南通网站开发公司花都网站建设公司
目录
一、库的操作
1.1创建数据库
1.2创建数据库案例
1.3字符集和校验规则
(1)查看系统默认字符集以及校验规则
(2)查看数据库支持的字符集
(3)查看数据库支持的字符集校验规则
(4)校验规则对数据库的影响
1.4操纵数据库
(1)查看数据库
(2)显示创建语句
(3)修改数据库
(4)数据库删除
1.5备份和恢复
(1)备份
(2)还原
(3)注意事项
1.6查看连接情况
二、表的操作
2.1创建表
2.2查看表结构
(1)显示所有表
(2)查看表结构
(3)查看表中的数据
2.3修改表
(1)向表中插入数据
(2)在表添加一个成员变量
(3)修改某个成员变量的类型
(4)删除某个成员变量
(5)修改表名
(6)修改成员变量名
2.4删除表
一、库的操作
1.1创建数据库
语法:
create database [if not exists] db_name [create_specification] [create_specification];
注:
- create和databese是关键字。
- db_name为你想要创建的库的名字。
- 句子结尾需要带分号;
- create_specification:分为数据库编码集和数据库字符集的校验集
- [ ]中的是可选项。
数据库编码集 -- 数据库未来存储数据的格式。
数据库校验集 -- 支持数据库进行字段比较使用的编码,本质也是一种读取数据库中数据采用的编码格式。
1.2创建数据库案例
- 创建名为 db1 的数据库
create database db1;
- 创建一个使用utf8字符集的db2数据库
create database db2 charset=utf8;
- 创建一个使用utf字符集,并带校对规则的 db3 数据库。
create database db3 charset=utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;
我们在配置环境一文曾经在配置文件中加过一行关于格式设置的指令:【MySQL】MySQL在Centos7环境下安装_mysql centos_青衫哥的博客-CSDN博客
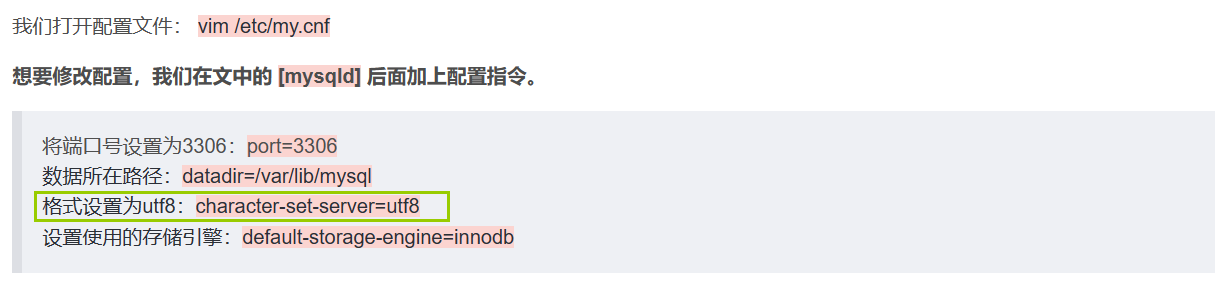
作用就是默认创建库使用utf8的格式。
1.3字符集和校验规则
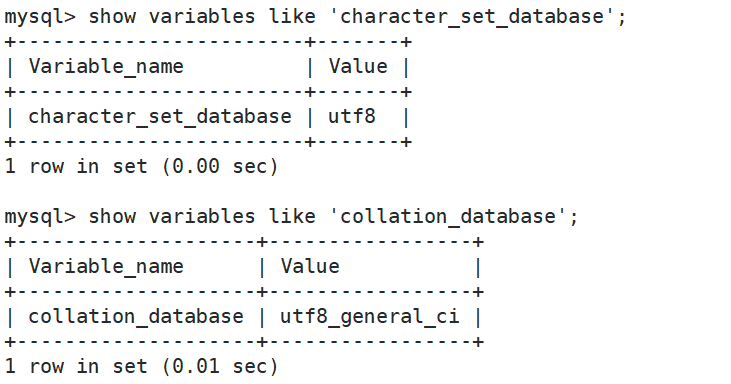
(1)查看系统默认字符集以及校验规则
show variables like 'character_set_database' ;show variables like 'collation_database' ;
(2)查看数据库支持的字符集
show charset;
字符集主要是控制用什么语言。比如utf8就可以使用中文。
(3)查看数据库支持的字符集校验规则
show collation;
(4)校验规则对数据库的影响
- 不区分大小写
- 创建一个数据库,校验规则使用utf8_ general_ ci[不区分大小写]
我们筛选字母a的时候,a和A都会筛选出来。

- 区分大小写
- 创建一个数据库,校验规则使用utf8_ bin[区分大小写]

1.4操纵数据库
(1)查看数据库
show databases;
(2)显示创建语句
show create database 数据库名;

- MySQL 建议我们关键字使用大写,但是不是必须的。
- 数据库名字的反引号``,是为了防止使用的数据库名刚好是关键字。
- /*!40100 default.... */ 这个不是注释,表示当前mysql版本大于4.01版本,就执行这句话。
(3)修改数据库
alter database db_name 修改内容;
说明: 对数据库的修改主要指的是修改数据库的字符集和校验规则。
例子:
我们将字符集修改为gbk之后,再查看就能看到创建字符集变为了gbk。

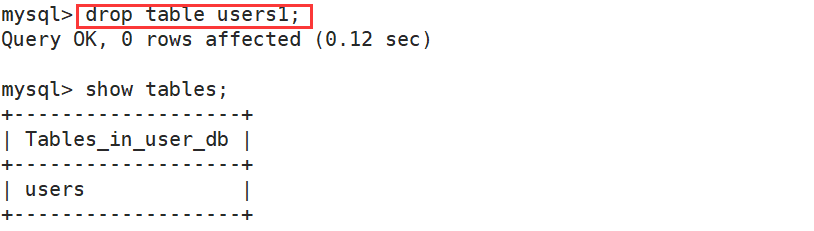
(4)数据库删除
drop database [if exists] db_ name;
- 数据库内部看不到对应的数据库
- 对应的数据库文件夹被删除,级联删除,里面的数据表全部被删
1.5备份和恢复
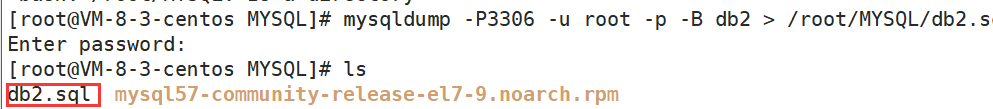
(1)备份
mysqldump -P3306 -u root -p 密码 -B 数据库名 > 数据库备份存储的文件路径
注意:是在命令行发送这条指令,不是在数据库中发送。

(2)还原
source 文件路径;
注:这条指令需要在mysql中输入。
输入后会在mysql中执行文件中保存的命令。
(3)注意事项
- 如果备份的不是整个数据库,而是其中的一张表,怎么做?
mysqldump -uroot -p 数据库名 表名 1 表名2 > 数据库备份存储的文件路径
- 同时备份多个数据库
mysqldump -u root -p -B 数据库名 1 数据库名 2 ... > 数据库存放路径
1.6查看连接情况
show processlist;

二、表的操作
2.1创建表
create table table_name (
field1 datatype,
field2 datatype,field3 datatype)character set 字符集 collate 校验规则 engine 存储引擎;
注:
- table_name是创建的表的名字。
- field是创建的成员名。
- datatype是类型。
- 最后设置字符集、校验规则和存储引擎可以忽略,会设置为我们默认的选择。
- 成员类型后面可以接comment ‘内容’ 。
案例:

我们查看/var/lib/mysql/user_db目录下面,我们可以看到生成了两个文件

frm存储着表结构,ibd存储着表索引,其实还有一个文件:表数据,这里因为使用的引擎是innodb,所以表数据和表结构存储在了一起。
2.2查看表结构
(1)显示所有表
show tables;
(2)查看表结构
desc 表名;
案例:

(3)查看表中的数据
select * from 表名;
2.3修改表
(1)向表中插入数据
insert into 表名 values ( 数据1 );
案例:

既可以单条插入,也可以多条插入。
(2)在表添加一个成员变量
alter table 表名 add 成员名 类型 (after 成员);
注:加了after可以指定加在某个成员后面,如果不加默认加到最后。
案例:
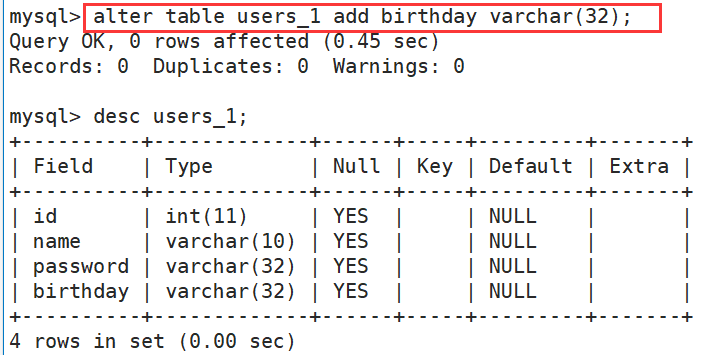
(3)修改某个成员变量的类型
alter table 表名 modify 成员名 类型;
案例:

(4)删除某个成员变量
alter table 表名 drop 成员名;
案例:
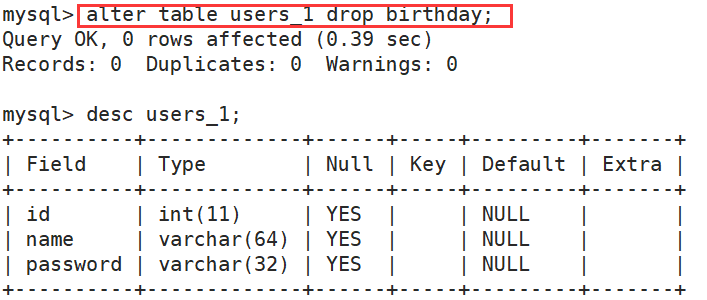
(5)修改表名
alter table 表名 rename 新表名;
案例:
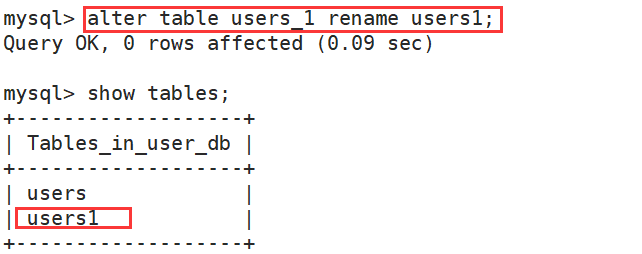
(6)修改成员变量名
alter table 表名 change 成员名 新成员名 类型;

2.4删除表
drop table [if not exists] 表名1,表名2......;
案例: