNode<[ESObject]> | null = null;private wrapBuilder: WrappedBuilder<[ESObject]> | null = null;private params: ESObject;setUIContext(uiContext: UIContext) {this.uiContext = uiContext;}/*** 填充全局状态保留能力弹窗的布局以及内容* @param wrapBuilder 布局* @param params 内容*/fillGlobalStateDialog(wrapBuilder: WrappedBuilder<[ESObject]>, params: ESObject) {this.wrapBuilder = wrapBuilder;this.params = params;this.refreshNode();}makeNode(uiContext: UIContext): FrameNode | null {if (this.rootNode != null) {// 返回FrameNode节点return this.rootNode.getFrameNode();}// 返回null控制动态组件脱离绑定节点return null;}refreshNode() {if (!this.uiContext) {return;}// 创建节点,需要uiContextthis.rootNode = new BuilderNode(this.uiContext)// 创建组件this.rootNode.build(this.wrapBuilder, this.params)this.rebuild();}
}/*** 全局弹窗配置项*/
interface GlobalStateDialogConfig {isShowGlobalStateDialog?: boolean; // 显隐控制:true显示/false隐藏wrapBuilder?: WrappedBuilder<[ESObject]>; // 布局params?: ESObject; // 内容
}/*** 管理全局弹窗*/
export class GlobalStateDialogManager {private static globalStateDialogController: GlobalStateDialogNodeController = new GlobalStateDialogNodeController();static getGlobalStateDialogNodeController(): GlobalStateDialogNodeController {return GlobalStateDialogManager.globalStateDialogController;}/*** 控制全局弹窗的显隐及内容布局* @param globalStateDialogConfig 配置全局弹窗*/static operateGlobalStateDialog(globalStateDialogConfig: GlobalStateDialogConfig) {if (globalStateDialogConfig.isShowGlobalStateDialog !== undefined) {AppStorage.setOrCreate('isShowGlobalStateDialog', globalStateDialogConfig.isShowGlobalStateDialog);}if (globalStateDialogConfig.wrapBuilder) {GlobalStateDialogManager.globalStateDialogController.fillGlobalStateDialog(globalStateDialogConfig.wrapBuilder, globalStateDialogConfig.params);}}
}
- 使用Stack堆叠能力,为全局弹窗占位,且初始化相关数据。源码参考EntryView.ets.ets。
@Entry
@Component
struct EntryView {、、、aboutToAppear(): void {、、、GlobalStateDialogManager.getGlobalStateDialogNodeController().setUIContext(this.getUIContext());、、、}build() {Stack() {、、、// 全局状态保留能力弹窗GlobalStateDialog()}.alignContent(Alignment.BottomEnd).height('100%').backgroundColor($r('app.color.main_background_color'))}
}
高性能知识点
不涉及
工程结构&模块类型
utils // har类型
|---component
| |---GlobalStateDialog.ets // 全局状态保留能力弹窗