网站建设首选-云端高科seo关键字优化价格
Docker的资源控制:
对容器使用宿主机的资源进行限制,Docker 通过 Cgroup 来控制容器使用的资源配额,包括
CPU 内存 磁盘i/o
Docker 使用Linux自带的功能cgroup,Cgroup 是 ControlGroups 的缩写
C crontrol groups是Linux内核系统提供的一种可以限制,记录,隔离进程所使用的物理资源的机制,docker借助这个机制来实现资源的控制
cgroup本身是提供将进程进行分组化管理的功能和接口的基础结构,分配控制的机制来实现资源控制
Host:容器和宿主机共用一个网络命名空间
Container:容器和容器之间共用一个网络命名空间
其他的资源依然是隔离的,
-
CPU资源控制:
Linux通过CFS(completely Fair Scheduler 完全公平调度器),通过这个调度器来对各个进程对CPU的使用,CFS的调度器100ms.
我们自定义容器的调度周期,以及在这个周期之内,各个容器能够使用CPU的调度时间
--cpu-period设置容器调度CPU的周期
--cpu-quota 设置在每个周期内,容器可以使用CPU的时间
可以配合使用
CFS周期的有效范围是:1ms-1s --cpu-period 1000-1000000
容器使用CPU的配额时间必须,大于1ms, --cpu-quota的值,必须是>=1000
cd /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu
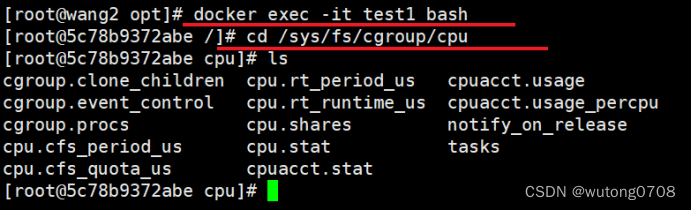
cpu.cfs_quota_us 容器占用的时间分片

如果配置是-1,那么容器在使用宿主机CPU的时间不做任何限制,想用多少用多少
cat cpu.cfs_period_us
表示 CFS 调度周期的长度,以微秒为单位。
在每个周期内,容器可以使用指定比例的 CPU 时间。默认情况下,cpu.cfs_period_us 的值是 100000(即 100 毫秒)
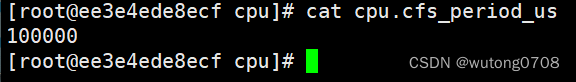
CFS调度周期的长度,微秒,容器可以使用指定比例的CPU时间,默认情况都是100毫秒
CFS调度器,100毫秒就是定义了一个周期,在这个周期内,调度任务(容器)的基本时间单位
cd /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu
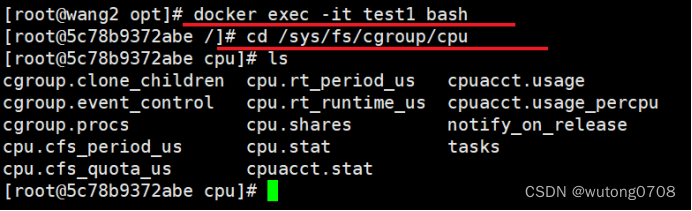
100毫秒一次调度器请求CPU资源,然后内核把CPU的资源分配给容器
Cpu.cfs_quota_us:调度器请求之后,根据配额,内核分配给容器使用CPU的时间
#进行CPU压力测试,正常启用的cpu,测试使用上限
正常创建容器(此时容器遵守的默认的占用CPU资源规则)
docker run -id --name c1 centos:7
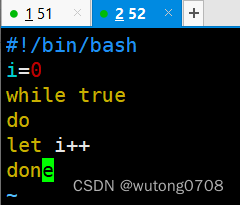
写一个循环脚本
先安装vim工具
yum -y install vim

#!/bin/bash
i=0
while true
do
let i++
done

chmod +x cpu.sh #赋权
./ cpu.sh #启动死循环脚本
top #可以看到这个脚本占了很多的cpu资源


CPU此时占用为100%,由此可以看出,如果在创建容器时不限制它CPU使用限制,是一件非常危险的事情,一旦某个容器的程序异常陷入死循环,将直接导致其他容器的中断
修改默认的容器时间分片上限规则,再次创建启动测试
cd /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/docker/
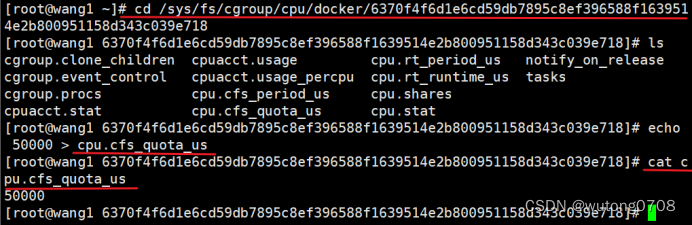

启动该容器的死循环脚本
另开一台终端查看

创建容器时指定容器的cpu资源占用量上限
#设置50%的比例分配CPU使用时间上限
docker run -itd --name test6 --cpu-quota 50000 centos:7 /bin/bash #可以重新创建一个容器并设置限额

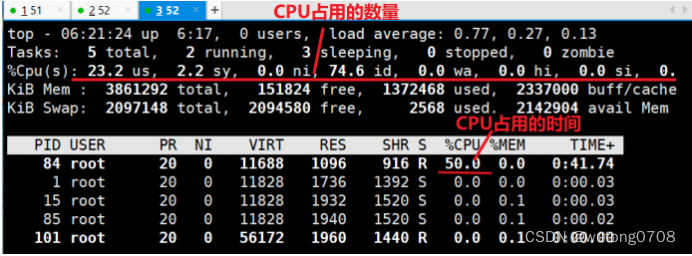
#可以看到cpu占用率接近50%,cgroups对cpu的控制起了效果
多cpu分配容器的使用上限

设置cpu资源的占用比
设置CPU的容器占用CPU的权重比,需要多个容器才能生效,创建容器时可以使用选项 --cpu-shares 数值(该数值要为1024的倍数,1024代表一份,当个容器占用cpu的份额由自身分配的份数除于所有容器占用cpu的份数,就为该容器所占用cpu资源的百分比)
--cpu-shares 指定容器占用cpu的份额,权重模式1024,1024代表一份,设置的值只能是1024的倍数
--cpu-shares 是给每个容器使用CPU设置了相对的权重,权重高的,可以使用的CPU的资源更多,但是,如果只有一个容器在运行,即使设置了权重,但是没有其他更高的权重容器来占用资源,权重低的容器依然不受限制
演示:
创建两个容器
Docker 通过 --cpu-shares 指定 CPU 份额,默认值为1024,值为1024的倍数。
#创建两个容器为 c1 和 c2,若只有这两个容器,设置容器的权重,使得c1和c2的CPU资源占比为1/3和2/3。
docker run -itd --name c1 --cpu-shares 512 centos:7
docker run -itd --name c2 --cpu-shares 1024 centos:7

#分别进入容器,进行压力测试
yum install -y epel-release
yum install -y stress

#stress 是一个用于模拟系统负载的工具,它可以测试系统在高负载条件下的稳定性。
stress -c 4 #产生四个进程,每个进程都反复不停的计算随机数的平方根

#查看容器运行状态(动态更新)
docker stats

可以看到在 CPU 进行时间片分配的时候,容器 c2 比容器 c1 多一倍的机会获得 CPU 的时间片。
但分配的结果取决于当时主机和其他容器的运行状态, 实际上也无法保证容器 c1 一定能获得 CPU 时间片。
比如容器 c1 的进程一直是空闲的,那么容器 c2 是可以获取比容器 c1 更多的 CPU 时间片的。
极端情况下,例如主机上只运行了一个容器,即使它的 CPU 份额只有 50,它也可以独占整个主机的 CPU 资源。
设置容器绑定CPU,容器只能使用指定的CPU内核
#先分配虚拟机1个CPU核数
docker run -itd --name test3 --cpuset-cpus 1 centos:7 /bin/bash

#进入容器,进行压力测试
yum install -y epel-release
yum install stress -y
stress -c 4
#退出容器,执行 top 命令再按 1 查看CPU使用情况

总结:
容器占用CPU时间
容器占用CPU的权重比(多个容器时,才有效)
容器占用CPU的内核数,绑定指定CPU的内核给容器使用
内存:
如和限制对内存的使用
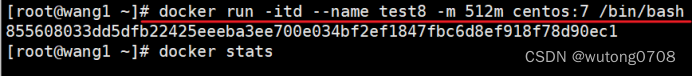

限制容器可用的swap 大小
//限制可用的 swap 大小, --memory-swap
docker run -itd --name test10 -m 512m --memory-swap=1g centos:7
限制使用swap:想要限制容器使用swap,必须和限制内存一块使用
如果限制了内存是512,swap是1G,那么容器实际上能够使用swap空间为1g-512m=512M
例如: -m 300m --memory-swap=1g 的含义为:容器可以使用300M 的物理内存,并且可以使用700M (1G - 300M)的swap。 设置为0或者不设置,则容器可以使用的 swap 大小为 -m 值的两倍。 如果 --memory-swap 的值和 -m 值相同,则容器不能使用swap。 如果 --memory-swap 值为 -1,它表示容器程序使用的内存受限,而可以使用的swap空间使用不受限制(宿主机有多少swap 容器就可以使用多少)。
总结:
如果不设置:-m 512m但是使用的swap的空间是-m的两倍
如果设置--memory-swap的值,和内存限制一样,容器就不能使用swap
-m 512m --memory-swap=1,内存受限制还是512M,但是容器使用swap空间不再受限制
磁盘i/o配额(了解):
读:
写:
限制容器在磁盘上的读速度:
--device-read-bps:限制某个设备上的读速度bps(数据量),单位可以是kb、mb(M)或者gb。
例:docker run -itd --name test11 --device-read-bps /dev/sda:1M centos:7 /bin/bash

限制容器在磁盘上的写速度:
--device-write-bps : 限制某个设备上的写速度bps(数据量),单位可以是kb、mb(M)或者gb。
例:docker run -itd --name test12 --device-write-bps /dev/sda:1mb centos:7 /bin/bash

演示:
#创建容器,并限制写速度
docker run -it --name test10 --device-write-bps /dev/sda:1mb centos:7 /bin/bash
![]()
dd if=/dev/zero of=test.out bs=1M count=10 oflag=direct #添加oflag参数以规避掉文件系统cache

Oflag=direct
在使用dd获取空字符集是从文件系统的缓存当中输入,速度是比较快的,禁用文件系统缓存,直接把数据写入磁盘,可以更真实的测试设备的性能,模拟直接写入物理设备的情况
限制容器读取的次数:
docker run -itd --name test4 --device-read-iops /dev/sda:100 centos:7 /bin/bash

限制读取操作,每秒100次
限制容器写入的次数:
docker run -itd --name test5 --device-write-iops /dev/sda:50 centos:7 /bin/bash

限制写入的操作,每秒50次
如何清理docker占用的磁盘空间
docker system prune -a
删除已经停止的容器
删除所有未被使用的网络设备
删除创建容器时的缓存,以及无用的数据卷,都是这条命令

总结今天的内容:
怎么对容器使用CPU进行限制(一定要会):
容器占用CPU的时间
容器占用CPU的权重
容器绑定CPU
容器对宿主机的内存使用限制:
-m
Swap:必须和限制内存一块使用
-m 512m --memory-wap=1g
磁盘i/o限制,了解即可
清理docker缓存
