下载做ppt的动画片的好网站企业宣传推广方案
Grounding DINO简单来说,它可以根据文字描述检测指定目标。此外,当Grounding DINO与stable diffusion结合,便可以实现更神奇的功能–自动P图。在专业领域中,GroundingDINO可以用来进行遥感影像解译,可以减少人工工作量。
Grounding DINO相对于其他方法有以下几点优势:
- 其transformer结构更接近于自然语言处理模型,因此更容易同时处理图片和文字;
- Transformer-based detector在处理大型数据集时被证明有优势;
- 作为DETR的变种,DINO能够完成end-to-end的训练,而且不需要NMS等额外的后处理。
github地址:https://github.com/IDEA-Research/GroundingDINO
官网和其他的一些教程上,其安装都是使用的Linux系统,对于一般使用windows作为开发环境的人来说,经常会遇到直接使用pip安装时报错的问题,那么可以考虑使用github源码的安装方式。
1.配置CUDA_HOME环境变量
linux环境可以直接使用
echo 'export CUDA_HOME=/path/to/cuda' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
echo $CUDA_HOME
来进行操作
windows环境就需要在环境变量中配置了
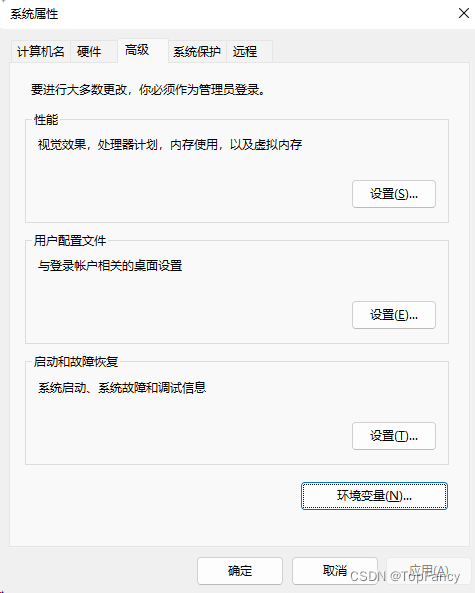
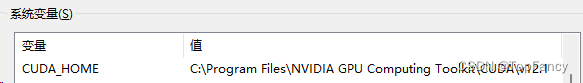
2.安装
推荐使用Conda虚拟环境进行安装,安装GroundingDINO之前先安装一下torch和torchvision,具体的环境配置可以参考之前的文章:【AI】PyTorch安装记录及Anaconda环境配置
直接在github上下载源码,然后进入项目中,将当前项目安装为依赖
# 下载源码
git clone https://github.com/IDEA-Research/GroundingDINO.git
# 进入项目中
cd GroundingDINO/
# 安装本项目
pip install -e .
# 下载预训练模型
mkdir weights
cd weights
wget -q https://github.com/IDEA-Research/GroundingDINO/releases/download/v0.1.0-alpha/groundingdino_swint_ogc.pth
cd ..
