东明住房和城乡建设局网站上海官网seo
1.HTTP
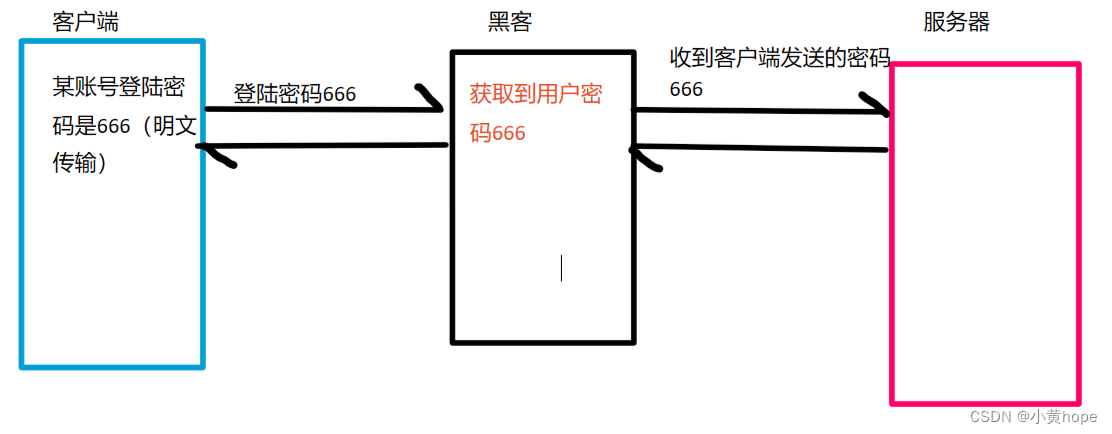
HTTP在传输数据时,通常都是明文传输,也就是传输的数据没有进行加密。在这种情况下,如果传输的是一些敏感数据,比如某银行卡密码,就很容易被别人截获到,这就对我们的个人利益产生了威胁。
HTTP传输数据时,数据安全无法得到保证:
2. HTTPS
如今,大多数网站使用的都是HTTPS。

对于HTTP的机制,HTTPS也同样适用。它们的区别在于,HTTPS在HTTP的基础上,在数据安全方面做了进一步改进。也就是说,HTTPS是基于HTTP,且进一步保证了数据的安全。
不加密的数据,放在网络中传输,就相当于"裸奔",黑客很容易就能获取到相关数据。数据安全问题受到了极大的威胁。
因此,在进行网络通信时,更安全的做法是,将传输的数据进行加密,特别是一些重要的数据,将数据加密之后,就算有人利用一些手段获取到了我们传输的数据,但由于数据是经过加密的,别人也很难破解数据,这样就在一定程度上保证了数据安全,HTTPS就做到了。
因此,如今大多数网站使用的都是HTTPS,HTTPS会将数据进行加密,加密的方式有:对称加密 和 非对称加密。
2.1 对称加密
对称加密,就是 客户端生成一个密钥,通过该密钥,可以对数据进行 加密 和 解密。客户端向服务器发送数据时,就会通过该密钥将数据进行加密,并将密钥传给服务器。
当服务器拿到数据和密钥后,就可以通过密钥对数据进行解密,从而拿到数据原文。不同的客户端,生成的密钥都不相同,因此服务器拿到不一样的密钥,就可以对 相应的数据 进行解密。
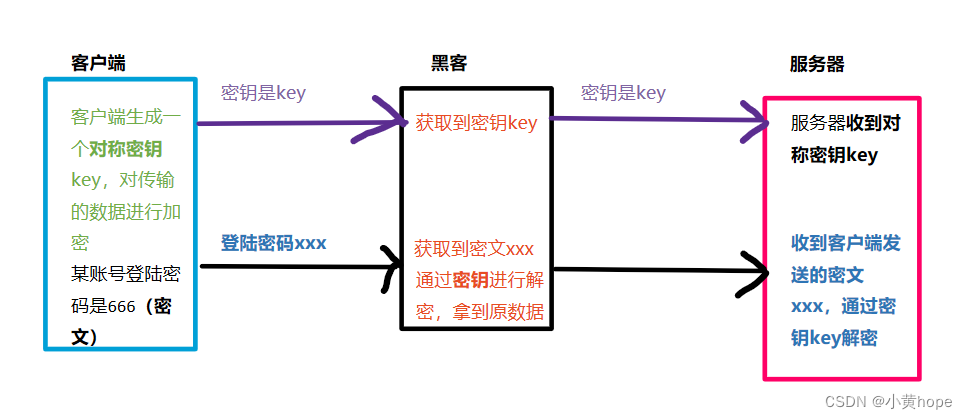
此时就存在一个问题,黑客也可以在数据传输的过程中,将密钥获取到,从而拿到数据原文,此时对 数据加密 也就形同虚设了。因此,密钥也应该被加密,这样即使黑客拿到密钥,但无法破解 加密的 密钥,就无法获取到原文数据了。对 密钥加密 就要需要 非对称加密 方式的帮助了。
2.2 非对称加密
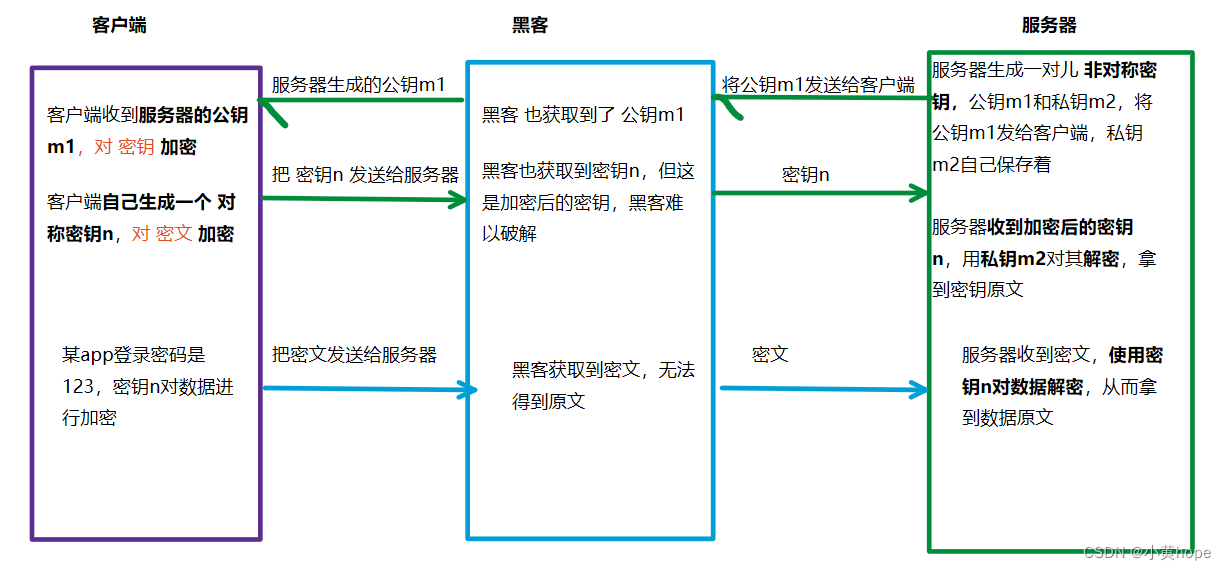
非对称加密,则是服务器生成一对儿密钥,分别是 公钥m1 和 私钥m2。可以通过公钥对数据进行加密,再通过私钥 对数据进行解密,反之也可。
双方在通信时,客户端会拿到 服务器持有的公钥m1,客户端也会以 对称加密 的方式生成一个密钥n。客户端会通过密钥n对数据加密,通过公钥m1对密钥n加密。
加密完成后,客户端就将 密文 和 加密后的密钥 发送给服务器,服务器就可以通过 私钥m2对加密过的 密钥 进行解密,拿到密钥原文。再通过 对称密钥n 对密文进行解密,从而拿到数据原文。
因此,对称加密 和 非对称加密 相结合,https使得数据安全得到了进一步保证,黑客想拿到数据原文,只获取到 加密的密钥 和 加密的数据,是不够的,因为黑客难以破解加密的密钥。
对称加密 和 非对称加密 两种方式相结合,通信过程如下:
通过以上方式,以 非对称加密的方式 对 对称密钥 加密,再通过 对称加密 对数据加密,从而保证数据的安全传输。这是 对称加密 和 非对称加密 两种加密方式的结合 来支持数据安全。
没有仅仅使用 非对称加密方式 来实现安全传输的 原因就在于 使用非对称加密 方式 所造成的成本开销较大,使得传输效率较低。因此 两种加密方式 相结合,不仅保证了数据的安全传输,也尽可能的减少开销成本。
此时,又有一个新的漏洞,即使 HTTPS 以 非对称加密 和 对称加密 相结合来传输数据,黑客仍能找到漏洞,将 服务器发送过来的 公钥 进行"偷梁换柱",从而窃取到数据,漏洞如下:
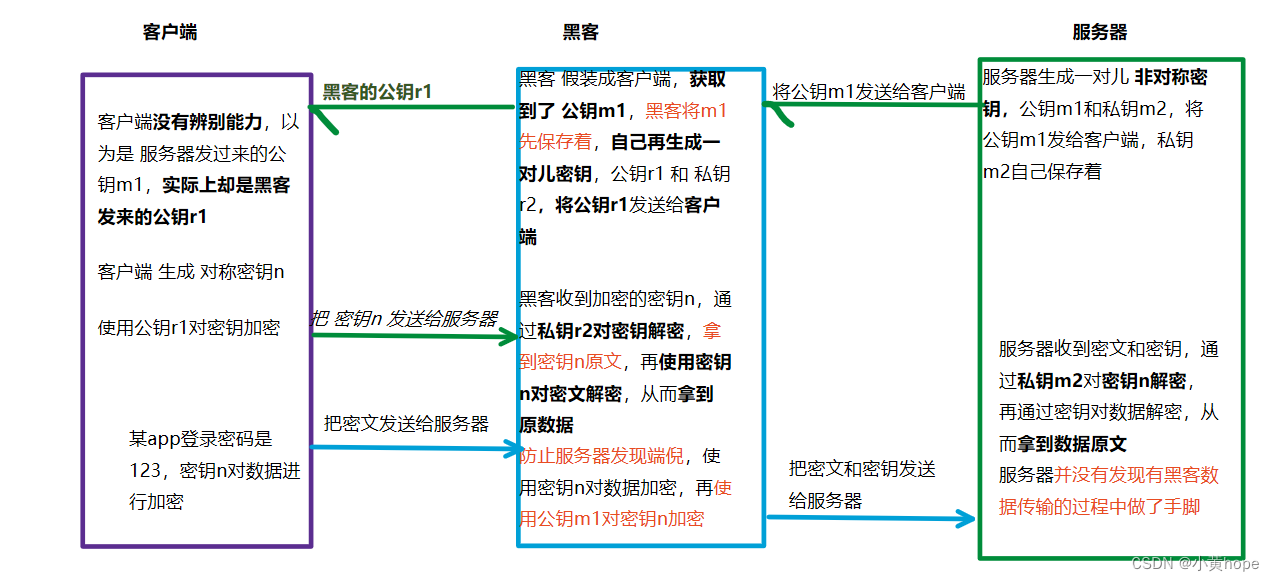
于是,黑客 就在数据的传输过程中 悄无声息的 做了手脚,客户端没有发现问题,服务器也没有发现问题,但数据已经被黑客窃取了。
因此,仅仅使用 对称加密 和 非对称加密 并不能真正保证数据的安全传输。客户端无法辨别自己收到的 公钥 到底是不是 服务器发过来的,无法完全信任。于是,就引入了第三方公证机构,客户端和服务器 都信任这个第三方机构,第三方机构就能 帮助客户端 鉴别这个公钥是否是服务器的公钥。
2.3 第三方公证机构
每个服务器在搭建的时候,都会以 非对称加密方式 生成一对儿 密钥,并且向 公证机构 提交审核材料(域名,服务器公钥,厂商等相关信息)。 公证机构就会对 材料进行审核,资质审核没问题的话,就会给服务器颁发一个证书(一段结构化数据),服务器则会保存好证书。
证书中的内容就包括 网站的域名,服务器的公钥,数字签名(颁发证书的时候,公证机构会根据证书的相关属性 计算出一个 校验和,并且公证机构也会 以 非对称加密 方式 生成一对儿 密钥,并且自己将私钥保留着,公钥则内置在 客户端的设备中。公证机构 通过 私钥 对 校验和加密,加密后的 校验和 就是 数字签名)等信息。
客户端向服务器发送信息之前,会先向服务器 索要证书。客户端收到服务器发送过来的证书,也就收到了 服务器的 公钥。收到证书后,客户端会有一个 "证书校验"的过程。这个过程就是为了 验证 证书中的公钥是不是服务器生成的公钥。
证书校验:校验的核心在于 “数字签名”,客户端通过设备内置的公钥 对数字签名解密,从而拿到 校验和。客户端再通过相同的方式 计算一遍校验和,如果自己计算的校验和 和 服务器发来的校验和 一致的话,则说明这个公钥就是 服务器的公钥。于是,客户端就可以放心的使用 服务器发来的公钥了。
有了以上过程,黑客就很难再窃取到数据了,即使黑客在客户端收到证书之前,先对证书进行篡改,比如 修改公钥(如果黑客替换了了服务器的公钥,那么客户端在进行校验和计算的时候,计算的校验和结果则会与证书中的校验和不一致),修改数字签名(既然无法替换公钥,干脆 黑客直接替换公钥,再替换 数字签名。但 数字签名 是被 公证机构的 私钥 加密过的,且公钥在客户端设备上,黑客无法拿到 校验和原数据),申请一个证书(服务器的证书内容无法更改的话,黑客能否直接申请一个证书,直接在服务器证书的传输过程中,直接替换掉证书,但是 申请证书有资质审核的环节,因此黑客无法申请到证书)。
【总结HTTPS加密机制】
(1)通过 对称加密 和 非对称加密 相结合,对 数据 和 密钥 加密;
(2)再引入 第三方公证机构,防止 有人 "偷梁换柱",替换服务器的公钥。
通过以上方式的相结合,HTTPS就可以在 极大程度上 保证了 数据的安全传输。因此,如今绝大多数的网站使用的都是HTTPS。

