wordpress phpdisk下载优化大师app
目录
- 1 插值法概述
- 2 插值法原理
- 3 拉格朗日插值
- 4 牛顿插值
- 5 三次Hermite插值(重点)
- 6 三次样条插值(重点)
- 7 各种插值法总结
- 8 n 维数据的插值
- 9 插值法拓展
- 10 课后作业
1 插值法概述
数模比赛中,常常需要根据已知的函数点进行数据、模型的处理和分析,而有时候现有的数据是极少的,不足以支撑分析的进行,这时就需要使用一些数学的方法,“模拟产生”一些新的但又比较靠谱的值来满足需求,这就是插值的作用。
那什么是插值法?

插值法又可以分为以下三类:

❗️ 注意:
- 针对于建模比赛,我们一般只讨论多项式插值和分段插值,三角插值一般要用到傅里叶变换等复杂的数学工具。
2 插值法原理
一维插值 问题:
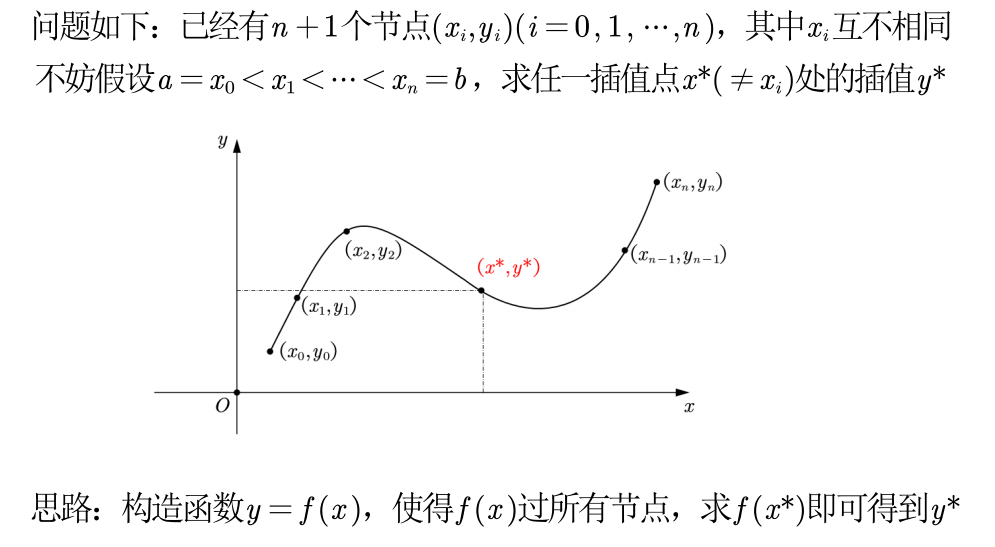

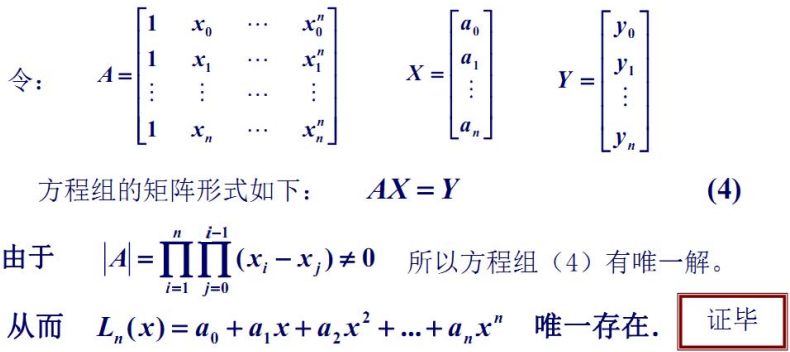
❗️ 注意:
- 只要 n+1 个节点互异,满足上述插值条件的多项式是唯一的
- 如果不限制多项式的次数,插值多项式并不唯一
3 拉格朗日插值
在数值分析中,拉格朗日插值法是以法国十八世纪数学家约瑟夫∙路易斯∙拉格朗日命名的一种多项式插值方法。在若干个不同的地方得到相应的观测值,拉格朗日插值法可以找到一个多项式,其恰好在各个观测的点取到观测到的值。
😋 举例:
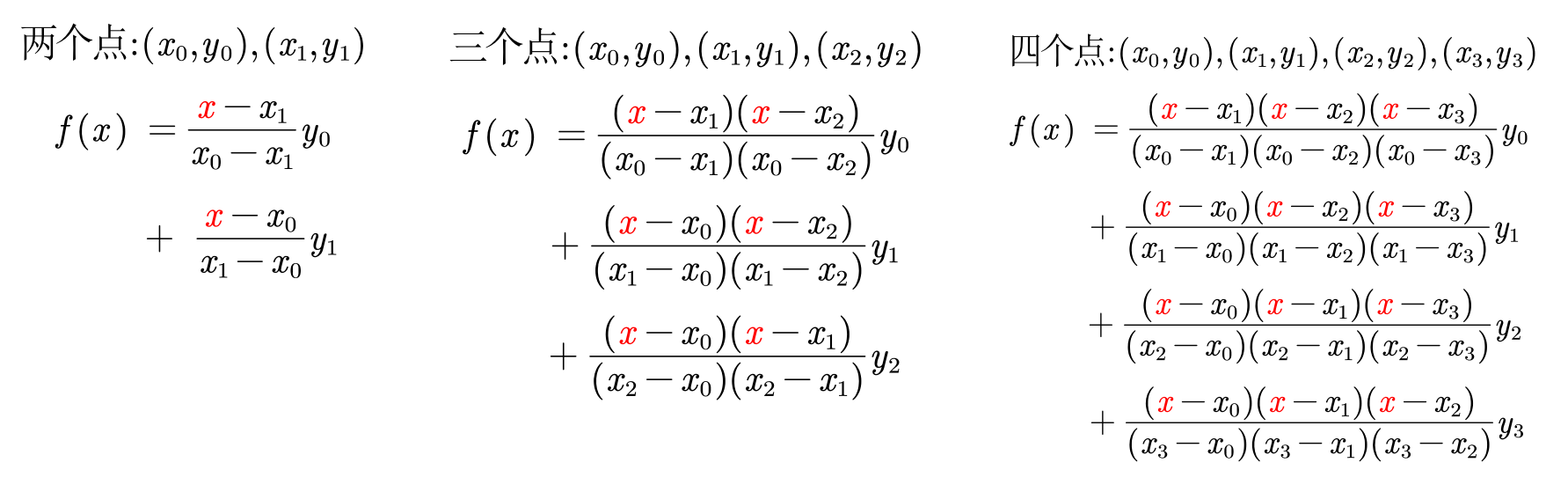
由上述简单的例子可得,拉格朗日插值多项式:

但是使用拉格朗日插值有个很大的缺点:龙格现象(Runge phenomenon)
- 高次插值会产生龙格现象,即在两端处波动极大,产生明显的震荡。在不熟悉曲线运动趋势的前提下,不要轻易使用高次插值。
😋 举例:

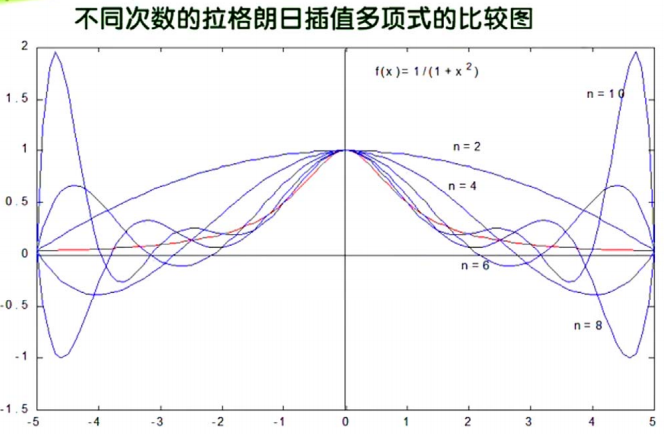
我们已经知道了
- 插值多项式次数高精度未必显著提高
- 插值多项式次数越高摄入的误差可能显著增大
那么如何提高插值精度?—— 采用 分段低次插值

4 牛顿插值

与拉格朗日插值的对比:



❗️注意:
- 所以我们几乎不用拉格朗日插值和牛顿插值,更多的是用下面介绍的埃尔米特(Hermite)插值以及三次样条插值
5 三次Hermite插值(重点)
不但要求在节点上的函数值相等,而且还要求对应的导数值也相等,甚至要求高阶导数也相等,满足这种要求的插值多项式就是 Hermite 插值多项式。

直接使用 Hermite 插值得到的多项式次数较高,也存在着龙格现象,因此在实际应用中,往往使用分段三次 Hermite 插值多项式 (PCHIP)

6 三次样条插值(重点)

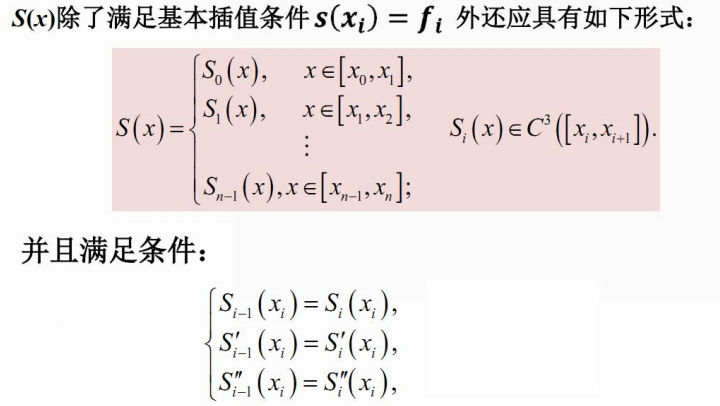

7 各种插值法总结
由于拉格朗日插值和牛顿插值仅仅要求插值多项式在插值节点处与被插函数有相等的函数值,而这种插值多项式却不能全面反映被插值函数的性态,我们一般不用。
三次Hermite插值与样条插值结果对比
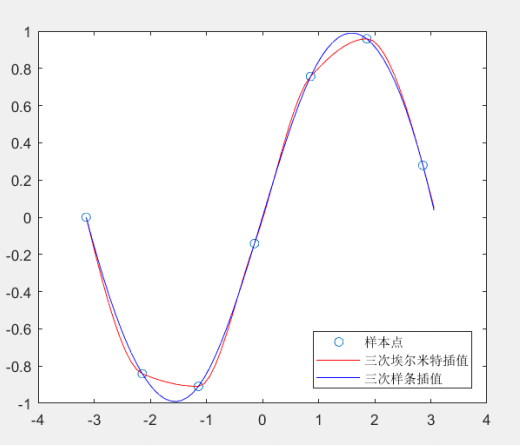
可以看出,三次样条生成的曲线更加光滑。在实际建模中,由于我们不知道数据的生成过程,因此这两种插值都可以使用。
8 n 维数据的插值

9 插值法拓展
以上插值算法也可用于短期预测
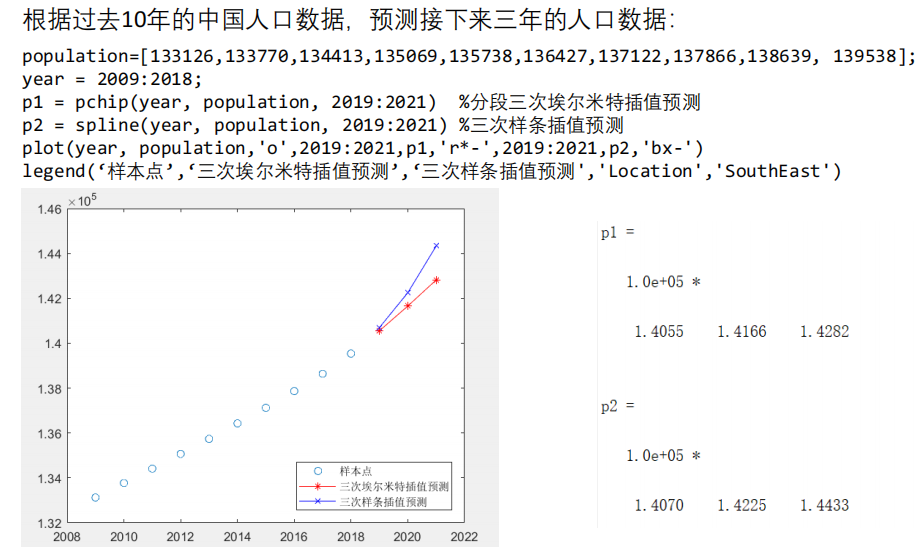
❗️注意:
- 实际建模过程中,大家尽量不要用插值算法来预测,上面只是给大家举的一个小例子;如果要预测,可以选择拟合算法,也可以使用之后要学的专门用于预测的算法。
10 课后作业
建模实例:MathorCup 第六届A题 淡水养殖池塘水华发生及池水净化处理
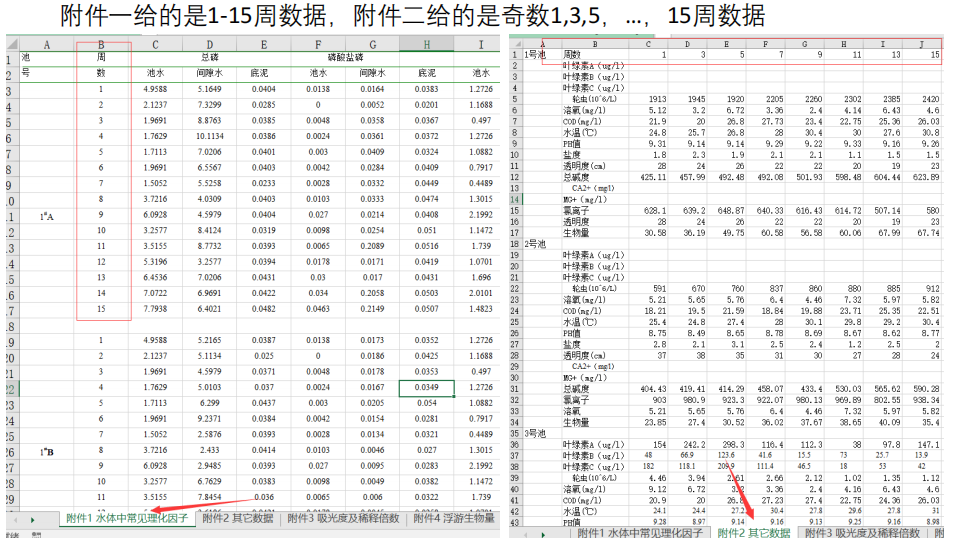
华中农业大学特等奖文章

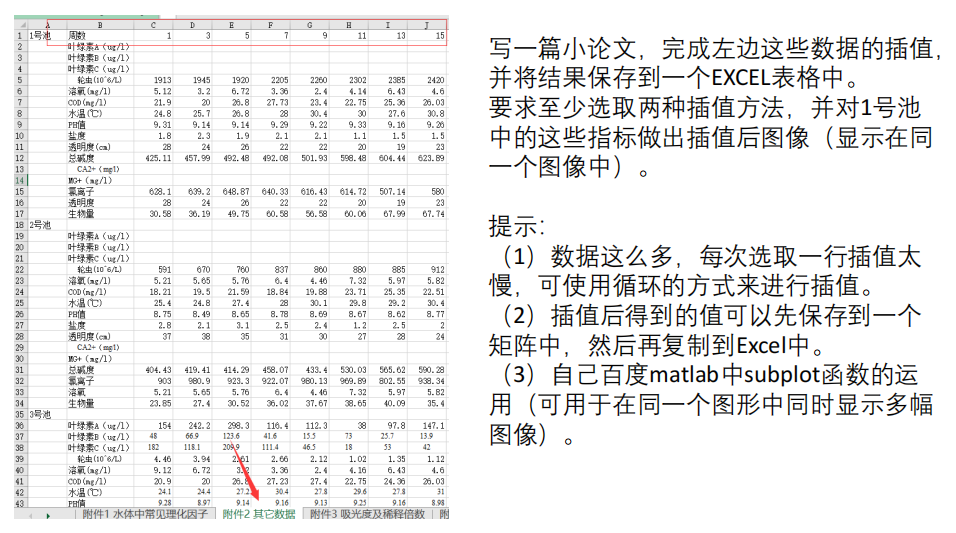
参考答案:
