合肥网站建设过程如何让百度收录自己的网站信息
前言
这是最近的碰到的那个 和响应式相关的问题 特定的操作之后响应式对象不“响应“了 引起的一系列的文章
主要记录的是 vue 的相关实现机制
呵呵 理解本文需要 vue 的使用基础, js 的使用基础
测试用例
用例如下, 我们这里核心关注 事件的处理流程

问题的调试
整个事件的处理是 dom -> ElButton -> VueComponent.emit -> HelloWorld.handleClick
从面向对象的角度上面来看, ElButton.handleClick 是一个模板方法, 一部分固定的组件本身的业务处理, 一部分留给使用实例的地方来进行处理
ElButton 接管的是点击之后的所有业务, 他会做一些 ElButton 点击之后的自己需要处理的一部分业务, 然后还会 emit 一个 click 事件, 这个事件的处理是 留给具体的组件实例来关注的 [比如 HelloWorld 中的 el-button 就是一个组件实例]
我们这里从 dom基层 往上看
真实的再 dom 上面绑定事件 是在这里绑定, 这里封装了一层 function
这里面调用的传入的 handler, 传入的 handler 为一个 invoker, invoker 里面对应的是 el-button 的 handler 绑定的事件
这里就是上面的 dom -> ElButton 的这步转换

传入的函数为, 这里就是上面的 ElButton -> VueComponent.emit 的这步转换

绑定 dom 事件这里, 是在创建 dom 元素的时候, 有一系列创建的时候调用的钩子
这里 updateDOMListeners 中根据当前 VNode 来更新所有的 dom 的事件处理函数
这一这里有一层 createFnInvoker 的包装处理, 因此 回调函数是 invoker, 然后 invoker 再去调用的 handleClick

然后 VueComponent 的 事件处理器 到 VNode 的事件处理器 的转换是在组件对应的 render 函数

这部分就是 Vue 本身的事件处理相关
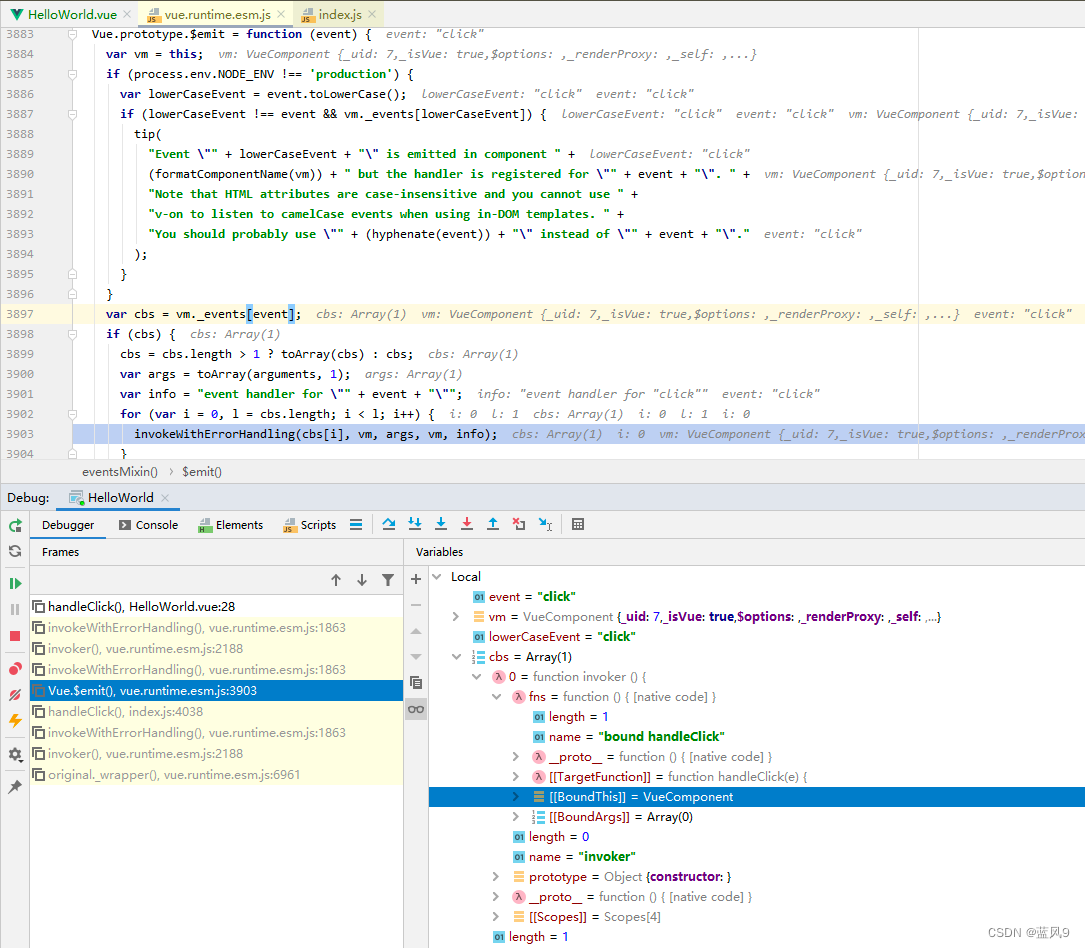
从注册的 事件处理表 中获取 click 对应的回调列表, 然后 依次调用
这里的 vm._events[‘click’] 对应的函数是 封装了一层 invoker 之后的 HelloWorld.handleClick
这里就是上面的 VueComponent.emit -> HelloWorld.handleClick 的这步转换
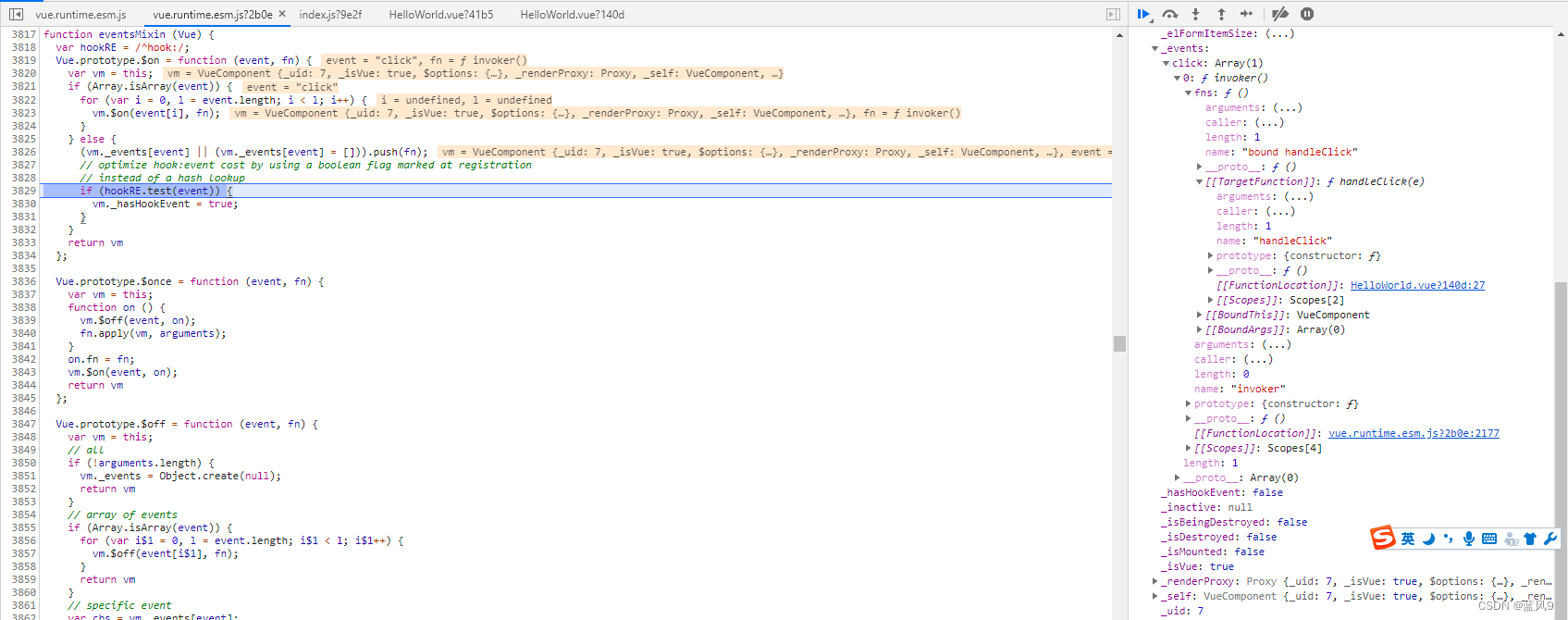
然后这个 ElButton 对应的 VueComponent 实例初始化的地方如下, initEvents 的地方会注册相关事件
初始化 Vue 组件的时候 注册 listener
这个可以再 VueComponent 的对象的 _events 上面查看, 这里注册的是 VueComponent 的事件管理
完
