百度免费网站制作seo双标题软件

本文收录于【#云计算入门与实践 - AWS】专栏中,收录 AWS 入门与实践相关博文。
本文同步于个人公众号:【云计算洞察】
更多关于云计算技术内容敬请关注:CSDN【#云计算入门与实践 - AWS】专栏。
本系列已更新博文:
- [ 云计算 | AWS 实践 ] Java 应用中使用 Amazon S3 进行存储桶和对象操作完全指南
- [ 云计算 | AWS 实践 ] Java 如何重命名 Amazon S3 中的文件和文件夹
- [ 云计算 | AWS 实践 ] 使用 Java 列出存储桶中的所有 AWS S3 对象
- [ 云计算 | AWS 实践 ] 使用 Java 更新现有 Amazon S3 对象
- [ 云计算 | AWS 实践 ] 基于 Amazon S3 协议搭建个人云存储服务
文章目录
- 一、前言
- 二、关于 MinIO
- 2.1 什么是 MinIO
- 2.2 对象存储的工作原理
- 三、安装 MinIO
- 3.1 使用 Docker 安装 MinIO
- 3.2 测试访问 MinIO
- 四、使用 MinIO 相关配置及操作
- 4.1. MinIO 客户端相关配置操作
- 4.1.1 部署安装MinIO Client可执行程序
- 4.1.2 MinIO 客户端相关配置操作
- 4.2 MiniIO 控制台相关配置操作
- 五、使用 Java 操作 MinIO 对象(原生操作与亚马逊 Java SDK操作)
- 5.1 原生操作 MinIO
- 5.2 使用亚马逊 Java API 操作 MinIO
- 六、文末总结
一、前言
MinIO 是一个高性能的对象存储系统。它被设计为云原生存储系统的替代方案。事实上,其 API 与 Amazon S3 完全兼容;MinIO 也提供兼容阿里云等国内云厂商的 API,由于本文篇幅问题,在本博文中,只介绍亚马逊 AWS 与其关联的案例以及如何快速使用 MinIO。
二、关于 MinIO
2.1 什么是 MinIO
Minio 是 GlusterFS 创始人之一 Anand Babu Periasamy 发布新的开源项目。MinIO 从一开始就被设计为完全兼容 Amazon S3 存储 API 的替代方案。
传说是最兼容的 S3 替代方案,同时还提供可比的性能和可扩展性。
MinIO 还提供多种部署选项。它可以作为本机应用程序在大多数流行的架构上运行,也可以使用 Docker 或 Kubernetes 部署为容器化应用程序。
此外,MinIO 是开源软件。 组织可以根据 AGPLv3 许可证(许可协议点击这里)的条款免费使用它。请注意,除了在线文档和 MinIO 用户社区之外,此选项不提供任何支持。对于大型企业,还可以提供带有专门支持的付费订阅。
MinIO 的 GitHub 地址:https://github.com/minio/minio
由于其 S3 API 兼容性、在各种部署中运行的能力以及开源特性,MinIO 是一款出色的开发和测试以及 DevOps 工具场景。
2.2 对象存储的工作原理
对象存储的概念与标准 Linux 文件系统类似,但我们使用存储桶和对象来代替目录和文件.
存储桶可以像目录一样嵌套到层次结构中,而对象可以被认为只是字节的集合。这些集合可以是任意字节数组或普通文件,例如图像、PDF 等。
一个示例对象存储系统可能如下所示:
/
/images/imge1.pngimage2.jpg
/videos/video1.mp4
/users//bluetata/status-report.docx
就像目录和文件一样,存储桶和对象也可以拥有权限。 这允许对数据进行细粒度的访问控制,特别是在拥有许多用户的大型组织中。
三、安装 MinIO
3.1 使用 Docker 安装 MinIO
如前所述,MinIO 几乎适用于所有平台。有适用于 Windows、Linux 和 MacOS 的独立安装程序。然而,出于开发和测试目的,最简单的入门方法是使用容器化发行版。
MinIO 需要一个持久卷来存储配置和应用程序数据。但是,出于测试目的,可以通过简单地传递一个目录(/data在下面的示例中)来启动 MinIO 。该目录是在容器启动时在容器文件系统中创建的。但是容器退出后所有的数据都丢失了。如果打算持久化,进行挂载即可。
docker run \-p 9000:9000 \-p 9001:9001 \-e "MINIO_ROOT_USER=MINIO_ROOT_USER" \-e "MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD=MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD" \minio/minio server /data --console-address ":9001"
执行状态截图如下
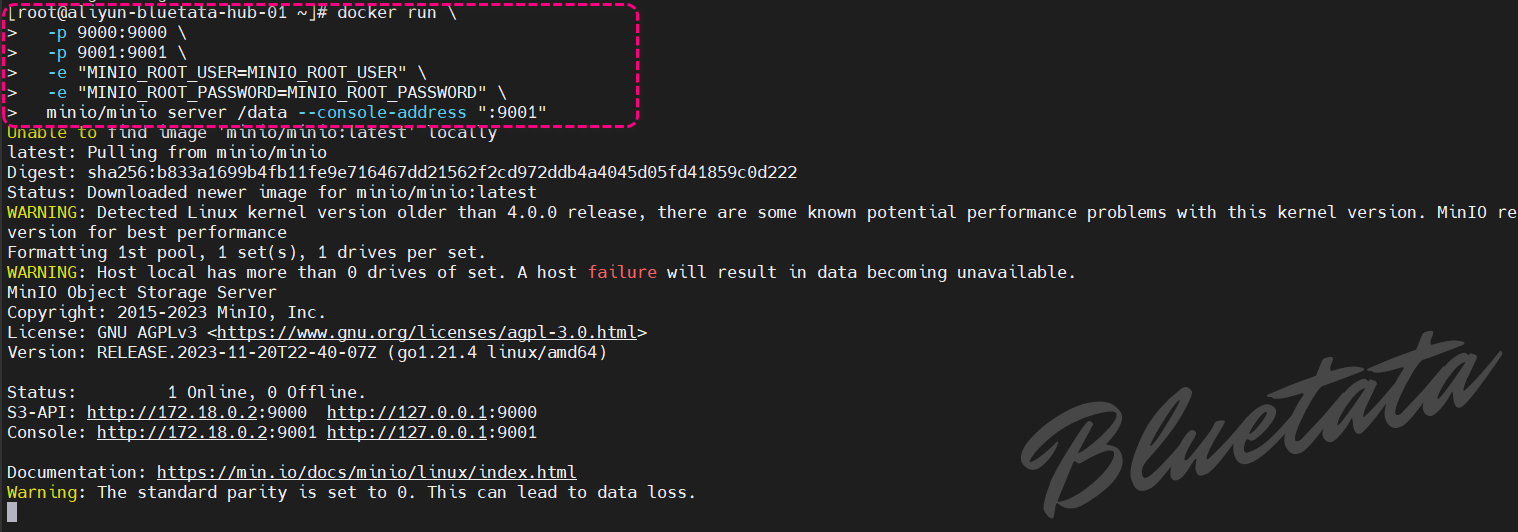
虽然容器化部署非常适合评估 MinIO,但需要注意一些限制。
具体来说,一些高级功能(例如版本控制、对象锁定和存储桶复制)将不起作用。这些功能需要MinIO的分布式部署,这在单服务器部署中是不可用的。
另外注意上述的命令已经设置了 MinIO 的用户名和密码。如果此处没有设置也可以按照后文客户端在设置一次。
3.2 测试访问 MinIO
可以直接访问:http://你的ip地址:9001/login 来访问你的 MinIO
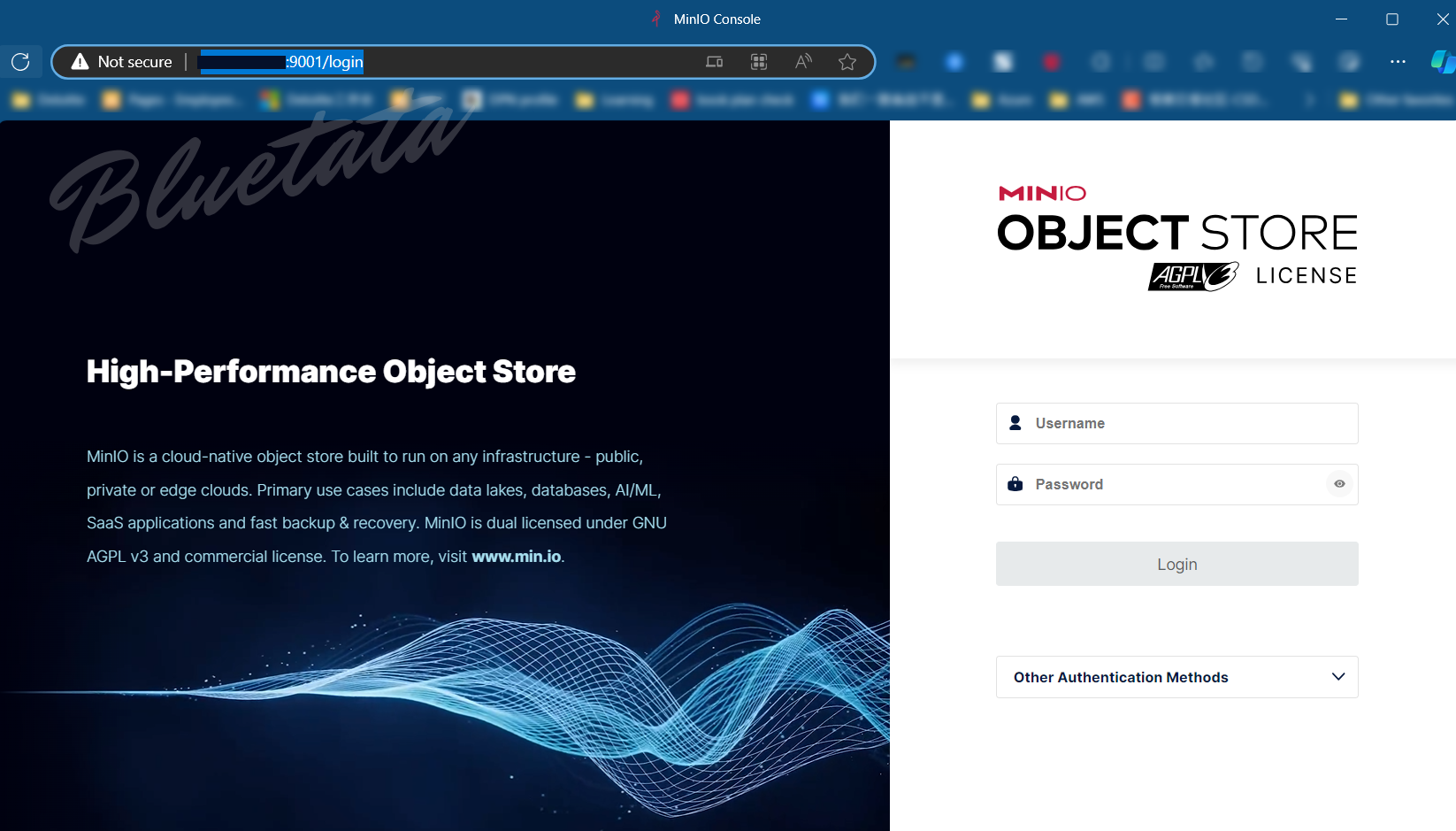
四、使用 MinIO 相关配置及操作
可以通过多种不同的方式与 MinIO 服务器交互以及管理存储桶和对象。下面,我们就来一一讲解。
4.1. MinIO 客户端相关配置操作
4.1.1 部署安装MinIO Client可执行程序
首先要在自己的系统中部署 MinIO Client 可执行程序,不然所有的 mc 命令都会不识别,会出现如下错误:
-bash: mc: command not found
解决办法是:
wget https://dl.minio.io/client/mc/release/linux-amd64/mc
chmod +x mc
sudo mv mc /usr/local/bin
4.1.2 MinIO 客户端相关配置操作
MinIO 客户端 提供与 Linux 文件管理命令相同的命令,例如cp和ls等,但专为本地和远程存储系统而设计。它与 AWS S3 完全兼容,其语法模仿 AWS 客户端工具的语法。
使用 MinIO 客户端的第一步是将其配置为与云存储系统通信。让我们将其指向上面的容器化部署:
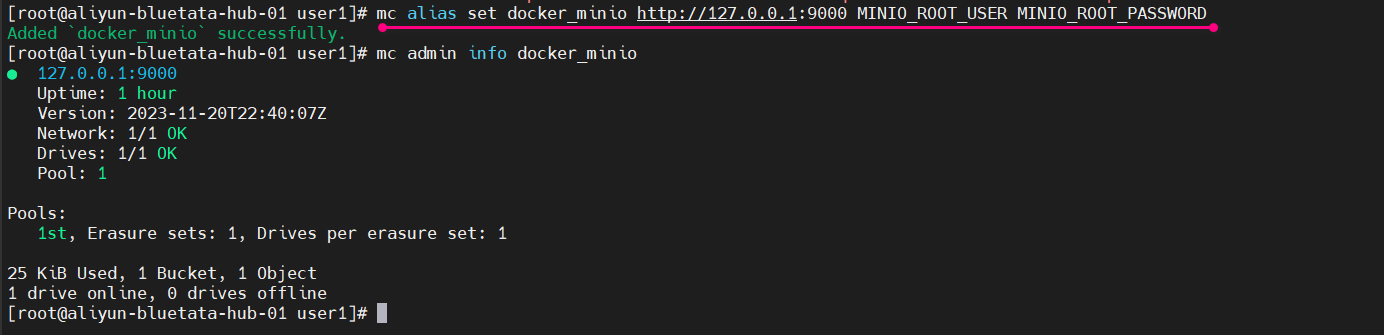
mc alias set docker_minio http://127.0.0.1:9000 MINIO_ROOT_USER MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD
这个命令是使用 MinIO Client(mc)设置一个别名(alias)。具体来说,它创建了一个名为 docker_minio 的别名,连接到地址为 http://127.0.0.1:9000 的 MinIO 实例,并使用用户名 MINIO_ROOT_USER 和密码 MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD 进行身份验证。
这里是单独的为客户端配置,如果已经按照上述的在安装过程中设置了用户名与密码,可以直接访问即可。
我们可以使用admin子命令验证连接:
[root@aliyun-bluetata-hub-01 user1]# mc admin info docker_minio
● 127.0.0.1:9000Uptime: 1 hourVersion: 2023-11-20T22:40:07ZNetwork: 1/1 OKDrives: 1/1 OKPool: 1Pools:1st, Erasure sets: 1, Drives per erasure set: 125 KiB Used, 1 Bucket, 1 Object
1 drive online, 0 drives offline执行的截图如下:
现在,我们可以开始执行创建存储桶和对象等基本操作。许多 MinIO 客户端子命令模仿熟悉的 Linux 命令:
- cp:在文件系统之间复制文件或对象。
- ls:列出存储桶中的文件或对象。
- mb:创建存储桶(类似于 Linux 上的 mkdir)。
- mv:将文件或对象从一个文件系统移动/重新定位到另一个文件系统。
- rb:删除存储桶(类似于 Linux 上的 rmdir)。
- rm:删除文件或对象。
大多数子命令都适用于本地文件系统和云存储。例如,我们可以使用以下命令序列创建新的存储桶,将文件复制到该存储桶中,在存储桶之间移动对象,然后删除存储桶:
mc mb user1
mc cp ~/test.pdf prattm
mc mb user2
mc cp user1/test.pdf user2
mc rb user1
mc ls user2
[2023-11-22 21:39:10 MDT] 491K test.pdf
4.2 MiniIO 控制台相关配置操作
在 MinIO 部署中管理数据的另一种方法是使用基于 Web 的管理控制台。通过容器化部署,我们首先在 Web 浏览器中打开地址 http://127.0.0.1:9001。我们使用默认凭据登录MINIO_ROOT_USER/ MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD。
如果你是远程服务器,那么 ip 就换成你的远程服务器公网 ip 即可。
我们可以创建我们的第一个存储桶:
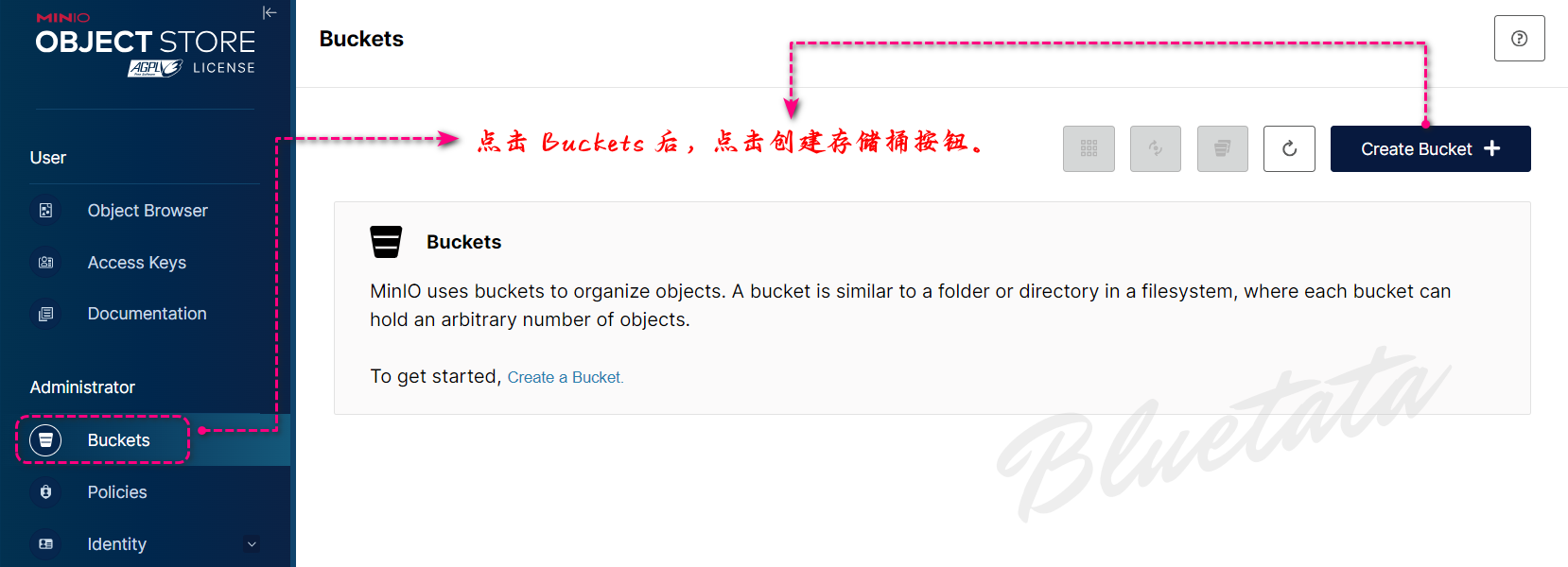
进入到创建存储桶页面后,直接输入所要创建的名称后,点击创建存储桶。
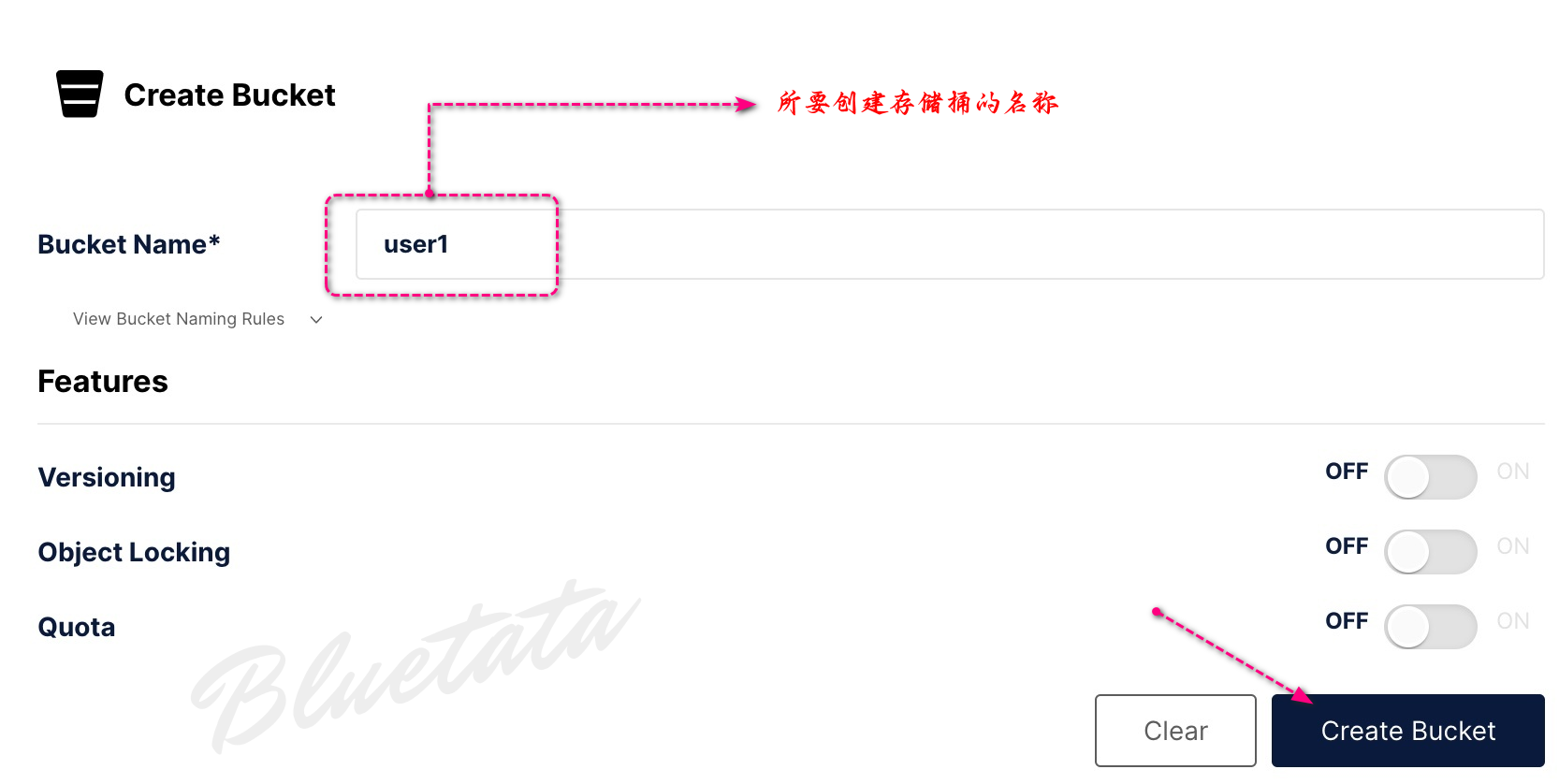
在这之前我们有讲过:并非所有选项(例如版本控制)都适用于我们的容器化部署。
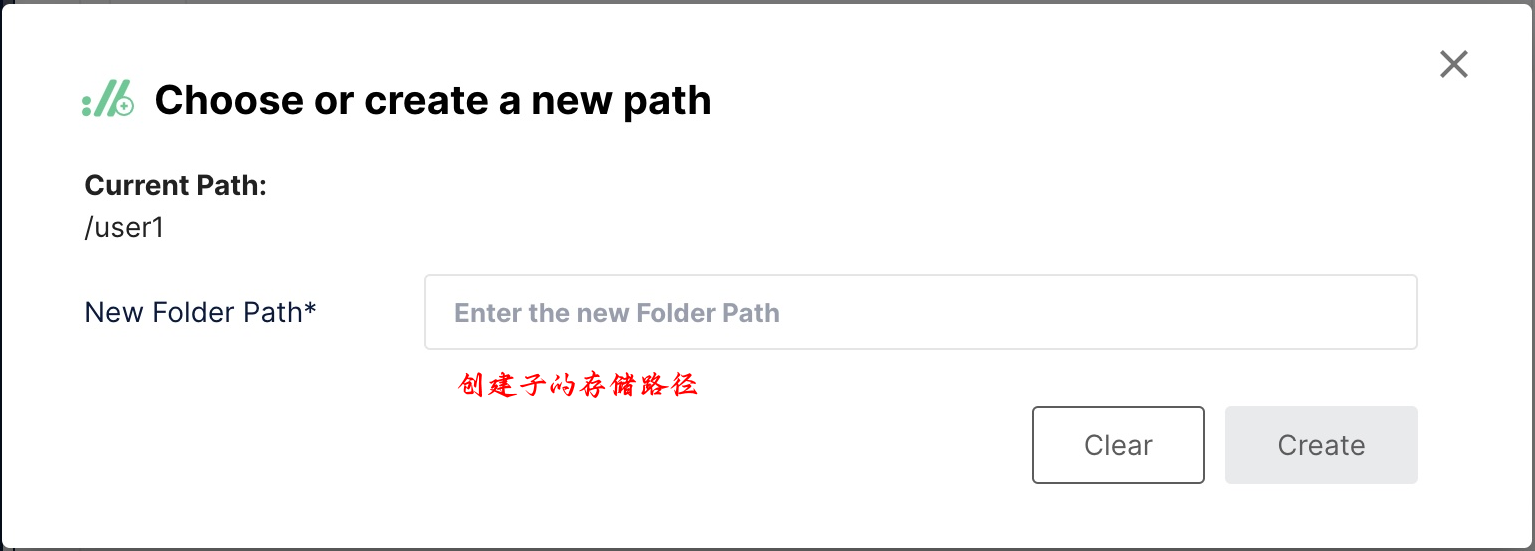
现在,我们可以导航到对象浏览器并单击我们的新存储桶。首先,我们可以使用创建新路径按钮创建子存储桶:
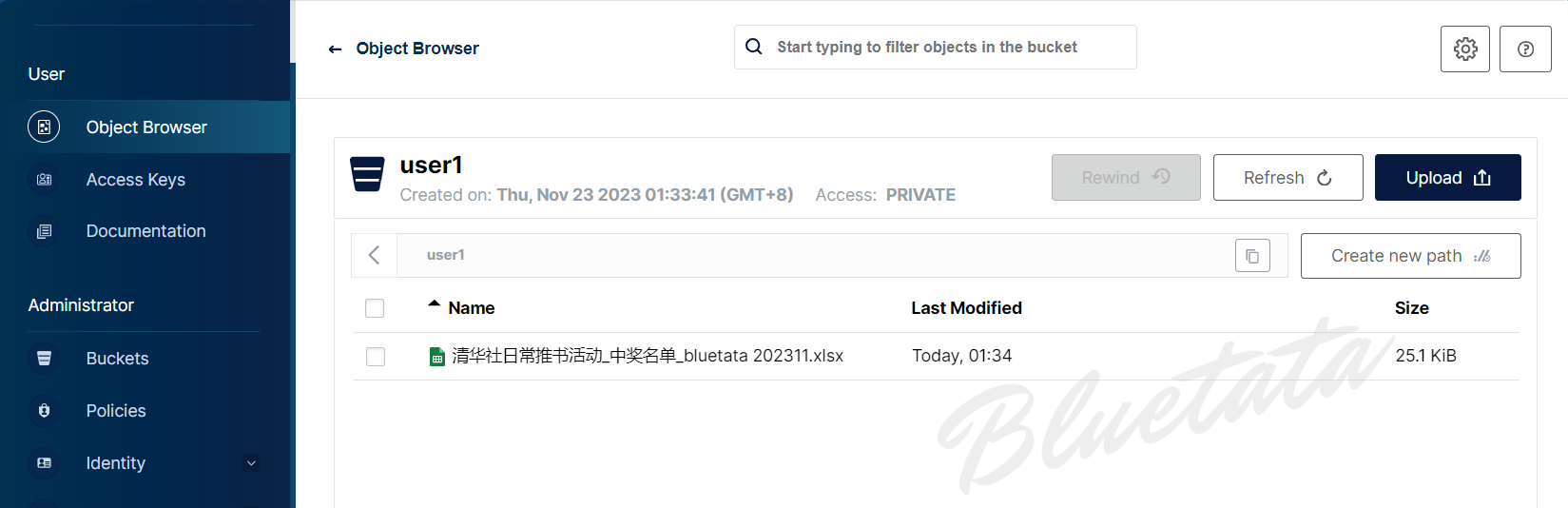
另外我们还可以将文件作为新对象上传到存储桶中:
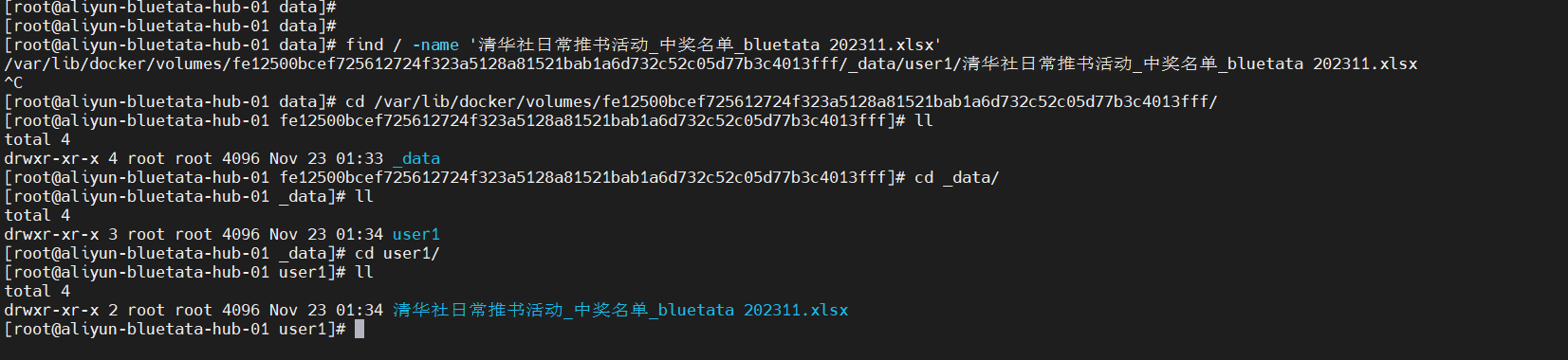
上传成功后,后台服务器存储文件的位置:
一般来说,MinIO 管理控制台的功能与命令行客户端的功能相同。然而,它确实有一些细微的差别。
首先,客户端不可能像命令行客户端那样在存储桶之间移动对象。
另外,命令行客户端还有许多子命令在管理控制台中并不存在。例如,diff、du 和 pipe 子命令都模仿了标准的 Linux 命令,在管理控制台中没有相应的命令。
五、使用 Java 操作 MinIO 对象(原生操作与亚马逊 Java SDK操作)
5.1 原生操作 MinIO
我们将介绍的使用 MinIO 的最后一种方法是使用 Java SDK。首先,我们在应用程序中包含所需的依赖项:
<dependency><groupId>io.minio</groupId><artifactId>minio</artifactId><version>8.5.2</version>
</dependency>
使用 Java SDK 的第一步是创建客户端实例:
MinioClient minioClient =MinioClient.builder().endpoint("http://127.0.0.1:9000").credentials("minioadmin", "minioadmin").build();
此客户端可以使用命令行工具和管理控制台执行我们之前看到的所有相同操作。例如我们可以创建一个Bucket:
minioClient.makeBucket(MakeBucketArgs.builder().bucket("user1").build());
然后,我们可以将文件作为对象上传到该存储桶中:
minioClient.putObject(PutObjectArgs.builder().bucket("user1").object("Resume.pdf").stream(new FileInputStream("/tmp/Resume.pdf").build());
最后,让我们看看如何从存储桶中获取对象:
try (InputStream stream =minioClient.getObject(GetObjectArgs.builder().bucket("user2").object("Resume.pdf").build())) {// Read the stream
}
5.2 使用亚马逊 Java API 操作 MinIO
同样的在使用之前先要引入依赖包
<dependency><groupId>software.amazon.awssdk</groupId><artifactId>s3</artifactId><version>2.21.0</version>
</dependency>
下面直接贴出使用 Amazon JDK 操作对象的相关代码:
public class S3Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{AmazonS3 s3Client= S3Utils.getS3Client("MINIO_ROOT_USER","MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD","http://172.0.0.1:9000");List<Bucket> bucketList=s3Client.listBuckets();List<Bucket> myBuckets=bucketList.stream().filter(bucket -> bucket.getName().equals("bucket01")).collect(Collectors.toList());if(myBuckets.size() < 1){s3Client.createBucket("bucket01");}putObject(s3Client);S3Object s3Object = s3Client.getObject("bucket01","test2.jpg");downLoadObject(s3Object);System.out.println(bucketList);ListObjectsV2Result result = s3Client.listObjectsV2("bucket01");List<S3ObjectSummary> objects = result.getObjectSummaries();for (S3ObjectSummary os : objects) {System.out.println("含有的文件:" + os.getKey());}// 共享文件generatePresignedUrl(s3Client,"bucket01", "test2.jpg");}public static void putObject(AmazonS3 s3Client) throws Exception{File localFile=new File("D:\\bluetata\\test1.txt");ObjectMetadata metadata = new ObjectMetadata();metadata.setContentType("text/plain");//metadata.setContentLength(5);String s3FileFullPath = UUID.randomUUID()+"a.txt";PutObjectResult putResult = s3Client.putObject("bucket01", s3FileFullPath, new FileInputStream(localFile), metadata);System.out.println(putResult);}public static void downLoadObject(S3Object s3Object) throws Exception{File targetFile=new File("D:\\bluetata\\test2.jpg");OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(targetFile);try(BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(s3Object.getObjectContent())){int len ;byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];while((len=bufferedInputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){out.write(buffer, 0, len);}out.flush();}catch (IOException e){GlobalException.throwException(e.getMessage());}out.close();}public static String generatePresignedUrl(AmazonS3 s3Client,String bucketName, String key){GeneratePresignedUrlRequest urlRequest = new GeneratePresignedUrlRequest(bucketName, key);Date expirationDate = null;try {expirationDate = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").parse("2021-09-19");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}//设置过期时间urlRequest.setExpiration(expirationDate);URL url =s3Client.generatePresignedUrl(urlRequest);System.out.println(url);return url.getPath();}}
六、文末总结
文章探讨了 MinIO 这一高性能对象存储系统的重要性和功能。它具备兼容 Amazon S3 API、多种部署选项以及开源特性等优势,适用于各种场景,从开发测试到 DevOps 工具应用。
文中详细介绍了 MinIO 的安装、配置和操作方式,涵盖了使用 Docker 安装、命令行客户端操作、控制台管理、以及使用 Java 原生操作和亚马逊 Java SDK 操作 MinIO 对象的方法。这些方法不仅帮助用户理解 MinIO 的基本操作,还展示了其与其他系统的兼容性和灵活性,使其成为一个强大而多功能的存储解决方案。
[ 本文作者 ] bluetata
[ 原文链接 ] https://bluetata.blog.csdn.net/article/details/134566027
[ 最后更新 ] 11/23/2023 2:15
[ 版权声明 ] 如果您在非 CSDN 网站内看到这一行,
说明网络爬虫可能在本人还没有完整发布的时候就抓走了我的文章,
可能导致内容不完整,请去上述的原文链接查看原文。
