做理财的网站深圳网站建设维护
如果对es的基础知识有不了解的可以看
es看这个文章就会使用了
1.分布式集群场景下的使用
单机的elasticsearch做数据存储,必然面临两个问题:海量数据存储问题、单点故障问题。
- 海量数据存储问题:将索引库从逻辑上拆分为N个分片(shard),存储到多个节点
- 单点故障问题:将分片数据在不同节点备份(replica )
ES集群相关概念:
-
集群(cluster):一组拥有共同的 cluster name 的 节点。
-
节点(node) :集群中的一个 Elasticearch 实例
-
分片(shard):索引可以被拆分为不同的部分进行存储,称为分片。在集群环境下,一个索引的不同分片可以拆分到不同的节点中
解决问题:数据量太大,单点存储量有限的问题。
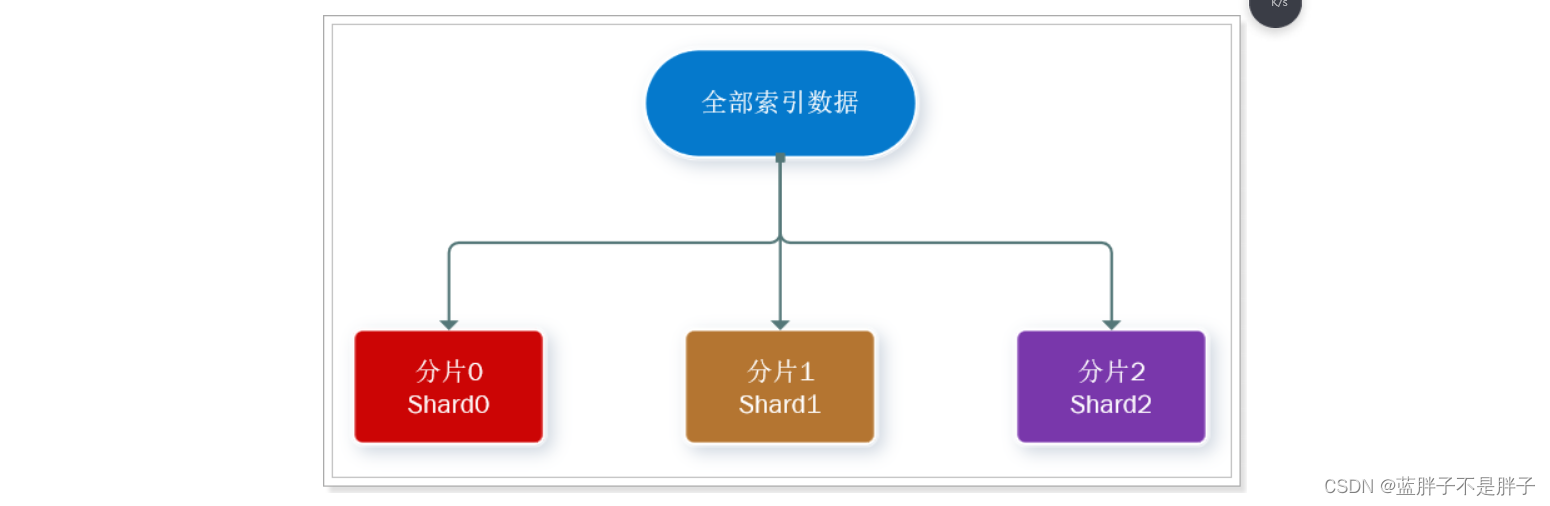
此处,我们把数据分成3片:shard0、shard1、shard2
-
主分片(Primary shard):相对于副本分片的定义。
-
副本分片(Replica shard)每个主分片可以有一个或者多个副本,数据和主分片一样。
数据备份可以保证高可用,但是每个分片备份一份,所需要的节点数量就会翻一倍,成本实在是太高了!
为了在高可用和成本间寻求平衡,我们可以这样做:
- 首先对数据分片,存储到不同节点
- 然后对每个分片进行备份,放到对方节点,完成互相备份
这样可以大大减少所需要的服务节点数量,如图,我们以3分片,每个分片备份一份为例:
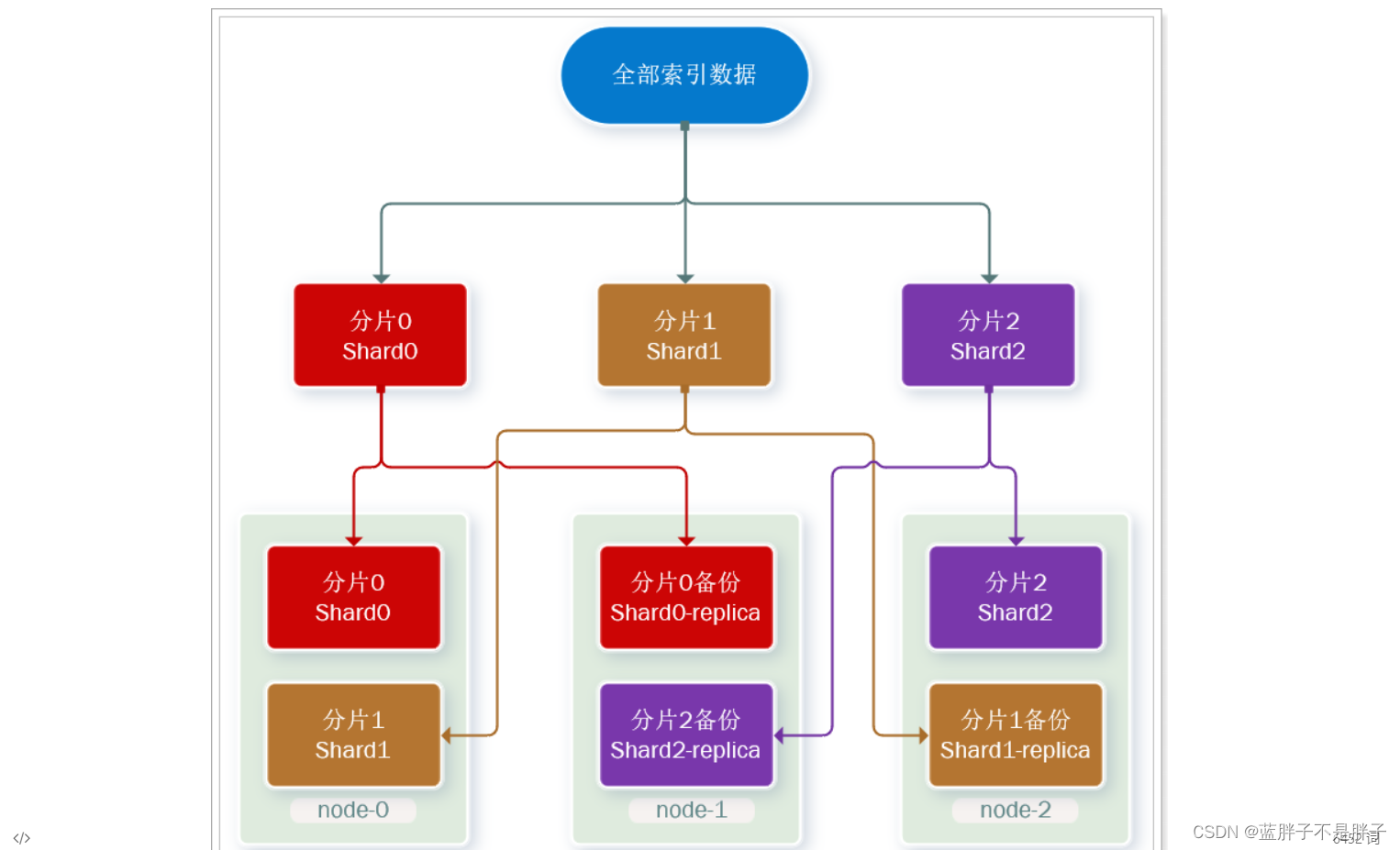
现在,每个分片都有1个备份,存储在3个节点:
- node0:保存了分片0和1
- node1:保存了分片0和2
- node2:保存了分片1和2
这样单一结点就算宕机,也可以备用
2.0.搭建ES集群
2.部署es集群
我们会在单机上利用docker容器(docker容器之间相互独立)运行多个es实例来模拟es集群。不过生产环境推荐大家每一台服务节点仅部署一个es的实例。
部署es集群可以直接使用docker-compose来完成,但这要求你的Linux虚拟机至少有4G的内存空间
2.1.创建es集群
首先编写一个docker-compose文件(yml或者yaml),内容如下:
- 9200端口已经在之前的结点中使用了,要么停止要么改端口,这三个结点都没有设置插件数据卷,实际开发记得指明
-
- discovery.seed_hosts 这里都是同一网络 ,实际开发中不同结点都是在不同网络机器上 比如 - discovery.seed_hosts=Machine1_IP:9200,Machine3_IP:9200
version: '2.2'
services:es01:image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.15.0container_name: es01environment:- node.name=es01- cluster.name=es-docker-cluster- discovery.seed_hosts=es02,es03- cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02,es03- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"volumes:- data01:/usr/share/elasticsearch/dataports:- 9210:9200networks:- elastices02:image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.15.0container_name: es02environment:- node.name=es02- cluster.name=es-docker-cluster- discovery.seed_hosts=es01,es03- cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02,es03- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"volumes:- data02:/usr/share/elasticsearch/dataports:- 9201:9200networks:- elastices03:image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.15.0container_name: es03environment:- node.name=es03- cluster.name=es-docker-cluster- discovery.seed_hosts=es01,es02- cluster.initial_master_nodes=es01,es02,es03- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"volumes:- data03:/usr/share/elasticsearch/datanetworks:- elasticports:- 9202:9200
volumes:data01:driver: localdata02:driver: localdata03:driver: localnetworks:elastic:driver: bridge
我的镜像名
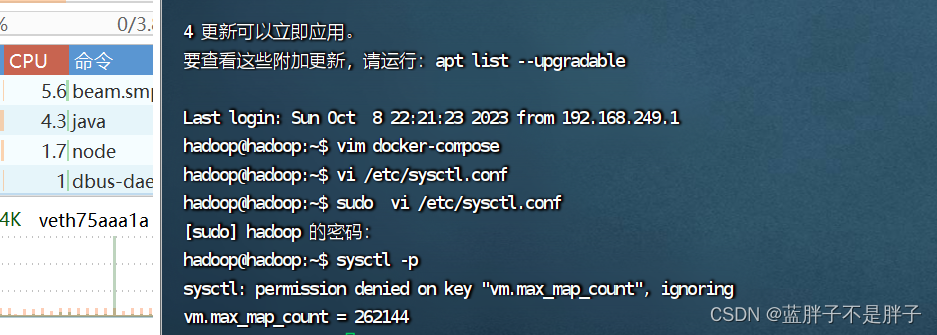
es运行需要修改一些linux系统权限,修改/etc/sysctl.conf文件
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
添加下面的内容:
vm.max_map_count=262144
然后执行命令,让配置生效:
sysctl -p
在docker-c通过docker-compose启动集群:
docker-compose up -d
如果报错 bootstrap checks failed. You must address the points described in the following [1] lines before starting Elasticsearch.
bootstrap check failure [1] of [1]: max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]
那么说明是内存警告问题 错误消息指出虚拟内存区域的 vm.max_map_count 参数设置得太低。
检查当前的 vm.max_map_count 值:运行以下命令来检查当前值:
sysctl vm.max_map_count
如果当前值低于 262144,那么你需要增加它。
增加 vm.max_map_count 的值:你可以使用以下命令来增加虚拟内存区域的值:
sudo sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
这会立即更改 vm.max_map_count 的值,但在系统重新启动后会重置为默认值。如果要永久更改此设置,你需要编辑 /etc/sysctl.conf 或 /etc/sysctl.d/ 下的配置文件,并添加或修改以下行:
vm.max_map_count=262144
然后保存文件并重新加载配置:
sudo sysctl -p
重新启动 Elasticsearch:一旦你增加了 vm.max_map_count 的值,重新启动 Elasticsearch,问题应该得到解决。
启动成功
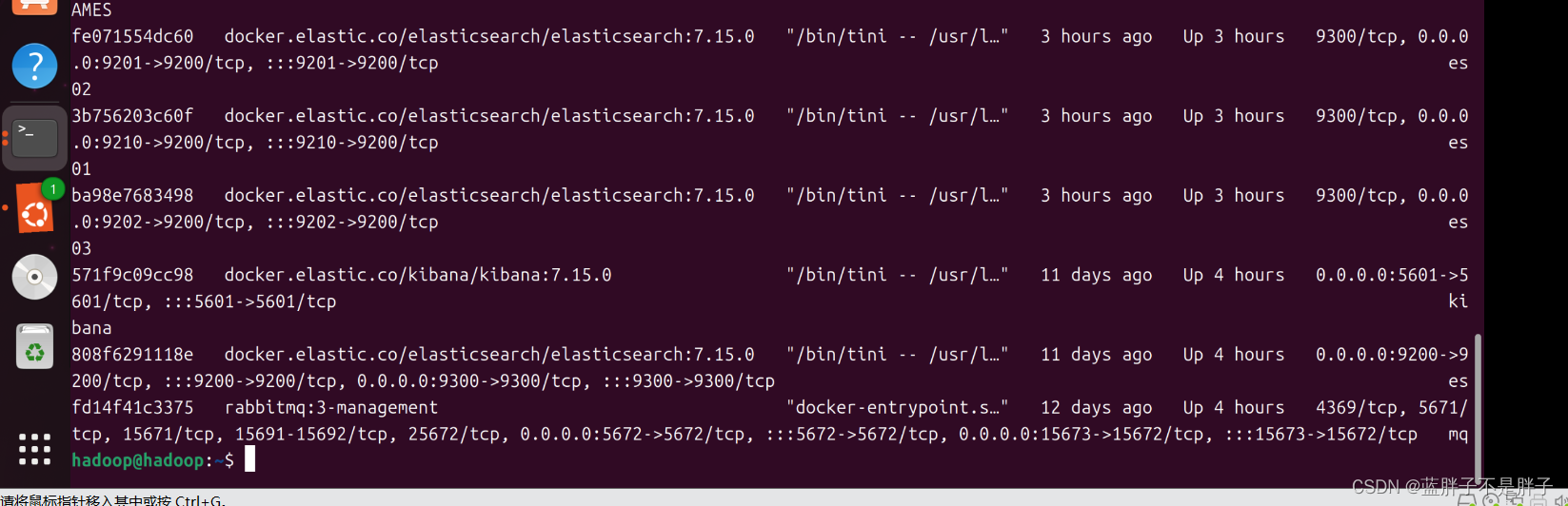
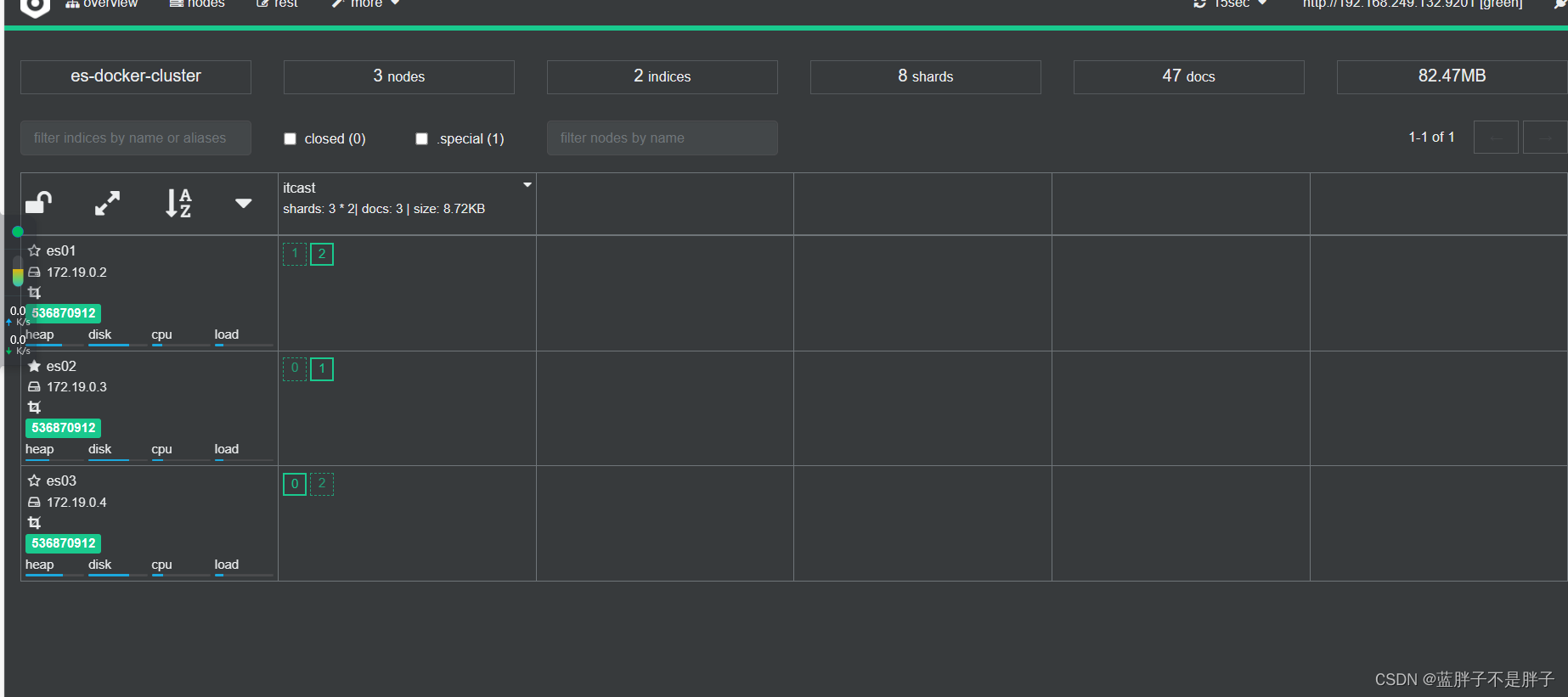
2.2.集群状态监控
kibana可以监控es集群,不过新版本需要依赖es的x-pack 功能并且默认是监控但点es,配置比较复杂。
这里推荐使用cerebro来监控es集群状态,官方网址:https://github.com/lmenezes/cerebro
解压即可使用,非常方便。
解压好的目录如下:
进入对应的bin目录:
双击其中的cerebro.bat文件即可启动服务。
访问http://localhost:9000 即可进入管理界面:
输入你的elasticsearch的任意节点的地址和端口,点击connect即可:
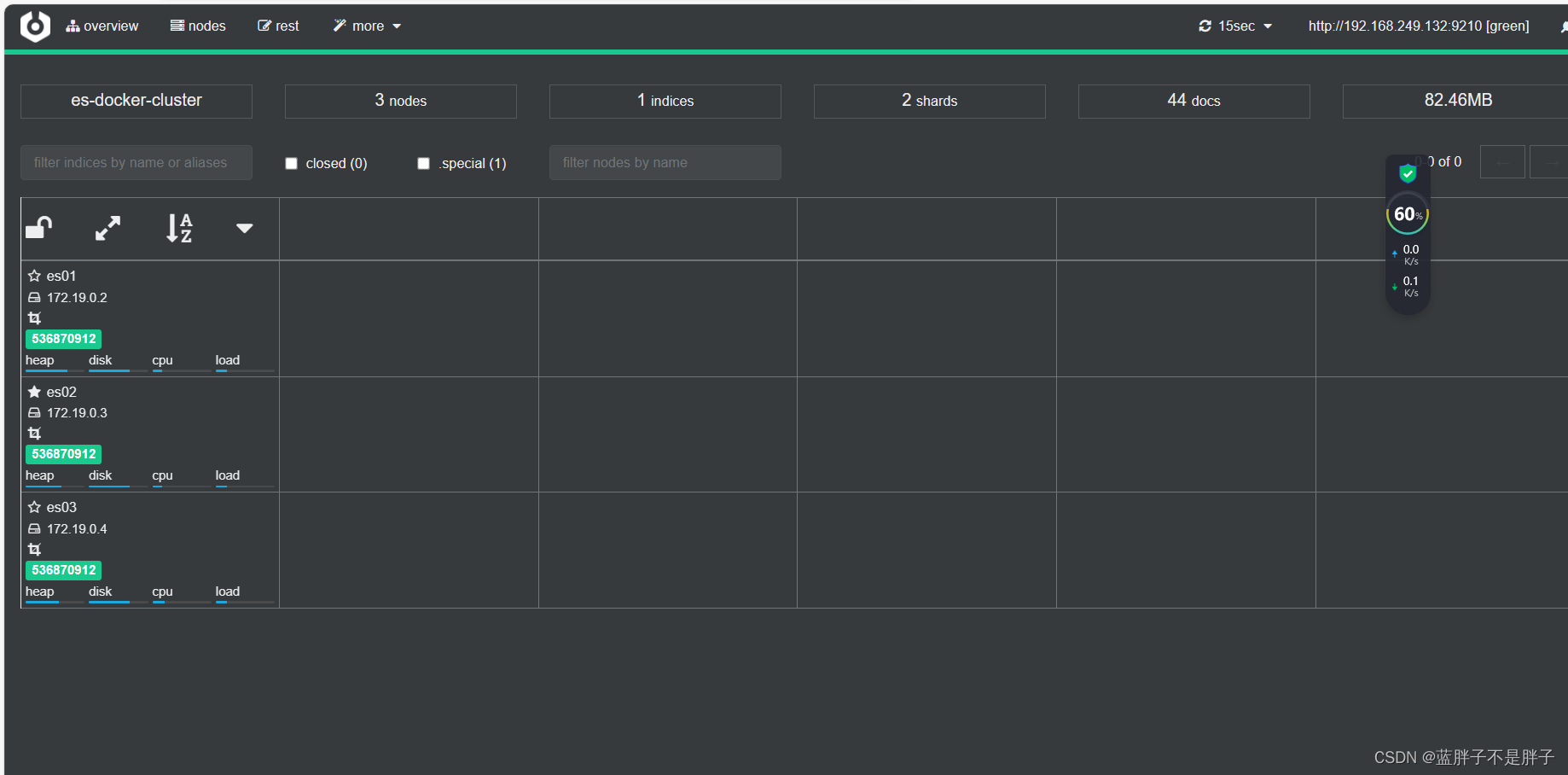
绿色的条,代表集群处于绿色(健康状态)。
图标星星是实的是当前主节点,其他的是备用结点

2.3.创建索引库
1)利用kibana的DevTools创建索引库
(这里集群不使用这种方式)
在DevTools中输入指令:
PUT /itcast
{"settings": {"number_of_shards": 3, // 分片数量"number_of_replicas": 1 // 副本数量},"mappings": {"properties": {// mapping映射定义 ...}}
}
2)利用cerebro创建索引库
利用cerebro还可以创建索引库:
172是我的虚拟机所在的虚拟地址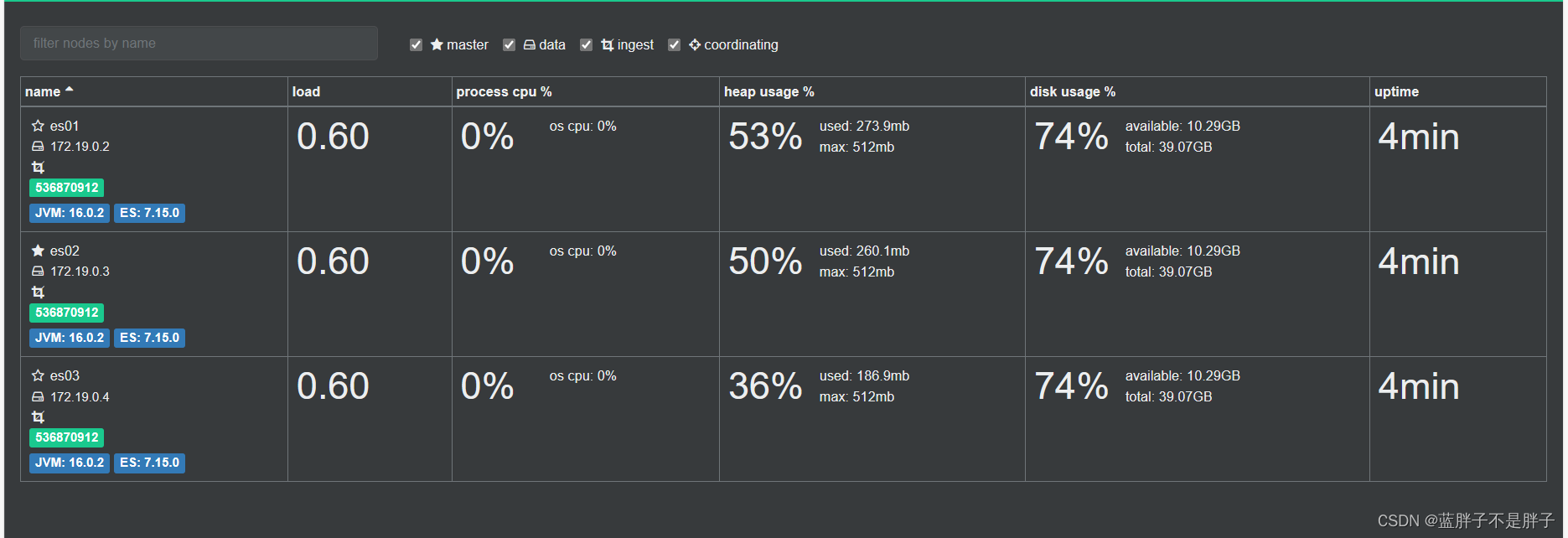
填写索引库信息:
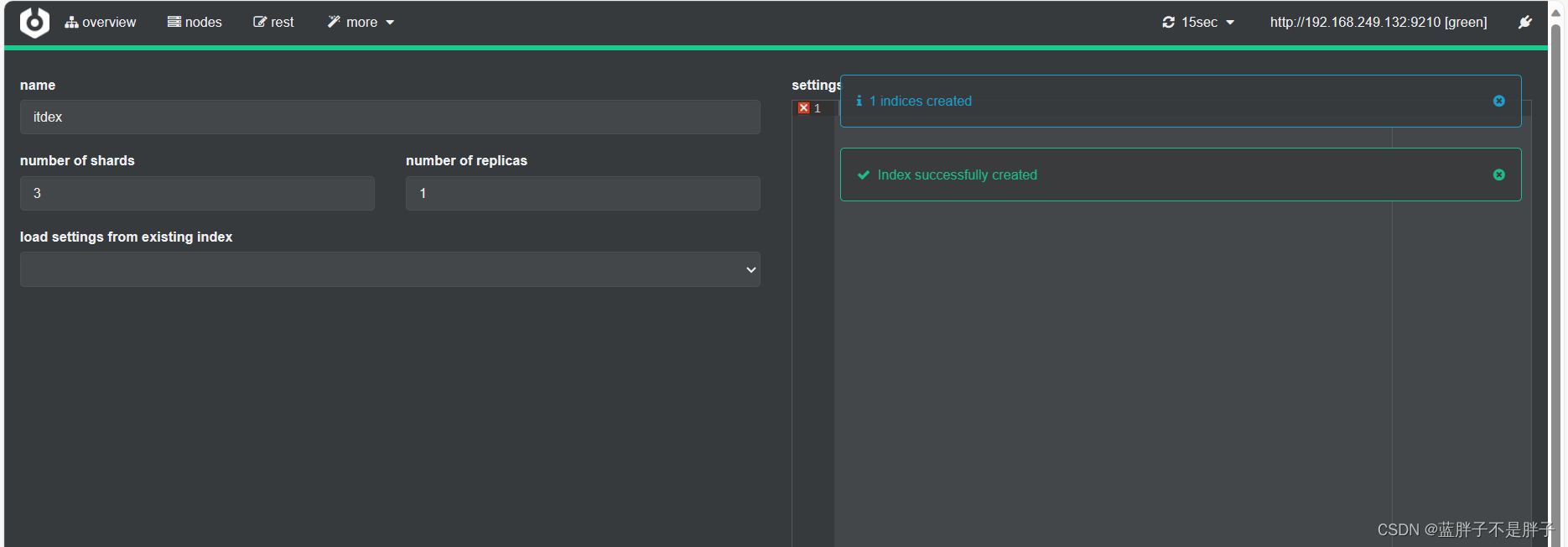
- 选项分别是索引名 几个分片 几个备份
点击右下角的create按钮:
2.4.查看分片效果
回到首页,即可查看索引库分片效果:
首页可以看到索引数据
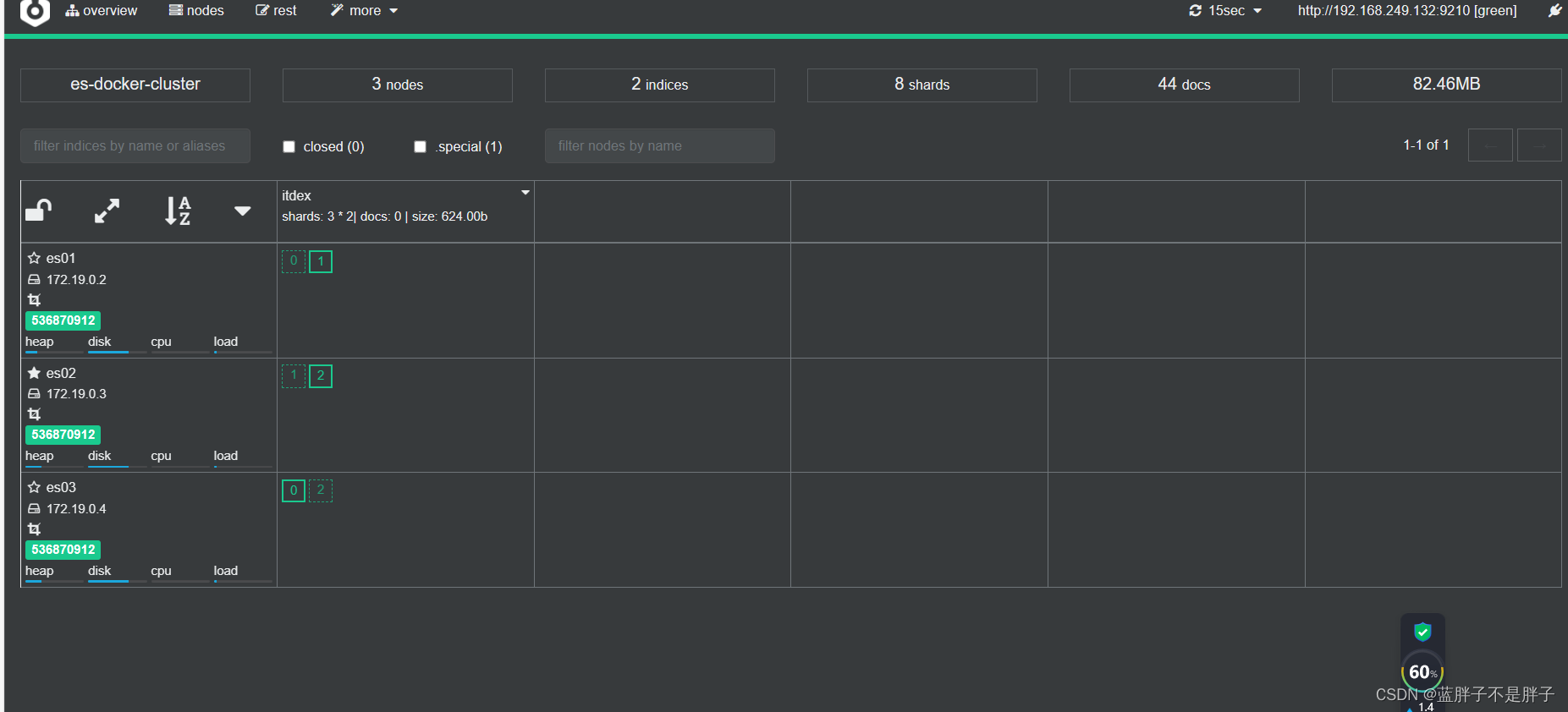
索引存储分为三个分片每个文档分片备份一份所以是6个数据,点击任意分片就可以看到索引信息
这样就可以保证任意结点宕机 ,其他结点把备份数据传递给宕机接结点
3.0.集群脑裂问题
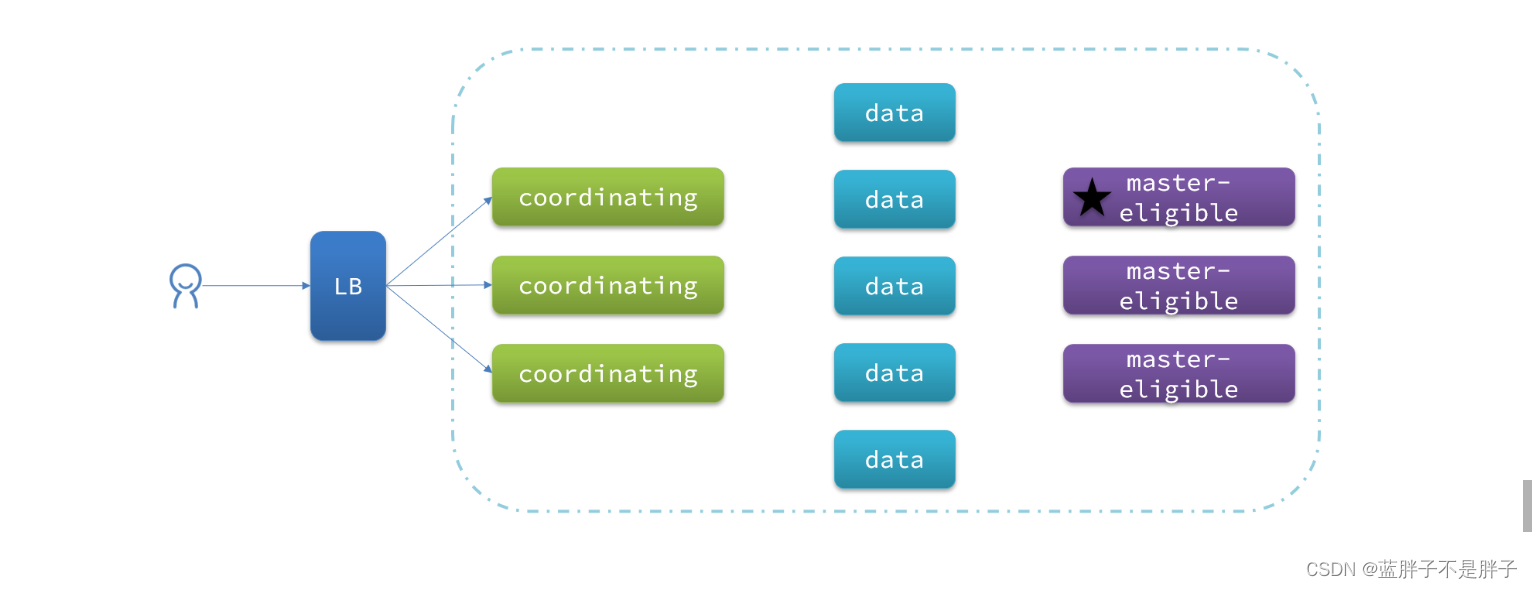
3.1.集群职责划分
elasticsearch中集群节点有不同的职责划分:
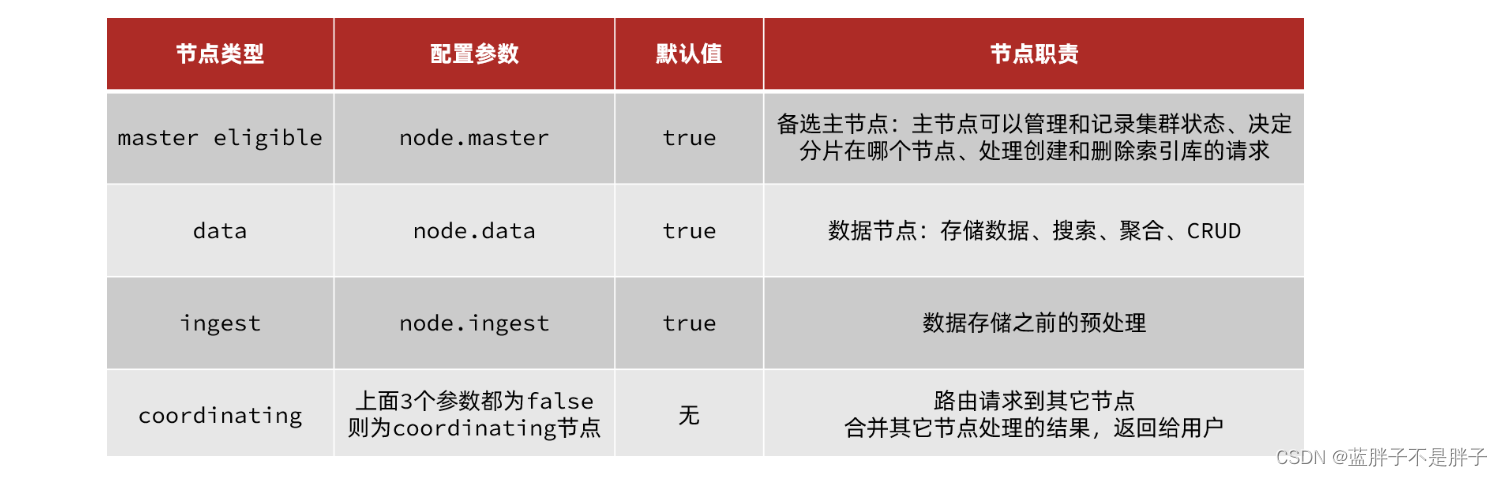
默认情况下,集群中的任何一个节点都同时具备上述四种角色。
但是真实的集群一定要将集群职责分离:
- master节点:对CPU要求高,但是内存要求第
- data节点:对CPU和内存要求都高
- coordinating节点:对网络带宽、CPU要求高
职责分离可以让我们根据不同节点的需求分配不同的硬件去部署。而且避免业务之间的互相干扰。
一个典型的es集群职责划分如图:
3.2.脑裂问题
但是采用分布式的主从架构的服务一般都会出现脑裂问题
脑裂是因为集群中的节点失联导致的。结点尚未宕机,但是失去通信(比如网络问题)
例如一个集群中,主节点与其它节点失联:
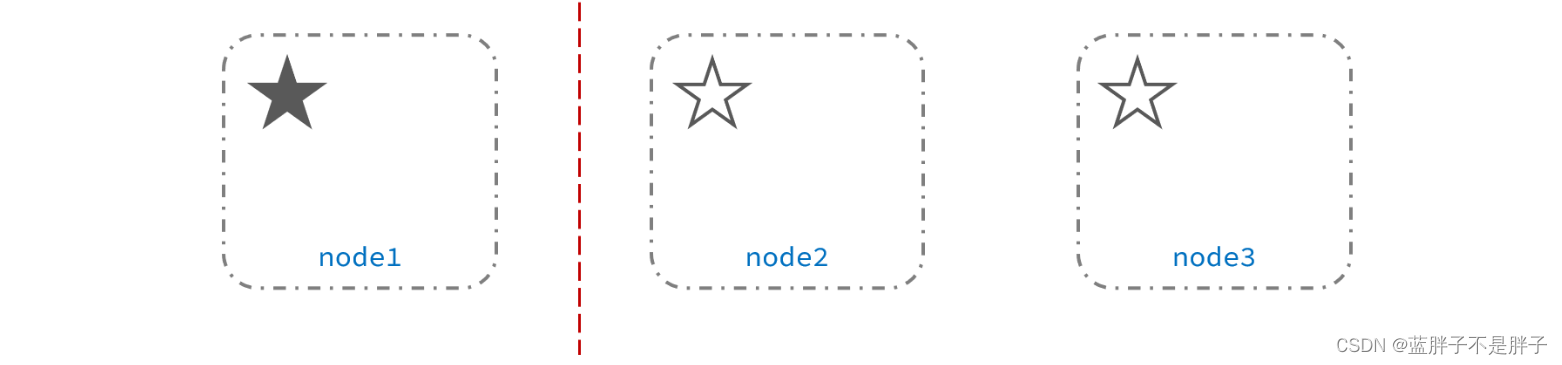
此时,node2和node3认为node1宕机,就会重新选主:
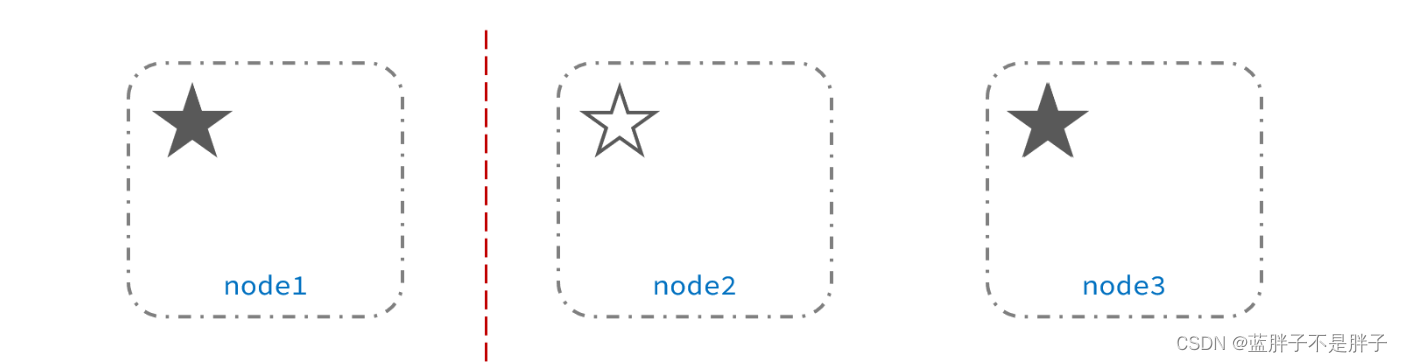
当node3当选后,集群继续对外提供服务,node2和node3自成集群,node1自成集群,两个集群数据不同步,出现数据差异,这个时候出现了俩个大脑
当网络恢复后,因为集群中有两个master节点,集群状态的不一致,出现脑裂的情况:
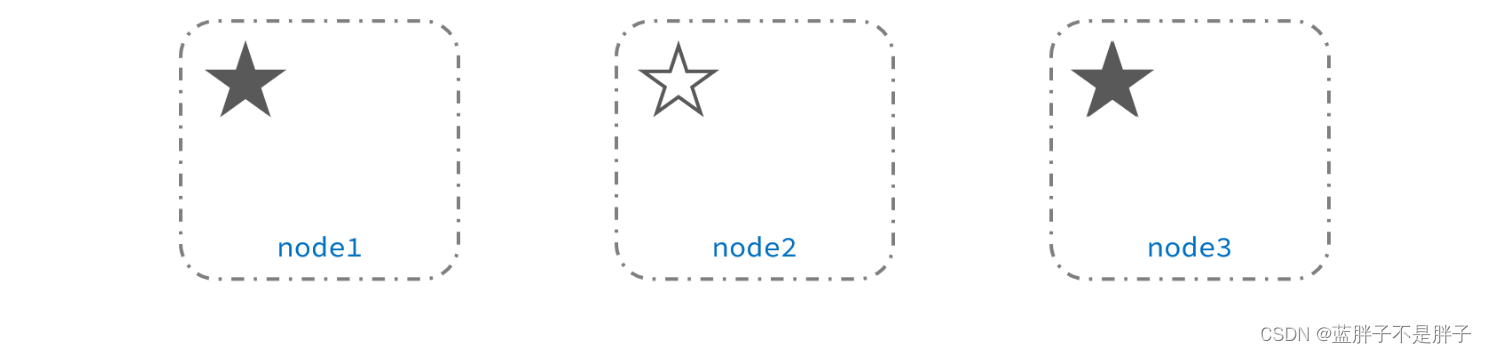
解决脑裂的方案是,要求选票超过 ( eligible节点数量 + 1 )/ 2 才能当选为主,因此eligible节点数量最好是奇数。对应配置项是discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes,在es7.0以后,已经成为默认配置,因此一般不会发生脑裂问题
例如:3个节点形成的集群,选票必须超过 (3 + 1) / 2 ,也就是2票。node3得到node2和node3的选票,当选为主。node1只有自己1票,没有当选救失去主节点身份。集群中依然只有1个主节点,没有出现脑裂。
3.3.小结
master eligible节点的作用是什么?
- 参与集群选主
- 主节点可以管理集群状态、管理分片信息、处理创建和删除索引库的请求
data节点的作用是什么?
- 数据的CRUD
coordinator节点的作用是什么?
-
路由请求到其它节点
-
合并查询到的结果,返回给用户
3.4.集群分布式存储
当新增文档时,应该保存到不同分片,保证数据均衡,那么coordinating node如何确定数据该存储到哪个分片呢?
3.4.1.分片存储测试
插入三条数据:
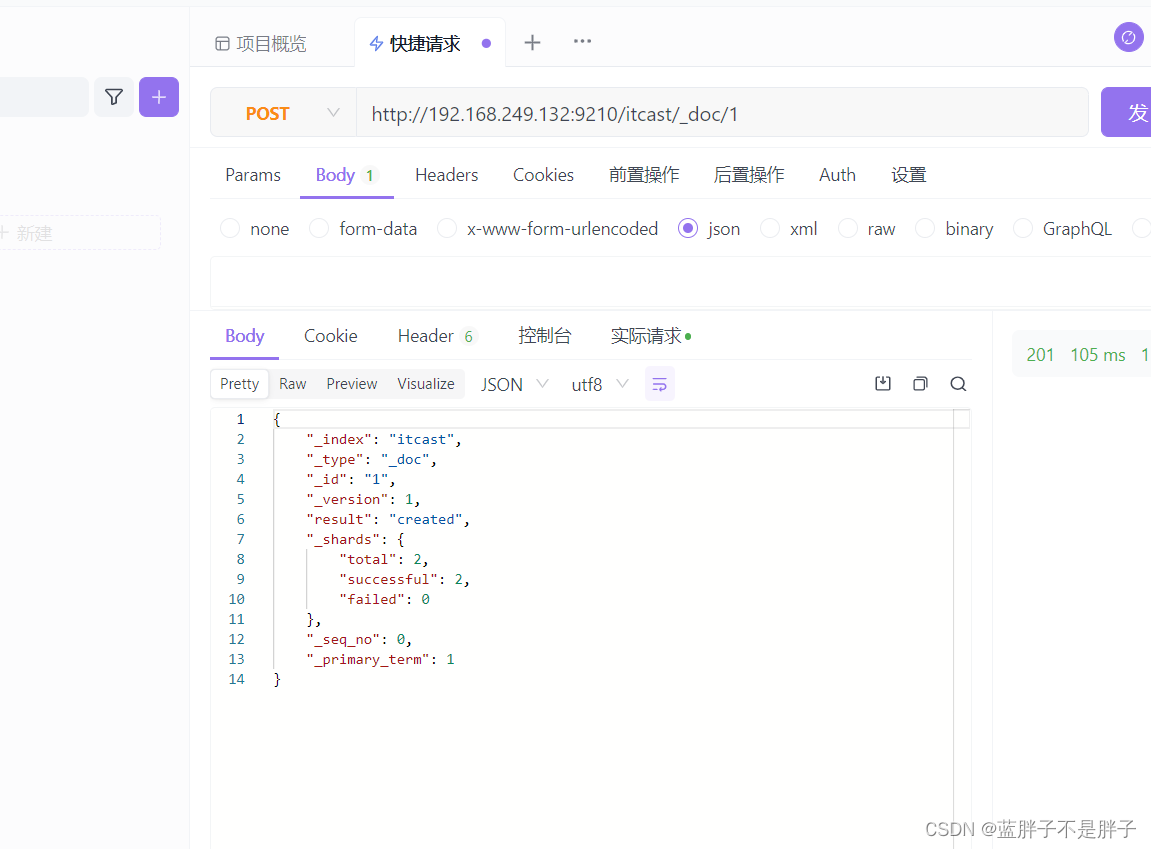
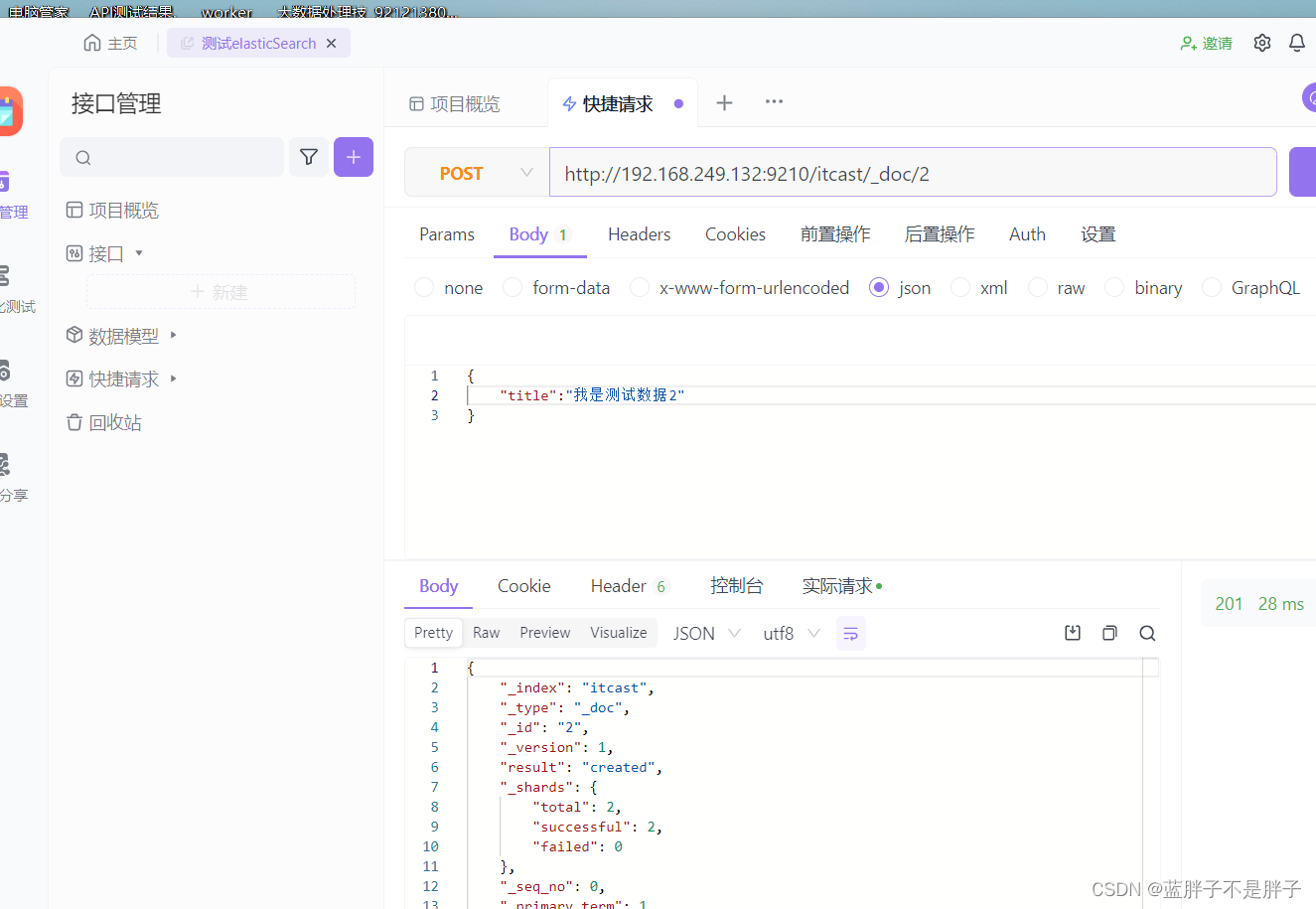
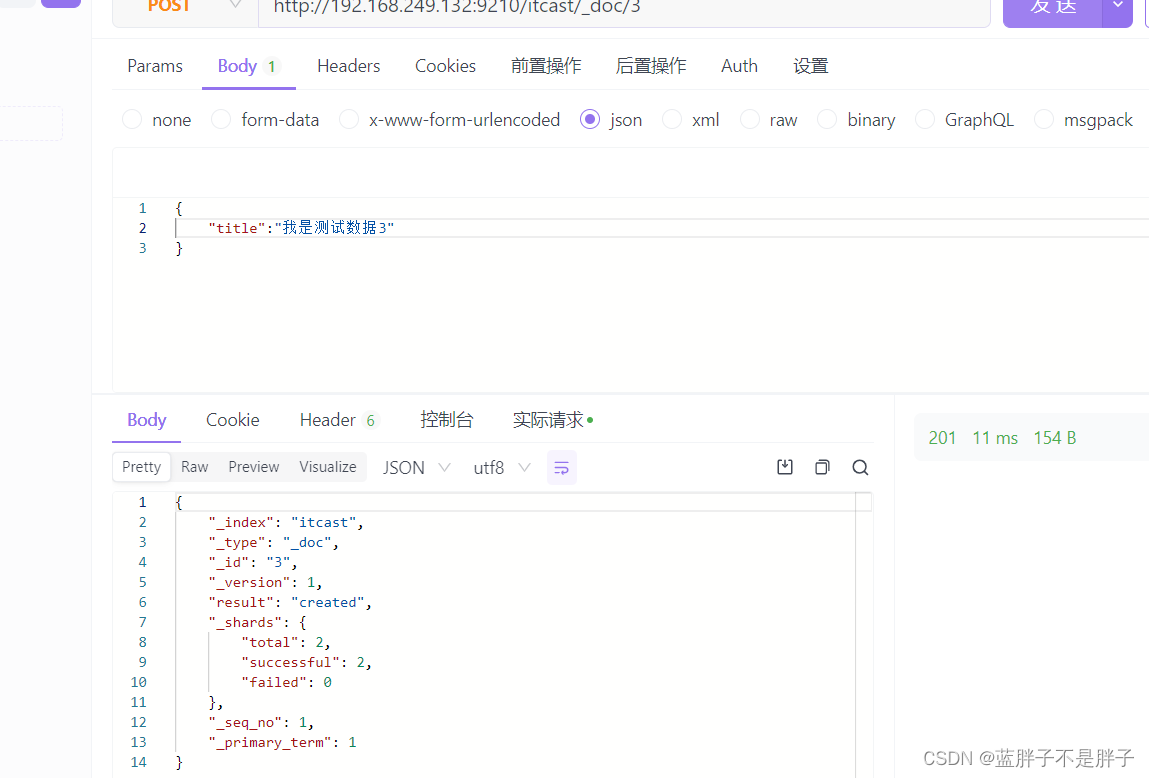
创建索引时候我没有没有添加索引mapping,也没有规定字段,在Elasticsearch中,如果你创建一个索引但没有显式定义映射(mapping)或字段(mapping),Elasticsearch会使用动态映射(dynamic mapping)来处理你插入的文档数据。动态映射允许Elasticsearch根据插入的文档数据自动推断字段的数据类型。
当你插入文档时,Elasticsearch会检查文档的字段,并根据字段值的类型自动创建相应的字段映射。例如,如果你插入一个包含字符串的字段,Elasticsearch会自动将其识别为文本字段,如果插入一个整数,它会将其识别为整数字段,以此类推。
测试可以看到,三条数据分别在不同分片,查询任意结点的数据
结果:
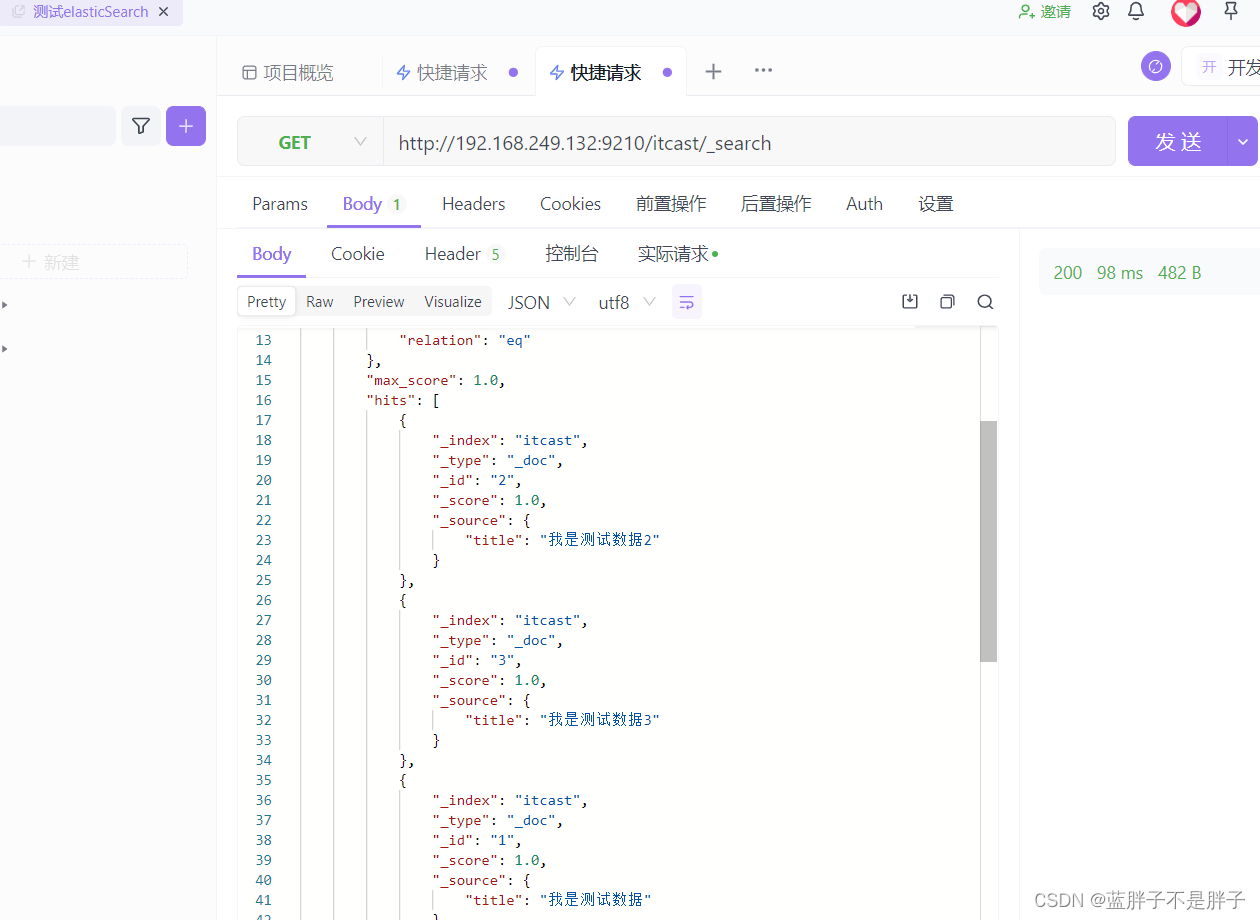
另一接待你查询
3.4.2.分片存储原理
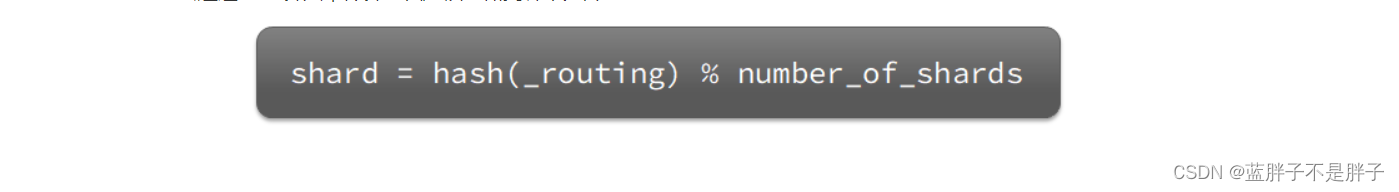
elasticsearch会通过hash算法来计算文档应该存储到哪个分片:
说明:
- )_routing默认是文档的id
- ) 算法与分片数量有关,因此索引库一旦创建,分片数量不能修改!
新增文档的流程如下:
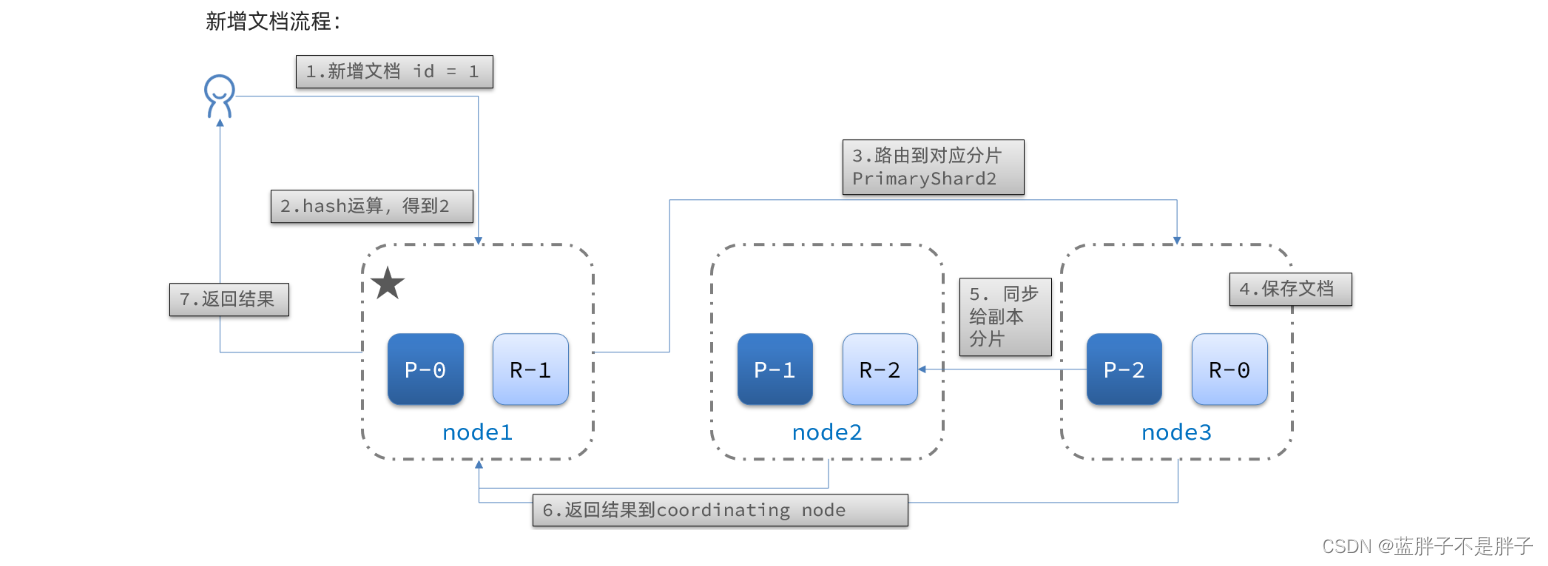
解读:
- 1)新增一个id=1的文档
- 2)对id做hash运算,假如得到的是2,则应该存储到shard-2
- 3)shard-2的主分片在node3节点,将数据路由到node3
- 4)保存文档
- 5)同步给shard-2的副本replica-2,在node2节点
- 6)返回结果给coordinating-node节点
3.4.3集群分布式查询
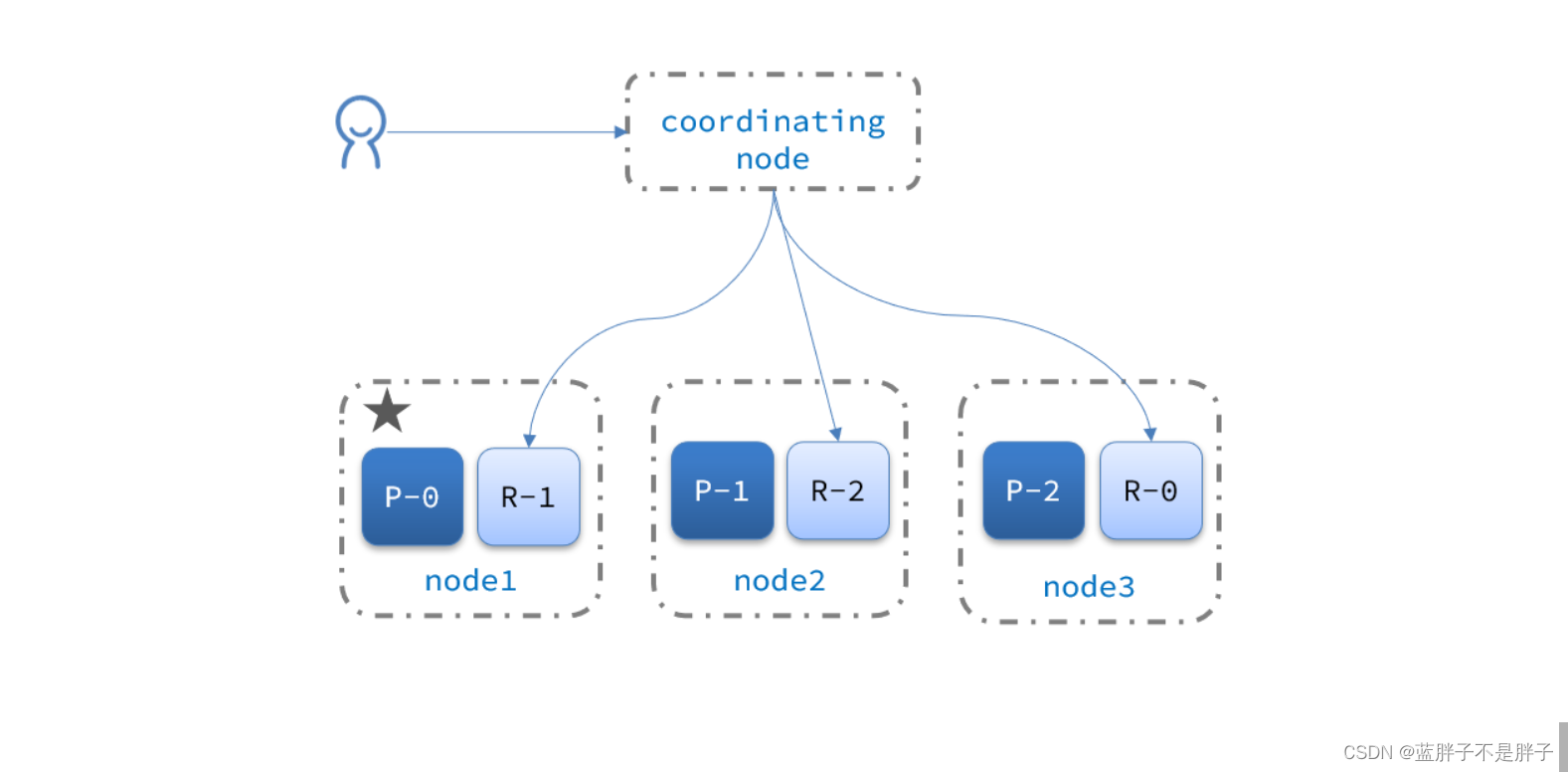
elasticsearch的查询分成两个阶段:
- scatter phase:分散阶段,coordinating node会把请求分发到每一个分片(查询检索一般是根据text来查询,不知道具体数据id,所以会给每个结点发送查询)
所以之前查询任一结点,都会查询到全部数据,因为请求打到了所有数据
- gather phase:聚集阶段,coordinating node汇总data node的搜索结果,并处理为最终结果集返回给用户
3.5.集群故障转移
集群的master节点会监控集群中的节点状态,如果发现有节点宕机,会立即将宕机节点的分片数据迁移到其它节点,确保数据安全,这个叫做故障转移。
1)例如一个集群结构如图:
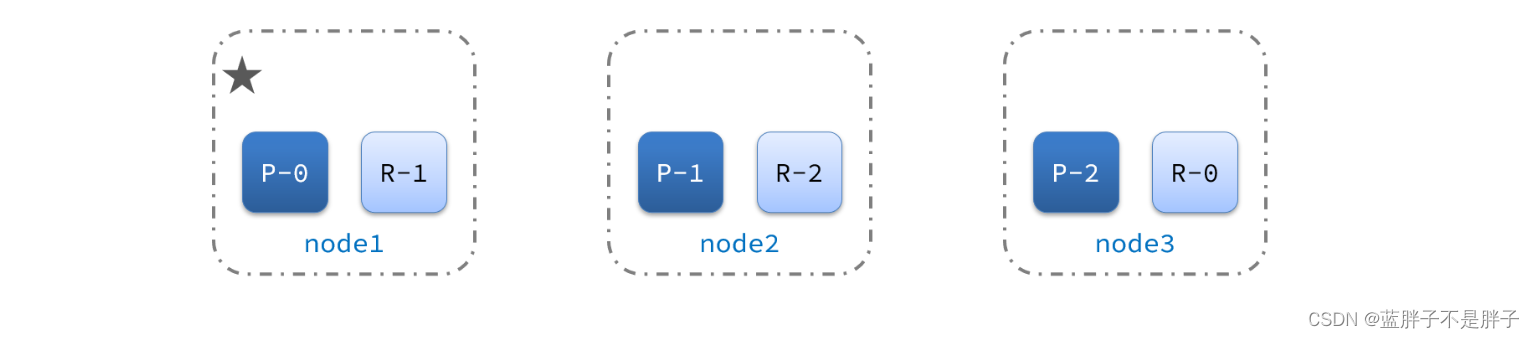
现在,node1是主节点,其它两个节点是从节点。
2)突然,node1发生了故障:
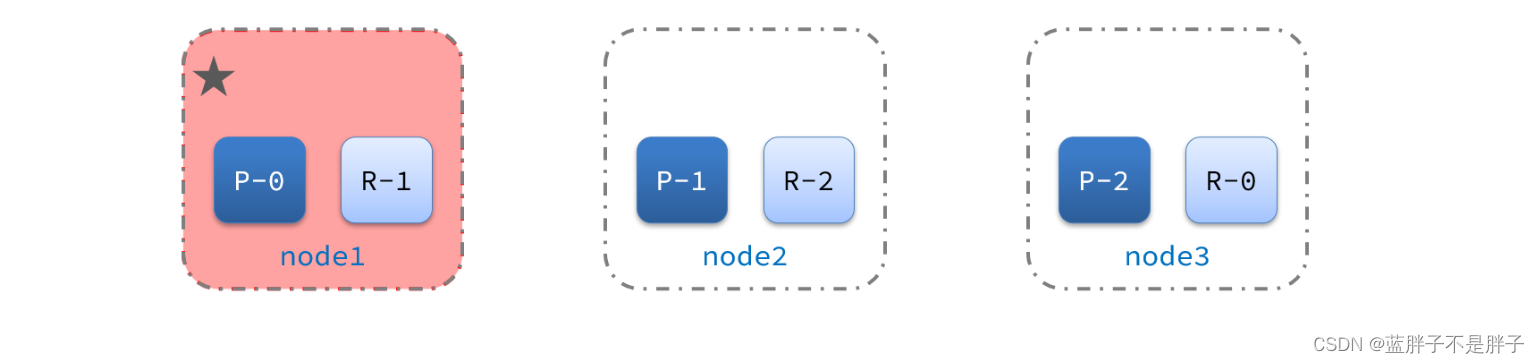
宕机后的第一件事,需要重新选主,例如选中了node2:
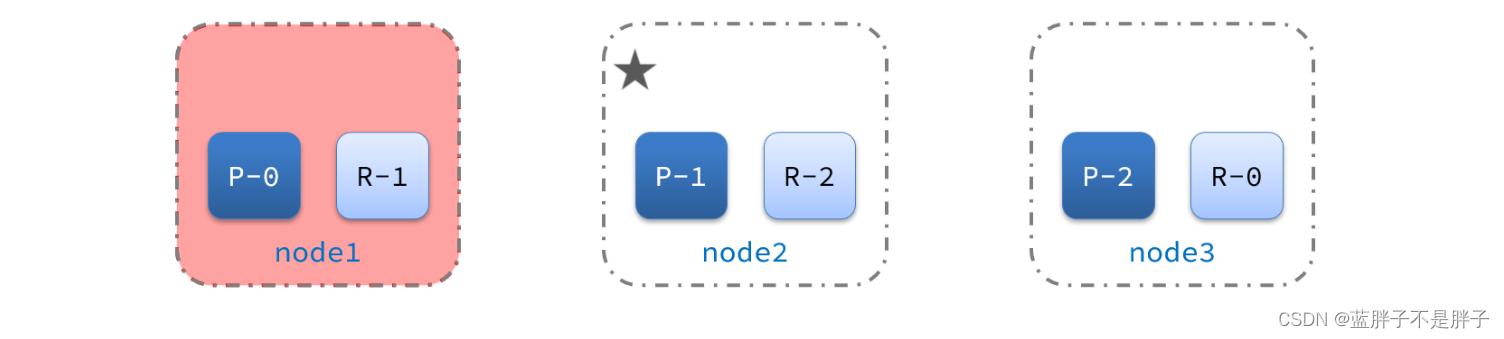
node2成为主节点后,会检测集群监控状态,发现:shard-1、shard-0没有副本节点。因此需要将node1上的数据迁移到node2、node3:
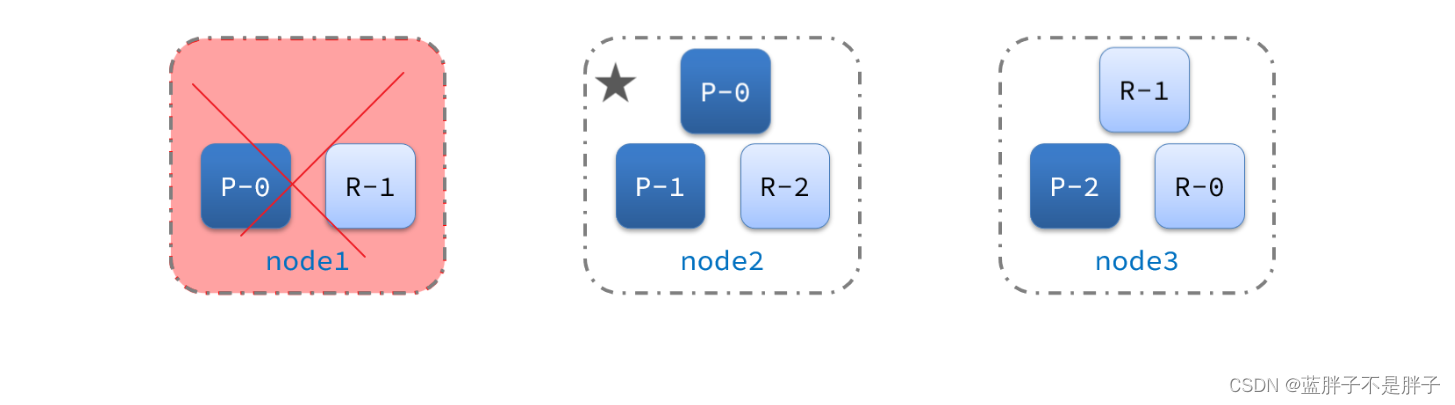
所以故障转移主要是进行了俩布,
- 主结点宕机后选择新节点为主结点
- 新的主节点为了保障宕机结点所存储的数据安全,第一时间转移到其他安全结点
这是es集群的默认策略 这里进行演示即可
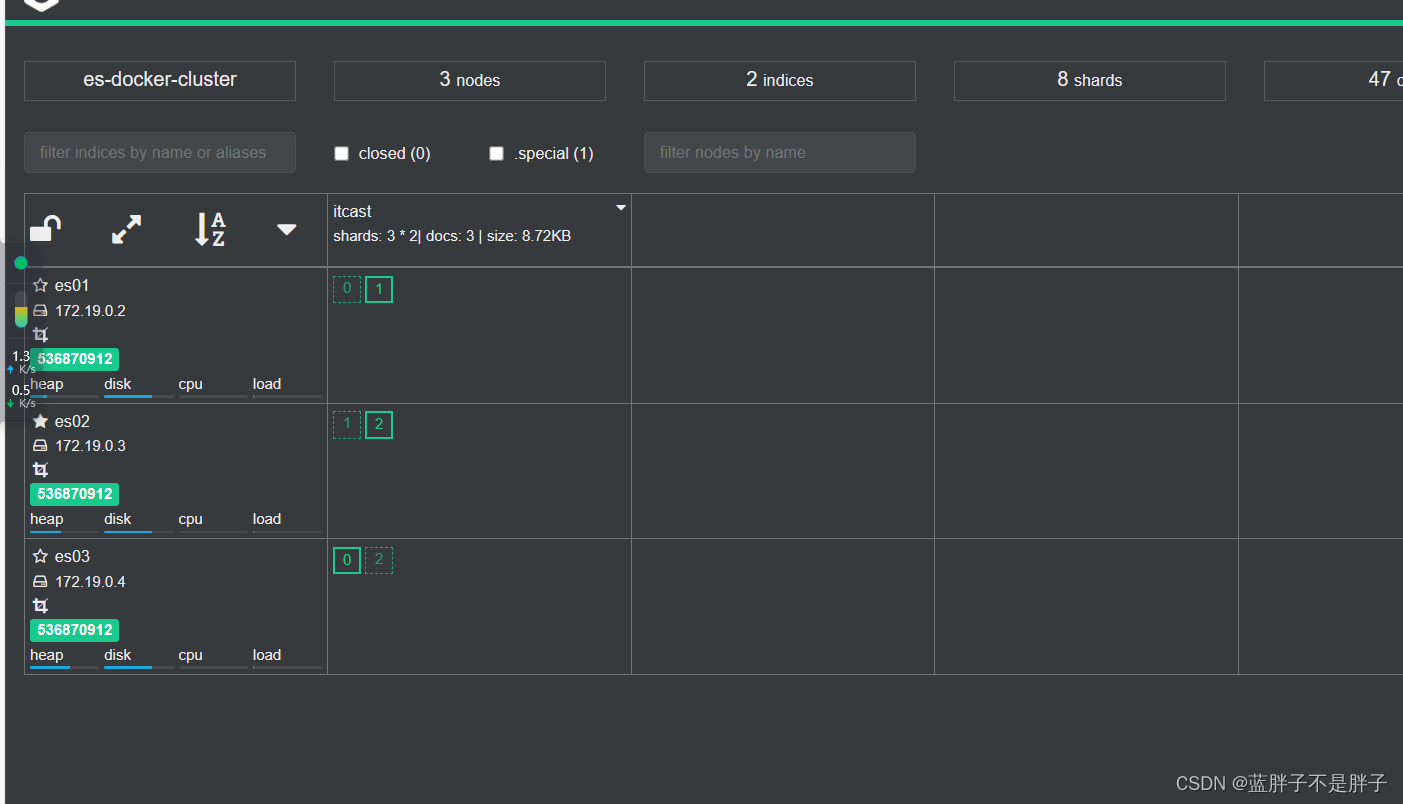
现在三个结点正常
关闭虚拟机的任一结点
等待一会后 集群自动迁移
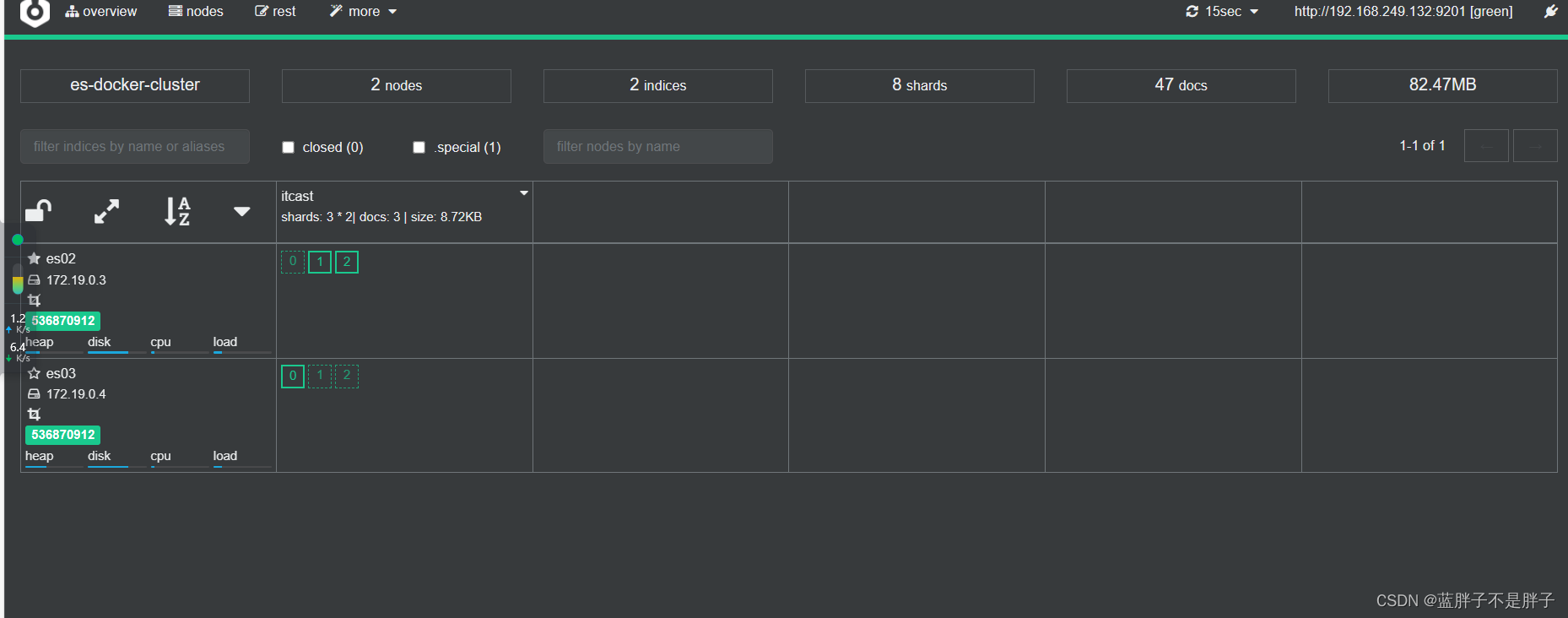
当es01重新启动后 数据均衡又会把数据分给挂掉的结点