温州手机网站制作多少钱电商运营培训课程有哪些
好了本篇继续介绍JProfiler的功能,让大家更好的理解和运用这个工具,当然可能文章不能更加直观,所以有需要的小伙伴可以自行寻找一下资源,因为主包暂时没有推荐的抱歉。这个是官方文档JProfiler帮助文档 - 内存分析
实时内存
分配调用树
这个是十分好用的功能,我们可以查看方法、类、包的分配情况,主包这边做一个演示打开服务后发送一个请求,然后就可以看到调用树了。
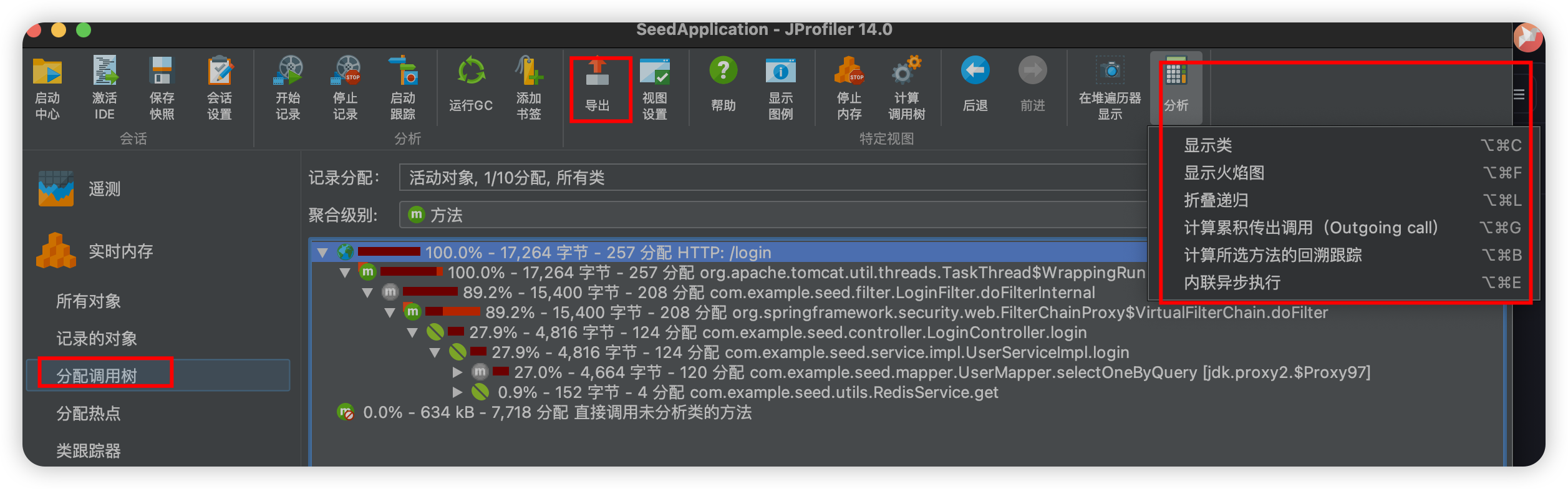
可以看到使用的是根据方法进行聚合的,然后这个请求会显示实际的调用链路,这个百分比就是整个阶段(也就是当前节点和子节点总共的内存分配占比)的内存占比,后面就是一共多少个字节,经历了多少次分配,分配源头是什么,以第一个举例就是,100%的内存占用——一共17264个字节,经历了257次分配,来源于http://login,然后右上角是可以显示火焰图的,火焰图怎么看主包这边就不演示了,还有就是可以选择导出的,我们导出成html或者xml都可以,主包一般都是导出成xml,然后不明白的直接扔给ai让他们分析就可以了。
这个功能可以看到方法、类、包中的分配情况,我们可以根据这个分配情况去锁定一个类或者一个方法,然后对分配异常的进行优化,也可以结合GC来分析是否是这个方法造成的内存泄漏问题。总之这个功能还是十分有效且好用的,小伙伴们快去尝试。
分析热点
简单来说就是用于定位哪些方法或者代码分配的内存的热点图,分配的多就占比多嘛。
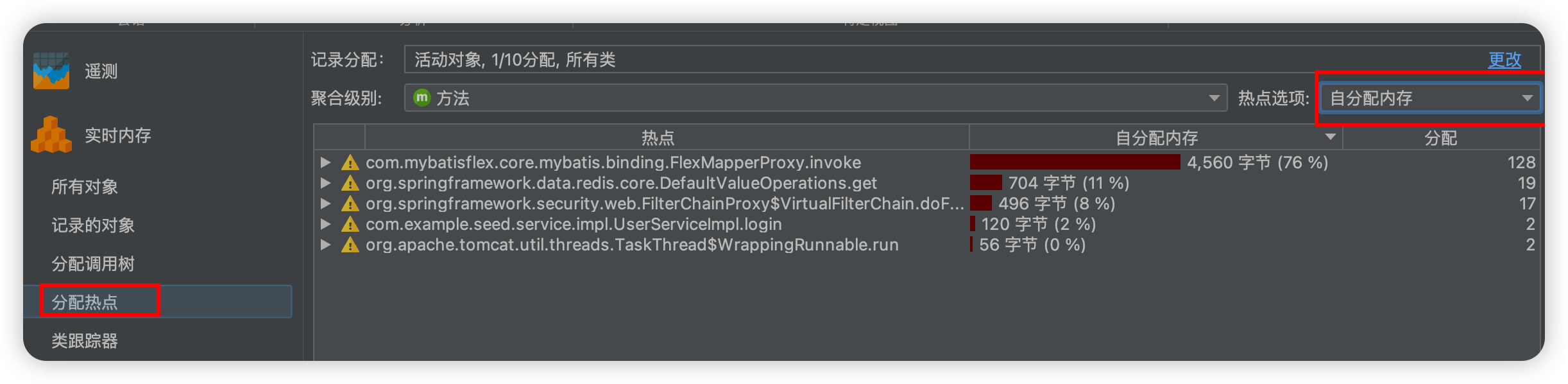
这个可以结合调用树非常直观的就可以看到那个类或方法使用的分配内存最多,然后我们再进行代码优化。
类追踪器
这个就很简单了,就是监控一个类被创建的次数,一般来说是针对我们的核心库的,比如我们一个方法中使用了String类,那这个类被创建了多少个对象,能不能优化?一般是用于解决这个的,当然也可以追踪我们自己的类,看这个类何时何地被创建了,这个功能比较简单就不演示了。
堆遍历器
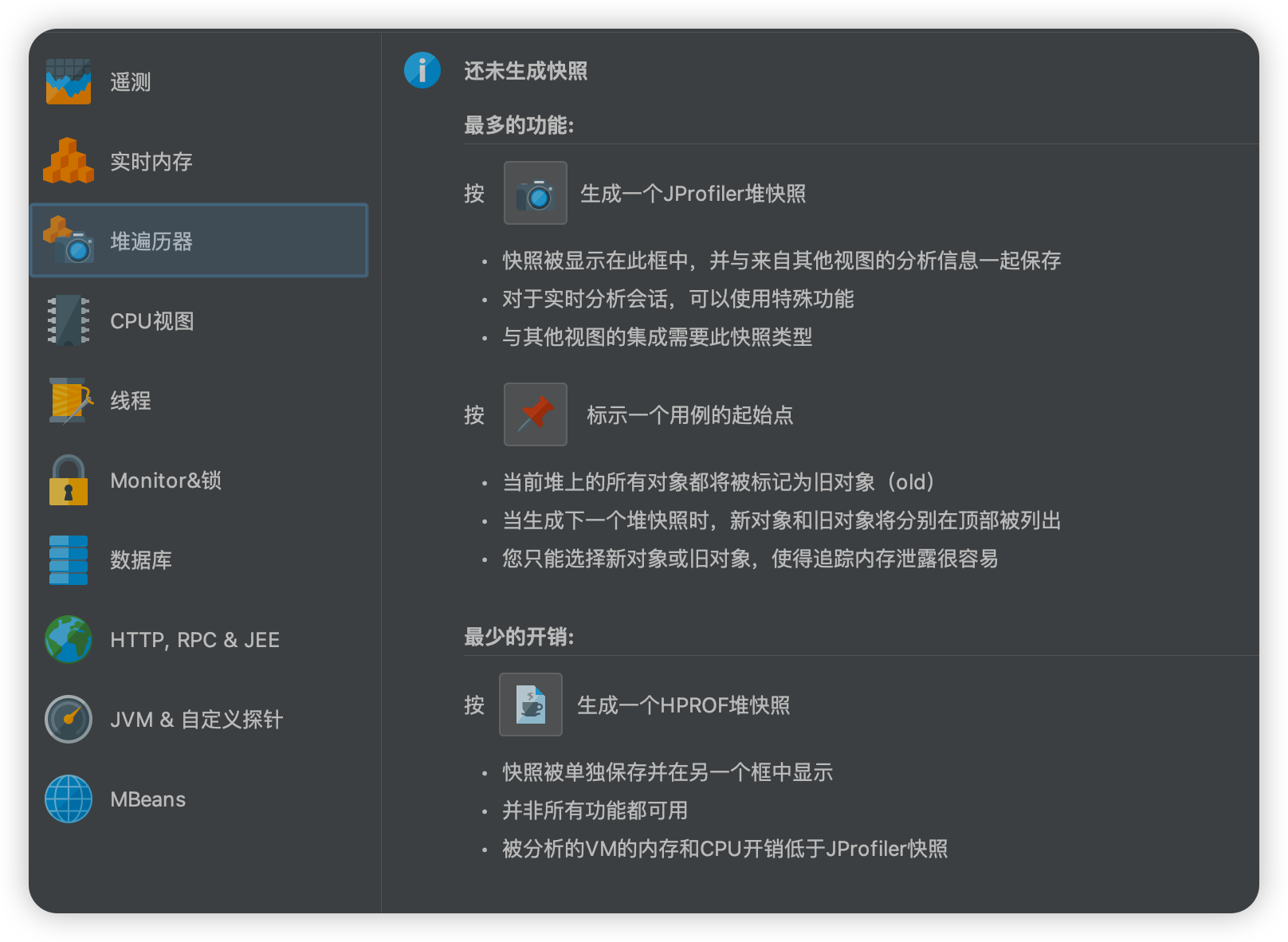
这个堆遍历器一共有三种方式,区别如下列表格,这边就说一下第二种,我们可以在测试一个方法之前选择标记起始点,然后再反复进行测试,最好生成快照,就可以对新旧对象进行比较,快速排查哪些对象没有被回收,从而达到定位内存泄漏的目的。
| 模式 | 生成JProfiler堆快照 | 标记用例起始点 | 生成HPROF堆快照 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 触发方式 | 点击“生成JProfiler堆快照”按钮 | 点击“标记用例起始点”按钮 | 点击“生成HPROF堆快照”按钮 |
| 快照用途 | 集成到JProfiler其他视图(如CPU、线程) | 专门用于追踪内存泄漏(新旧对象对比) | 独立保存,兼容性高(如MAT分析) |
| 功能支持 | 全功能支持(所有堆遍历器功能) | 仅内存泄漏分析(新旧对象分离) | 功能受限(部分分析不可用) |
| 性能开销 | 中等 | 最低(仅标记对象,不生成完整快照) | 最低(但生成时可能短暂STW) |
| 与其他视图集成 | ✅ 支持(如与CPU热点关联) | ❌ 不支持 | ❌ 不支持 |
| 典型场景 | 综合内存分析、性能优化 | 精准定位内存泄漏 | 导出快供其他工具(如MAT)分析 |
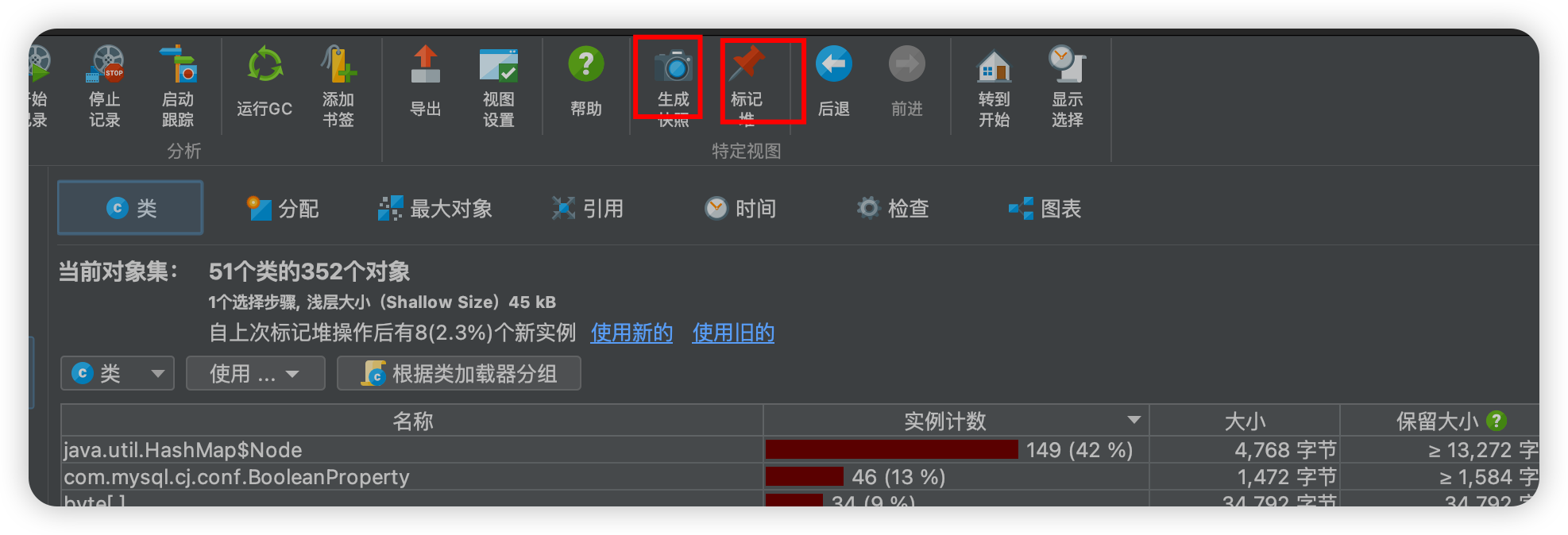
第二种的使用就是先点击生成快照,然后标记,然后发请求,最后再点击生成快照就可以看到有几个新的实例,但是我并没有看到对你,主包也查看了文档并没有说,所以这里不推荐第二种。
好了我们来说一下各个功能的作用,首先这个类视图可以查看当前快照一共有多少个类和多少个对象,可以点击使用然后选择特定的类,然后分配菜单就是就是一个分配树,假设选择了String类,那么分配就会显示是谁分配了这个类,分配了多少,引用分为
- 入引用(Incoming References):谁引用了该对象?
- 出引用(Outgoing References):该对象引用了谁?
也就是不同角度的引用数,根据这个引用树来判断是否出现内存泄漏,这个最大对象就是按对象大小排序,直接显示堆中占用内存最多的单个对象。识别“内存黑洞”(如超大数组或缓存)。时间就很简单了就是显示对象的创建时间(需启用时间戳记录),支持按时间范围过滤对象。追踪特定时间段内创建的对象(如某次操作后的内存增长)图表就是可视化对象引用关系,也就是刚刚说的引用结合使用。另外这个检查还是蛮有意思的官方文档也并没有详细的说明,但是我看功能还是挺好玩的,大火快去试试看。
CPU视图
这个一般情况下使用的不多,因为监测CPU会对吞吐量有影响,也就是说可能会影响用户线程,除非一些特定情况下要使用,因为我们一个内存大分析已经基本上可以确定问题了。
1.调用树(Call Tree)
功能就是显示所有方法调用的层级关系,包括每个方法的执行时间(自耗时和总耗时)。识别耗时最长的调用路径(如深层次的递归或循环调用)。分析框架内部方法(如Spring、Hibernate)的性能影响。如发现 UserService.save() 的80%时间消耗在 JPA EntityManager.flush() 上。
2. 热点(Hot Spots)
功能就是按方法统计耗时排名,直接显示最耗CPU的方法(支持过滤系统类)。快速定位高频或高耗时的单一方法(如JSON序列化、加密算法)。结合分配分析,判断耗时是否由内存分配引起。如String.format() 占用15%的CPU时间,提示可改用更高效的字符串拼接。
3. 调用图(Call Graph)
功能就是图形化展示方法之间的调用关系,用箭头宽度表示耗时占比。可视化复杂调用链路(如微服务间的RPC调用链)。识别冗余调用(如循环中重复执行的查询)。如图中显示 ControllerA → ServiceB → DaoC 的调用链占主导耗时。
另外四个用的就更加少了,主包这边就不一个一个说了,有兴趣的小伙伴上官方文档然后结合自己本地进行测试摸索吧。
线程和锁
这俩比较简单我就放一起说了,就是字面意思一个看线程的信息的比如是否阻塞啊是否等待啊这种的,另外一个就是看是否有死锁的线程的,总之是很好理解的。
数据库
这里主包只介绍这个JDBC了,因为大多数情况下都会用到这个,这个的用处还是非常大的。
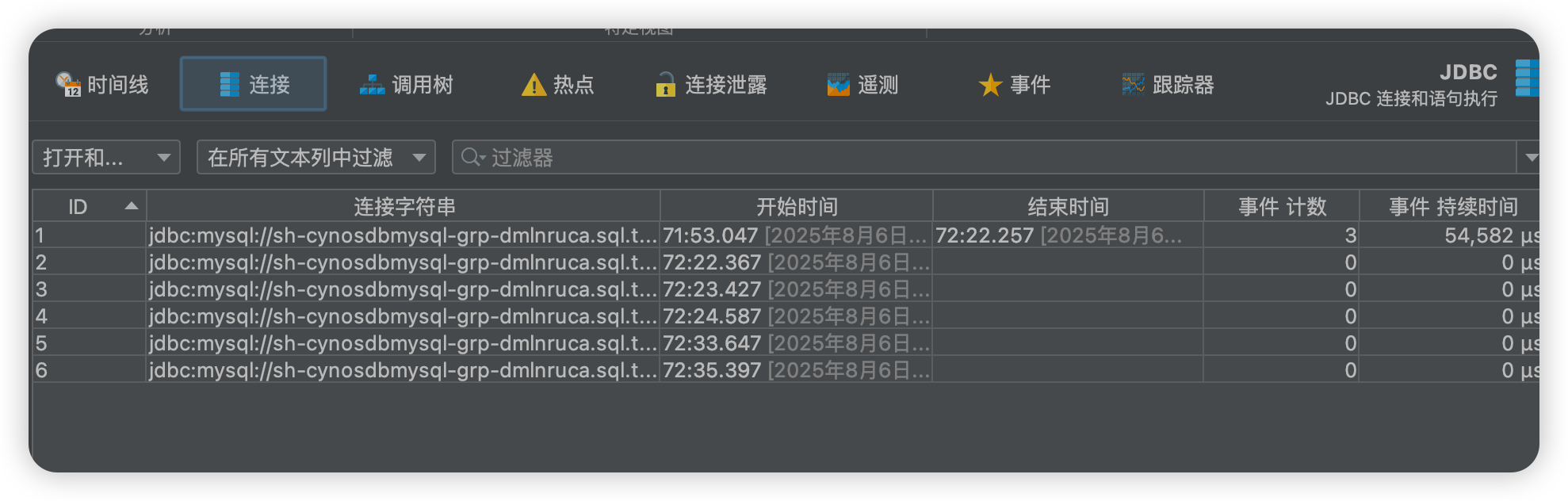
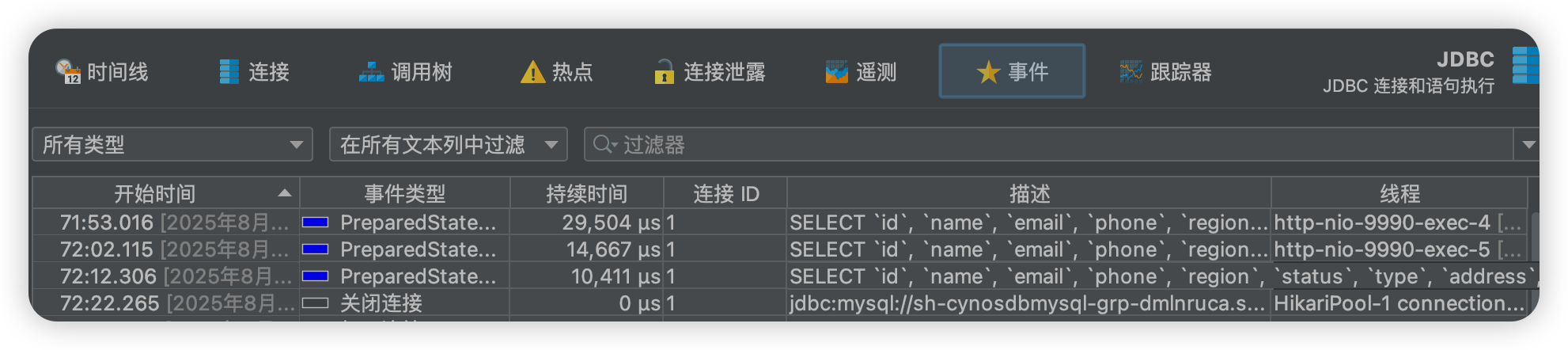
比如我们可以看到线程池连接和关闭的时间,可以看调用树查看调用的时间,这个就非常有用了,可以分析是否慢sql了,然后这个事件可以到开始时间等待一系列信息,点击连接泄漏可以查看链接泄漏的信息,总之是非常有用的。
总结
本篇把JProfiler的主要功能大概介绍了一遍,主要还是需要自己去实践,不然看再多也是无用的,而且建议搭配官方文档,因为好用的教学视频好像并没有,主包可能说的也有问题,欢迎指正,好了JVM监控篇就说完了,具体的调优后续主包看看怎么出吧。
