做外贸哪些网站好推广的公司
一 直接使用Rabbit MQ
在Java项目中使用Rabbit MQ可以通过引入Rabbit MQ的客户端Maven依赖,和Rabbit MQ建立连接进行通信。这种就属于是直接使用Rabbit MQ。
基本使用
创建连接后,使用channel向交换机发送消息
public class Producer {private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "hello";public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//创建一个连接工厂ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();//mq地址factory.setHost("124.223.183.227");//mq登录名factory.setUsername("pangpi");//登录名对应密码factory.setPassword("xxxxx");//channel 实现了自动 close 接口 自动关闭 不需要显示关闭try(Connection connection = factory.newConnection();Channel channel =connection.createChannel()) {/*** 生成一个队列* 1.队列名称* 2.队列里面的消息是否持久化 默认消息存储在内存中* 3.该队列是否只供一个消费者进行消费 是否进行共享 true 可以多个消费者消费* 4.是否自动删除 最后一个消费者端开连接以后 该队列是否自动删除 true 自动删除* 5.其他参数*/channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME,false,false,false,null);String message="hello world";/*** 发送一个消息* 1.发送到那个交换机* 2.路由的 key 是哪个* 3.其他的参数信息* 4.发送消息的消息体*/channel.basicPublish("",QUEUE_NAME,null,message.getBytes());System.out.println("消息发送完毕");}}
}
消费者通过给channel绑定回调方法,使得接收到消息后使用回调方法的逻辑去处理消息
public class Consumer {private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "hello";public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();//mq地址factory.setHost("124.223.183.227");//mq登录名factory.setUsername("pangpi");//登录名对应密码factory.setPassword("xxxx");Connection connection = factory.newConnection();Channel channel = connection.createChannel();System.out.println("等待接收消息....");//推送的消息如何进行消费的接口回调DeliverCallback deliverCallback=(consumerTag,delivery)->{String message= new String(delivery.getBody());System.out.println(message);};//取消消费的一个回调接口 如在消费的时候队列被删除掉了CancelCallback cancelCallback=(consumerTag)->{System.out.println("消息消费被中断");};/*** 消费者消费消息* 1.消费哪个队列* 2.消费成功之后是否要自动应答 true 代表自动应答 false 手动应答* 3.消费者接收到消息的回调* 4.消费者未成功消费的回调*/channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME,true,deliverCallback,cancelCallback);}
}消费组
消费组是指多个消费者组成一个集体,一起消费某个队列的消息,这样就能使得消息分流到不同的消费者中,从而提高某个队列的消费能力。
根据上面的代码抽取连接建立的工具类
public class RabbitMqUtils {//得到一个连接的 channelpublic static Channel getChannel() throws Exception{//创建一个连接工厂ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();factory.setHost("182.92.234.71");factory.setUsername("admin");factory.setPassword("123");Connection connection = factory.newConnection();Channel channel = connection.createChannel();return channel;}
}
创建两个消费者一起去消费同一个队列的消息
public class Worker01 {private static final String QUEUE_NAME="hello";public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Channel channel = RabbitMqUtils.getChannel();DeliverCallback deliverCallback=(consumerTag,delivery)->{String receivedMessage = new String(delivery.getBody());System.out.println("接收到消息:"+receivedMessage);};CancelCallback cancelCallback=(consumerTag)->{System.out.println(consumerTag+"消费者取消消费接口回调逻辑");};System.out.println("C1消费者启动等待消费......");channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME,true,deliverCallback,cancelCallback);}
}
//----------------------------------------------
public class Worker02 {private static final String QUEUE_NAME="hello";public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Channel channel = RabbitMqUtils.getChannel();DeliverCallback deliverCallback=(consumerTag,delivery)->{String receivedMessage = new String(delivery.getBody());System.out.println("接收到消息:"+receivedMessage);};CancelCallback cancelCallback=(consumerTag)->{System.out.println(consumerTag+"消费者取消消费接口回调逻辑");};System.out.println("C2消费者启动等待消费......");channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME,true,deliverCallback,cancelCallback);}
}
启动一个生产者往队列中发送消息
public class Task01 {private static final String QUEUE_NAME="hello";public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {try(Channel channel=RabbitMqUtils.getChannel();) {channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME,false,false,false,null);//从控制台当中接受信息Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);while (scanner.hasNext()){String message = scanner.next();channel.basicPublish("",QUEUE_NAME,null,message.getBytes());System.out.println("发送消息完成:"+message);}}}
}
通过程序执行发现生产者总共发送 4个消息,消费者 1和消费者 2分别分得两个消息,并且是按照有序的一个接收一次消息
消息应答
消息应答机制,是为了保证消息不丢失,具体做法是消费者在接收到消息并且处理该消息之后,告诉Rabbit MQ它已经处理了,Rabbit MQ可以把该消息删除了。如果Rabbit MQ半天没有接收到应答,那么它将会把消息重新发送给其他的消费者。
消息应答分为:手动应答和自动应答,如何抉择就需要在高吞吐量和数据传输安全性方面做权衡,自动应答仅适用在消费者可以高效并以某种速率能够处理这些消息的情况下使用。
public class Task02 {private static final String TASK_QUEUE_NAME = "ack_queue";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {try (Channel channel = RabbitMqUtils.getChannel()) {channel.queueDeclare(TASK_QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入信息");while (sc.hasNext()) {String message = sc.nextLine();channel.basicPublish("",TASK_QUEUE_NAME,null, message.getBytes("UTF-8"));System.out.println("生产者发出消息" + message);}}}
}
批量应答消息,就是将当前消息之前的消息一起应答。
public class Work03 {private static final String ACK_QUEUE_NAME="ack_queue";public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Channel channel = RabbitMqUtils.getChannel();System.out.println("C1等待接收消息处理时间较短");//消息消费的时候如何处理消息DeliverCallback deliverCallback=(consumerTag,delivery)->{String message= new String(delivery.getBody());SleepUtils.sleep(1);System.out.println("接收到消息:"+message);/*** 1.消息标记 tag* 2.是否批量应答未应答消息*/channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(),false);};//采用手动应答boolean autoAck=false;channel.basicConsume(ACK_QUEUE_NAME,autoAck,deliverCallback,(consumerTag)->{System.out.println(consumerTag+"消费者取消消费接口回调逻辑");});}
}
public class Work04 {private static final String ACK_QUEUE_NAME="ack_queue";public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Channel channel = RabbitMqUtils.getChannel();System.out.println("C2等待接收消息处理时间较长");//消息消费的时候如何处理消息DeliverCallback deliverCallback=(consumerTag,delivery)->{String message= new String(delivery.getBody());SleepUtils.sleep(30);System.out.println("接收到消息:"+message);/*** 1.消息标记 tag* 2.是否批量应答未应答消息*/channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(),false);};//采用手动应答boolean autoAck=false;channel.basicConsume(ACK_QUEUE_NAME,autoAck,deliverCallback,(consumerTag)->{System.out.println(consumerTag+"消费者取消消费接口回调逻辑");});}
}
消费者2休眠30秒后,消息已经触发了ACK的范围,所以将会被消费者1进行消费
消息持久化
消息应答是保证消息到达生产者这个流程中不被丢失,而消息持久化是保证消息从生产者到Rabbit MQ不丢失。生产者会等到Rabbit MQ将消息持久化后才会将消息删除。
要想持久化消息,就要先持久化队列,然后在发送消息时绑定参数告诉Rabbit MQ这条消息需要持久化
队列实现持久化,需要在声明队列的时把durable参数设置为(true)持久化,如果之前声明的队列不是持久化的,需要把原先队列先删除,或者重新创建一个持久化的队列,不然就会出现错误

消息持久化需要消息生产者修改代码,MessageProperties.PERSISTENT_TEXT_PLAIN 添加这个属性。

需要注意的是,即使持久化了消息和队列也不能保证消息不丢失。
发布确认
生产者将信道设置成confirm模式,所有在该信道上面发布的消息都将会被指派一个唯一的 ID(从 1开始),一旦消息被投递到所有匹配的队列之后,broker就会发送一个确认给生产者(包含消息的唯一 ID),这就使得生产者知道消息已经正确到达目的队列了,如果消息和队列是可持久化的,那么确认消息会在将消息写入磁盘之后发出
broker回传给生产者的确认消息中 delivery-tag域包含了确认消息的序列号,此外 broker也可以设置basic.ack的 multiple域,表示到这个序列号之前的所有消息都已经得到了处理。
发布确认有多种方式:
单个确认发布:发布速度特别的慢
批量确认发布:发生故障导致发布出现问题时,不知道是哪个消息出现问题了
异步确认发布:复杂,但是性价比最高,无论是可靠性还是效率都没得说
异步确认发布代码如下:
/**
* 异步发布确认
* 安全且快速
*/
public static void publishMessageAsync() throws IOException, TimeoutException {//获取信道---封装好的函数Channel channel = RabbitUtils.createChannel();//创建队列String queueName = UUID.randomUUID().toString();channel.queueDeclare(queueName,true,false,false,null);//开启发布确认channel.confirmSelect();/*** 线程安全有序的一个hash表,适用于高并发* 1.能轻松的将序号与消息进行关联* 2.能轻松的批量删除内容,只要给到序号---key* 3.支持高并发*/ConcurrentSkipListMap<Long,String> outStandConfirm = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();/*** 创建确认成功回调* 第一个参数为消息的标记* 第二个参数为是否批量确认*/ConfirmCallback AckCallback = (deliveryTag,multiple)->{//删除已经确认的消息,剩下的就是未确认的if (multiple){//如果我们在设置却时是批量确认,那么全部清空ConcurrentNavigableMap<Long, String> confirm = outStandConfirm.headMap(deliveryTag);confirm.clear();}else {//如果不是批量确认,就删除当前已经确认的消息outStandConfirm.remove(deliveryTag);}};//创建确认失败回调//开发中,我们一般会对未确认的消息进行补发//而且确认成功的回调函数中已经把确认成功的消息删除了//那么我们可以直接使用map获取剩余的未成功的消息进行补发ConfirmCallback nAckCallback = (deliveryTag,multiple)->{String s = outStandConfirm.get(deliveryTag);System.out.println("未确认的消息"+s);};//添加消息监听器,监听哪些消息成功,哪些失败/*** 第一个参数表示,消息成功确认的回调* 第二个参数表示,消息失败确认的回调*/channel.addConfirmListener(AckCallback,nAckCallback);//发送消息for (int i = 0; i < PUBLISH_COUNT; i++){String message = "消息"+i;channel.basicPublish("",queueName,null,message.getBytes());//记录发送的消息outStandConfirm.put(channel.getNextPublishSeqNo(),message);}
}
不公平分发与预取值
消费者端存在一个未确认的消息缓冲区,开发人员能限制此缓冲区的大小,以避免缓冲区里面无限制的未确认消息问题。当消息塞满缓冲区后(消费者消费速度不够快),Rabbit MQ将不会继续向消费者发送消息。
通过channel.basicQos(prefetchCount);设置具体的数量,就可以限制缓冲区消息的数量。
public class Worker03 {//队列名称public static final String TASK_QUEUE_NAME = "ack_queue";public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {Channel channel = RabbitUtils.createChannel();System.out.println("C1等待接收消息处理时间较短");//设置接收消息回调函数DeliverCallback callback = (consumerTag,message)->{//沉睡SleepUtils.sleep(1);System.out.println("接收消息:"+new String(message.getBody(),"UTF-8"));/*** 手动应答* 1.消息的标记,告诉消息队列应答的消息是哪个* 2.是否批量应答消息,一般不批量,以免应答了不属于自己的消息*/channel.basicAck(message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(),false);};int prefetchCount = 1;//设置分发策略为1-->不公平分发(负载均衡)channel.basicQos(prefetchCount);//采用手动应答boolean autoAck = false;channel.basicConsume(TASK_QUEUE_NAME,autoAck,callback,me->{});}
}
二 交换机
交换机
RabbitMQ消息传递模型的核心思想是: 生产者生产的消息从不会直接发送到队列。实际上,通常生产者甚至都不知道这些消息传递传递到了哪些队列中。
相反,生产者只能将消息发送到交换机(exchange),交换机工作的内容非常简单,一方面它接收来自生产者的消息,另一方面将它们推入队列。交换机必须确切知道如何处理收到的消息。是应该把这些消息放到特定队列还是说把他们到许多队列中还是说应该丢弃它们。这就的由交换机的类型来决定。
Rabbit MQ的交换机有如下几种:
- 直接(direct):消息被发送到与消息的路由键(routing key)完全匹配的队列中
- 主题(topic) :类似direct交换机,但是可以利用通配符将一条消息同时匹配多个队列
- 标题(headers):消息被路由到队列的规则不再基于路由键(routing key),而是基于消息的标题属性
- 广播(fanout):将接收到的所有消息广播到它知道的所有队列中。
绑定-Binding
Binding是 交换机 和 队列 之间的桥梁,它告诉我们 交换机 和哪个队列进行了绑定关系。比如说下面这张图告诉我们的就是 X 与 Q1 和 Q2 进行了绑定

channel.queueBind("队列名称", "交换机名称", "路由key/可以为空");
- 需要注意的是,同一个路由key可以给多个队列绑定,同时一个队列也可以有多个路由key进行绑定,如下两种情况


交换机案例
构建一个简单的日志系统。它将由两个程序组成:第一个程序将发出日志消息,第二个程序是消费者。其中我们会启动多个消费者,分别对日志做不同的操做。
Fanout类型交换机
Fanout就是我们说的广播,这种模式需要将队列和交换机进行直接绑定即可,不需要使用路由或者topic等
下面的案例是将消息广播到多个队列中,每个队列连接一个消费者,同时它们的具体任务不同。

- 生产者代码,直接将消息发送到交换机即可,不需要指定路由等信息
public class EmitLog {private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "logs";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {try (Channel channel = RabbitUtils.getChannel()) {/*** 声明一个 exchange* 1.exchange的名称* 2.exchange的类型*/channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout");Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入信息");while (sc.hasNext()) {String message = sc.nextLine();channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, "", null, message.getBytes("UTF-8"));System.out.println("生产者发出消息" + message);}}}
}
- 消费1的代码,其中利用
queueBind将交换机和队列进行了绑定。此时向交换机发送消息就会直接发送到和交换机绑定的队列中
public class Consumer1 {private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "logs";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {Channel channel = RabbitUtils.getChannel();channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout");/*** 生成一个临时的队列 队列的名称是随机的* 当消费者断开和该队列的连接时 队列自动删除*/String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();//把该临时队列绑定我们的 exchange 其中 routingkey(也称之为 binding key)为空字符串channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "");System.out.println("等待接收消息,把接收到的消息打印在屏幕.....");DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");System.out.println("控制台打印接收到的消息"+message);};channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, deliverCallback, consumerTag -> { });}
}
- 消费者2
public class Consumer2 {private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "logs";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {Channel channel = RabbitUtils.getChannel();channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout");/*** 生成一个临时的队列 队列的名称是随机的* 当消费者断开和该队列的连接时 队列自动删除*/String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();//把该临时队列绑定我们的 exchange 其中 routingkey(也称之为 binding key)为空字符串channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "");System.out.println("等待接收消息,把接收到的消息写到文件.....");DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");File file = new File("C:\\work\\rabbitmq_info.txt");FileUtils.writeStringToFile(file,message,"UTF-8");System.out.println("数据写入文件成功");};channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, deliverCallback, consumerTag -> { });}
}
Direct类型交换机
Direct交换机可以根据消费者指定消息要发送的路由来将消息发送到指定的队列进行消费,主要利用的就是Binding
再次来回顾一下什么是 bindings,绑定是交换机和队列之间的桥梁关系。也可以这么理解:队列只对它绑定的交换机的消息感兴趣。绑定用参数:routingKey(路由) 来表示也可称该参数为 binding key,创建绑定我们用代码:channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "routingKey");绑定之后的意义由其交换类型决定。

如上,我们本次需要将消息根据指定的 orange、black、green发送到其绑定的具体队列上
- 消费者分别向四种路由发送消息,其中debug路由的消息不会被消费,因为我们接下来的队列绑定中不会绑定debug路由key
public class EmitLogDirect {private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "direct_logs";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {try (Channel channel = RabbitUtils.getChannel()) {channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT);//创建多个 bindingKeyMap<String, String> bindingKeyMap = new HashMap<>();bindingKeyMap.put("info","普通 info信息");bindingKeyMap.put("warning","警告 warning信息");bindingKeyMap.put("error","错误 error信息");//debug没有消费这接收这个消息 所有就丢失了bindingKeyMap.put("debug","调试 debug信息");for (Map.Entry<String, String> bindingKeyEntry: bindingKeyMap.entrySet()){String bindingKey = bindingKeyEntry.getKey();String message = bindingKeyEntry.getValue();channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME,bindingKey,message.getBytes("UTF-8"));System.out.println("生产者发出消息:" + message);null,}}}
}
- 消费者1,绑定了error路由key
public class Consumer1 {private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "direct_logs";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {Channel channel = RabbitUtils.getChannel();channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT);String queueName = "disk";channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "error");System.out.println("等待接收消息.....");DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");message="接收绑定键:"+delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey()+",消息:"+message;File file = new File("C:\\work\\rabbitmq_info.txt");FileUtils.writeStringToFile(file,message,"UTF-8");System.out.println("错误日志已经接收");};channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, deliverCallback, consumerTag -> {});}
}
- 消费者2,通过队列绑定了两个路由key
public class Consumer2 {private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "direct_logs";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {Channel channel = RabbitUtils.getChannel();channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT);String queueName = "console";channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "info");channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "warning");System.out.println("等待接收消息.....");DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");System.out.println("接 收 绑 定 键 :"+delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey()+",消息:"+message);};channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, deliverCallback, consumerTag -> {});}
}
Topics类型交换机
发送到类型是 topic 交换机的消息的 routing_key 不能随意写,必须满足一定的要求,它必须是一个单词列表,以点号分隔开。这些单词可以是任意单词,比如说:“stock.usd.nyse”。且单词列表最多不能超过 255 个字节。
在这个规则列表中,其中有两个替换符是大家需要注意的
- *(星号)可以代替一个单词
- #(井号)可以替代零个或多个单词
如下的一个绑定案例

那么这样绑定,发送消息时,指定不同的路由,会有不同的效果,如下
| quick.orange.rabbit | 被队列 Q1Q2 接收到 |
|---|---|
| lazy.orange.elephant | 被队列 Q1Q2 接收到 |
| quick.orange.fox | 被队列 Q1 接收到 |
| lazy.brown.fox | 被队列 Q2 接收到 |
| lazy.pink.rabbit | 虽然满足两个绑定但只被队列 Q2 接收一次 |
| quick.brown.fox | 不匹配任何绑定不会被任何队列接收到会被丢弃 |
| quick.orange.male.rabbit | 是四个单词不匹配任何绑定会被丢弃 |
| lazy.orange.male.rabbit | 是四个单词但匹配 Q2 |
- 生产者代码如下,按照上面的表格向交换机发送消息
public class EmitLogTopic {private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "topic_logs";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {try (Channel channel = RabbitUtils.getChannel()) {channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic");/*** Q1-->绑定的是* 中间带 orange带 3个单词的字符串(*.orange.*)* Q2-->绑定的是* 最后一个单词是 rabbit的 3个单词(*.*.rabbit)* 第一个单词是 lazy的多个单词(lazy.#)**/Map<String, String> bindingKeyMap = new HashMap<>();bindingKeyMap.put("quick.orange.rabbit","被队列 Q1Q2接收到");bindingKeyMap.put("lazy.orange.elephant","被队列 Q1Q2接收到");bindingKeyMap.put("quick.orange.fox","被队列 Q1接收到");bindingKeyMap.put("lazy.brown.fox","被队列 Q2接收到");bindingKeyMap.put("lazy.pink.rabbit","虽然满足两个绑定但只被队列 Q2接收一次");bindingKeyMap.put("quick.brown.fox","不匹配任何绑定不会被任何队列接收到会被丢弃");bindingKeyMap.put("quick.orange.male.rabbit","是四个单词不匹配任何绑定会被丢弃");bindingKeyMap.put("lazy.orange.male.rabbit","是四个单词但匹配 Q2");for (Map.Entry<String, String> bindingKeyEntry: bindingKeyMap.entrySet()){String bindingKey = bindingKeyEntry.getKey();String message = bindingKeyEntry.getValue();channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME,bindingKey,null,message.getBytes("UTF-8"));System.out.println("生产者发出消息" + message);}}}
}
- 消费者
public class ReceiveLogsTopic01 {private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "topic_logs";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {Channel channel = RabbitUtils.getChannel();channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic");//声明 Q1 队列与绑定关系String queueName="Q1";channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "*.orange.*");System.out.println("等待接收消息.....");DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");System.out.println(" 接收队列 :"+queueName+" 绑定键:"+delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey()+",消息:"+message);};channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, deliverCallback, consumerTag -> {});}
}
public class ReceiveLogsTopic02 {private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "topic_logs";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {Channel channel = RabbitUtils.getChannel();channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic");//声明 Q2 队列与绑定关系String queueName="Q2";channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "*.*.rabbit");channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "lazy.#");System.out.println("等待接收消息.....");DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");System.out.println(" 接收队列 :"+queueName+" 绑定键:"+delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey()+",消息:"+message);};channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, deliverCallback, consumerTag -> {});}
}
三 死信
死信队列
死信:顾名思义就是无法被消费的消息。producer将消息投递到broker或者直接到queue里了,consumer 从 queue 取出消息进行消费。
死信队列:某些时候由于特定的原因导致 queue 中的某些消息无法被消费,这样的消息如果没有后续的处理,就变成了死信,存放死信的队列就是死信队列。
应用场景:为了保证订单业务的消息数据不丢失,需要使用到 RabbitMQ 的死信队列机制,当消息消费发生异常时,将消息投入死信队列中。
**延迟队列:**用户在商城下单成功并点击去支付后在指定时间未支付时自动失效
死信的来源:
- 消息 TTL 过期
- 队列达到最大长度(队列满了,无法再添加数据到 mq 中)
- 消息被拒绝(basic.reject 或 basic.nack)并且 requeue=false.
死信案例
延迟队列实现
- 生产者向
normal_exchange交换机的zhangsan发送消息
public class Producer {private static final String NORMAL_EXCHANGE = "normal_exchange";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {try (Channel channel = RabbitMqUtils.getChannel()) {channel.exchangeDeclare(NORMAL_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT);//设置消息的 TTL 时间AMQP.BasicProperties properties = newAMQP.BasicProperties().builder().expiration("10000").build();//该信息是用作演示队列个数限制for (int i = 1; i <11 ; i++) {String message="info"+i;channel.basicPublish(NORMAL_EXCHANGE, "zhangsan", properties,message.getBytes());System.out.println("生产者发送消息:"+message);}}}
}
- 消费者1:这个消费者在创建队列时,就要指定当前队列的消息一旦成为死信后向哪个交换机(死信交换机)和路由key发送,最终将此队列和
normal_exchange进行绑定
public class Consumer01 {//普通交换机名称private static final String NORMAL_EXCHANGE = "normal_exchange";//死信交换机名称private static final String DEAD_EXCHANGE = "dead_exchange";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {Channel channel = RabbitUtils.getChannel();//声明死信和普通交换机 类型为 directchannel.exchangeDeclare(NORMAL_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT);channel.exchangeDeclare(DEAD_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT);//声明死信队列String deadQueue = "dead-queue";channel.queueDeclare(deadQueue, false, false, false, null);//死信队列绑定死信交换机与 routingkeychannel.queueBind(deadQueue, DEAD_EXCHANGE, "lisi");//正常队列绑定死信队列信息Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>();//正常队列设置死信交换机 参数 key 是固定值params.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", DEAD_EXCHANGE);//正常队列设置死信 routing-key 参数 key 是固定值params.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "lisi");String normalQueue = "normal-queue";channel.queueDeclare(normalQueue, false, false, false, params);channel.queueBind(normalQueue, NORMAL_EXCHANGE, "zhangsan");System.out.println("等待接收消息.....");DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");System.out.println("Consumer01 接收到消息"+message);};channel.basicConsume(normalQueue, true, deliverCallback, consumerTag -> {});}
}
- 消费者2:将死信队列和死信交换机进行绑定,消费死信队列的消息
public class Consumer02 {private static final String DEAD_EXCHANGE = "dead_exchange";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {Channel channel = RabbitUtils.getChannel();channel.exchangeDeclare(DEAD_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT);String deadQueue = "dead-queue";channel.queueDeclare(deadQueue, false, false, false, null);channel.queueBind(deadQueue, DEAD_EXCHANGE, "lisi");System.out.println("等待接收死信队列消息.....");DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");System.out.println("Consumer02 接收死信队列的消息" + message);};channel.basicConsume(deadQueue, true, deliverCallback, consumerTag -> {});}
}
队列达到最大长度的死信队列
- 消息生产者代码去掉 TTL 属性,不需要过期时间
public class Producer {private static final String NORMAL_EXCHANGE = "normal_exchange";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {try (Channel channel = RabbitMqUtils.getChannel()) {channel.exchangeDeclare(NORMAL_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT);//该信息是用作演示队列个数限制for (int i = 1; i <11 ; i++) {String message="info"+i;channel.basicPublish(NORMAL_EXCHANGE,"zhangsan",null, message.getBytes());System.out.println("生产者发送消息:"+message);}}}
}
- 消费者端只需要修改队列的设置参数,添加一个
x-max-length参数指定队列最大长度即可,为了方便理解代码,所以只需要关注params的参数设置
public class Consumer01 {//普通交换机名称private static final String NORMAL_EXCHANGE = "normal_exchange";//死信交换机名称private static final String DEAD_EXCHANGE = "dead_exchange";public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {//正常队列绑定死信队列信息Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>();//正常队列设置死信交换机 参数 key 是固定值params.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", DEAD_EXCHANGE);//正常队列设置死信 routing-key 参数 key 是固定值params.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "lisi");// 设置队列的最大长度,超过长度的将会被发送到死信队列params.put("x-max-length", 6)}
}
消息被拒绝的死信
- 这种情况的死信不需要代码进行演示,只需要设置params的参数绑定死信交换机和死信队列的路由key即可,因为这样只要队列消息一旦被拒绝就会被放到死信队列中
四 SpringBoot使用RabbitMQ
除了上面的直接使用RabbitMQ,还有一种方式使用RabbitMQ,是在Spring项目中,使用SpringBoot的Rabbit MQ依赖,使用注解的形式直接开发和使用Rabbit MQ,不需要去手动创建连接等。
先创建一个Maven项目,使用Jdk8
引入项目的依赖
<dependencies><!--RabbitMQ依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>fastjson</artifactId><version>1.2.47</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId></dependency><!--RabbitMQ测试依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.amqp</groupId><artifactId>spring-rabbit-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency>
</dependencies>
Spring配置文件
spring.rabbitmq.host=182.92.234.71
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=admin
spring.rabbitmq.password=123
案例简单使用
如下是本次案例的队列和交换机的结构图,两个队列的消息过期时间分别为10s和40s,消息过期后作为延迟消息放入到死信队列中进行消费。
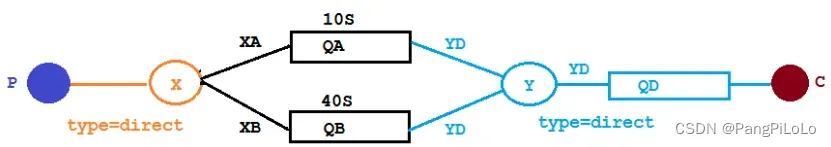
- 在SpringBoot中使用RabbitMQ,最好是在一个配置类中,将所有的队列以及交换机和绑定定义好
- 如下,通过生成Bean的方式,将交换机和队列构建为Bean对象,同时注入到Binging的构建Bean对象的方法中,然后生成出对应交换机和队列的绑定关系。
- 至于如何将队列和交换机以及绑定关系存入RabbitMQ或者说让RabbitMQ知道,那就是SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ的目的和结果了。
@Configuration
public class TtlQueueConfig {public static final String X_EXCHANGE = "X";public static final String QUEUE_A = "QA";public static final String QUEUE_B = "QB";public static final String Y_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE = "Y";public static final String DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE = "QD";// 声明 xExchange@Bean("xExchange")public DirectExchange xExchange(){return new DirectExchange(X_EXCHANGE);}// 声明 xExchange@Bean("yExchange")public DirectExchange yExchange(){return new DirectExchange(Y_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE);}//声明队列 A ttl为 10s并绑定到对应的死信交换机@Bean("queueA")public Queue queueA(){Map<String, Object> args = new HashMap<>(3);//声明当前队列绑定的死信交换机args.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", Y_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE);//声明当前队列的死信路由 keyargs.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "YD");//声明队列的 TTLargs.put("x-message-ttl", 10000);return QueueBuilder.durable(QUEUE_A).withArguments(args).build();}// 声明队列 A绑定 X交换机@Beanpublic Binding queueaBindingX(@Qualifier("queueA") Queue queueA,@Qualifier("xExchange") DirectExchange xExchange){return BindingBuilder.bind(queueA).to(xExchange).with("XA");}//声明队列 B ttl为 40s并绑定到对应的死信交换机@Bean("queueB")public Queue queueB(){Map<String, Object> args = new HashMap<>(3);//声明当前队列绑定的死信交换机args.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", Y_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE);//声明当前队列的死信路由 keyargs.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "YD");//声明队列的 TTLargs.put("x-message-ttl", 40000);return QueueBuilder.durable(QUEUE_B).withArguments(args).build();}//声明队列 B绑定 X交换机@Beanpublic Binding queuebBindingX(@Qualifier("queueB") Queue queue1B,@Qualifier("xExchange") DirectExchange xExchange){return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1B).to(xExchange).with("XB");}//声明死信队列 QD@Bean("queueD")public Queue queueD(){return new Queue(DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE);}//声明死信队列 QD绑定关系@Beanpublic Binding deadLetterBindingQAD(@Qualifier("queueD") Queue queueD,@Qualifier("yExchange") DirectExchange yExchange){return BindingBuilder.bind(queueD).to(yExchange).with("YD");}
}
- 生产者,只需要注入一个
RabbitTemplate既可向对应的交换机和队列发送消息。其中XA和XB是路由key
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("ttl")
@RestController
public class SendMsgController {@Autowiredprivate RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;@GetMapping("sendMsg/{message}")public void sendMsg(@PathVariable String message){log.info("当前时间:{},发送一条信息给两个 TTL队列:{}", new Date(), message);rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("X", "XA", "消息来自 ttl为 10S的队列: "+message);rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("X", "XB", "消息来自 ttl为 40S的队列: "+message);}
}
- 消费者代码通过使用
RabbitListener来监听消息。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DeadLetterQueueConsumer {@RabbitListener(queues = "QD")public void receiveD(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {String msg = new String(message.getBody());log.info("当前时间:{},收到死信队列信息{}", new Date().toString(), msg);}
}
