上海网站优化公司百度深圳总部
01 背景
我们之前在使用ArcGIS出现导出Excel中文乱码及shp添加字段3个字被截断的情况,我们有以下应对策略:
![]()
推荐阅读:ArcGIS导出Excel中文乱码及shp添加字段3个字被截断?
那如果我们使用ArGIS Pro出现上述问题,该如何解决呢?
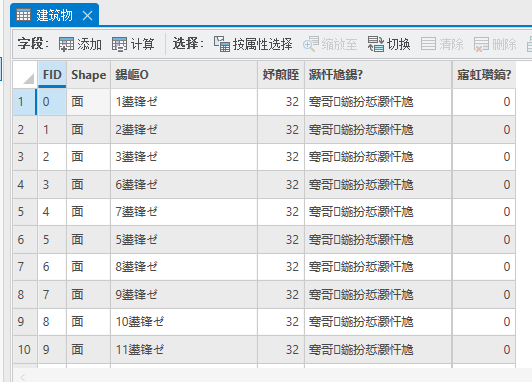
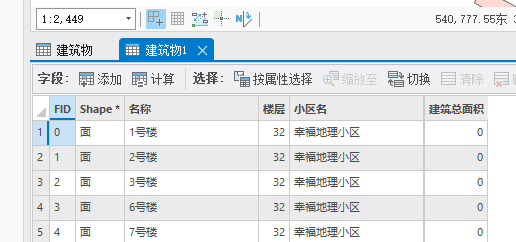
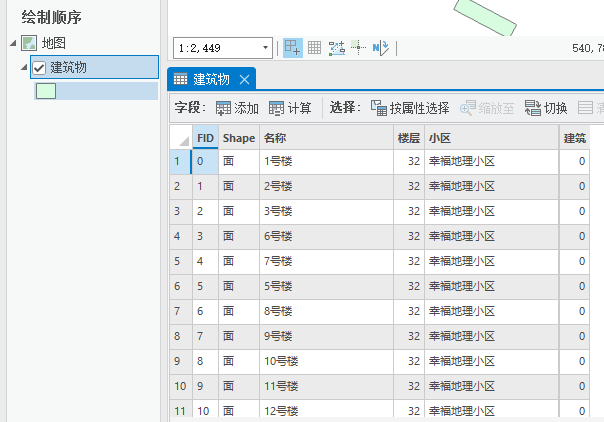
例如,我们要对下列的shp数据添加一个字段,字段名称为“建筑总面积”,
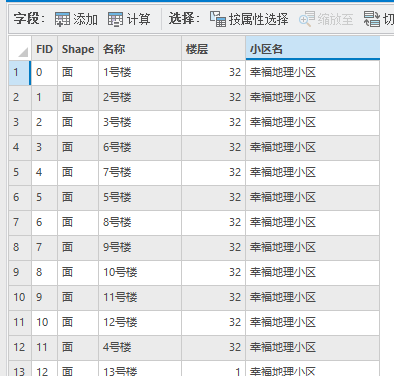
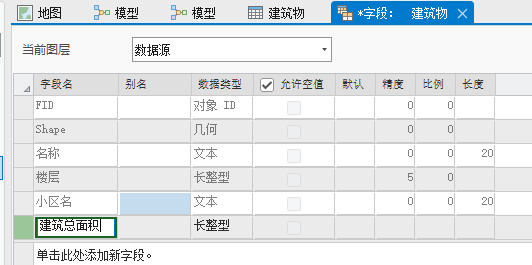
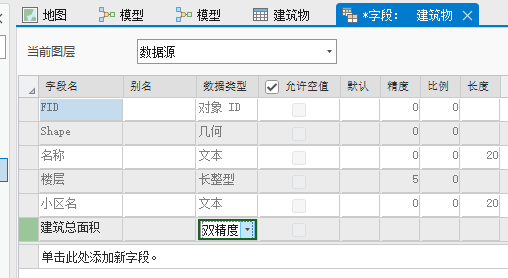
当我们保存的时候
保存后,字段就被自动截断为三个字,
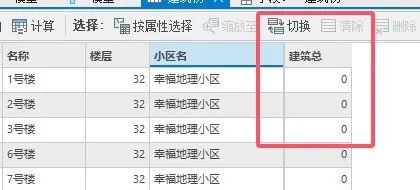
原因就是,shp的字段是名称是限制10个字符的,采用默认的utf-8的编码,一个汉字是3个字符,10个字符只能容纳3个汉字,如果我们把编码改为GBK,一个汉字占用2个字符,就可以最多容纳5个字符。
还有当我们打开一个shp发现属性表乱码时我们可以怎么解决?
02 解决方案
解决方案也很简单,和之前ArcGIS10.X系列的解决方案是一样的。
我们主要介绍4个方面的内容:
-
cmd命令提示符更改注册表
-
注册表管理器手动更改注册表
-
修改无效的原因(cpg文件)
-
属性表乱码的解决
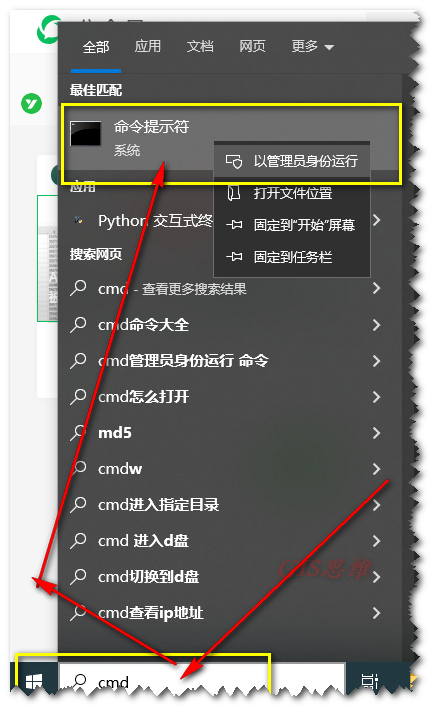
1 cmd命令提示符更改注册表
在开始搜索栏输入cmd,以管理员模式启动CMD(命令提示符):
输入如下代码:
ArcGIS Pro更改字符编码注册表语句:
reg add HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\ESRI\ArcGISPro\Common\CodePage /v dbfDefault /t REG_SZ /d 936 /f
输入后按Enter
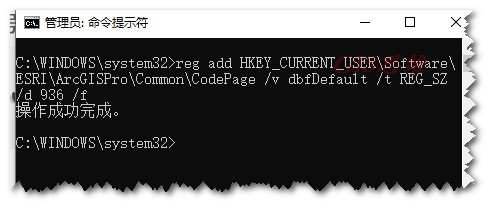
提示成功后重启ArcGIS Pro即可。
2 注册表管理器手动更改注册表
在开始搜索栏输入注册表管理器,
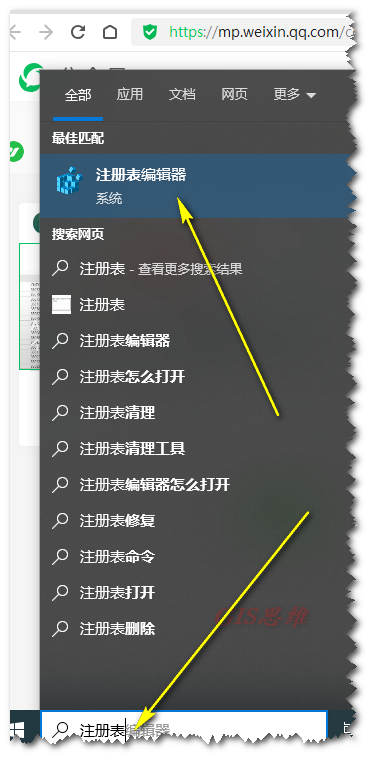
找到
\HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\ESRI\ArcGISPro\Common\CodePage
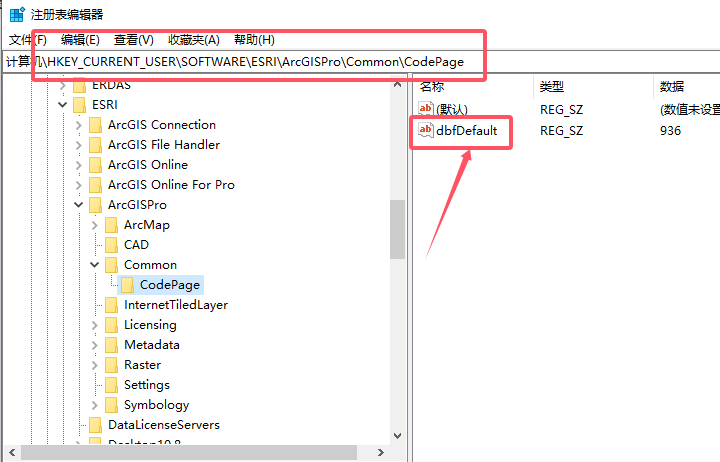
对dbfDefault右键选择修改为936
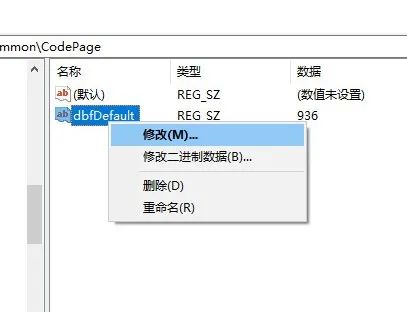
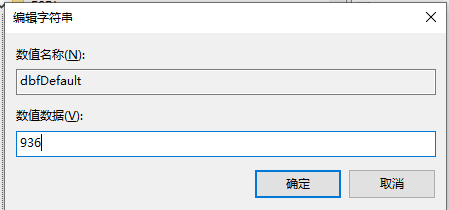
确定后重启软件即可

3 修改无效的原因(CPG文件)
有时候我们在修改以上注册表的时候还是没能解决以上问题,那会是什么问题导致的呢?
我们这个时候可以观察,最初的shp的组成文件里面一般有一个cpg文件。
什么是cpg文件呢?.cpg 是shp文件组织结构的 可选文件,指定用于标识要使用的字符集的代码页。
参考下列:Shapefile 文件扩展名
https://desktop.arcgis.com/zh-cn/arcmap/latest/manage-data/shapefiles/shapefile-file-extensions.htm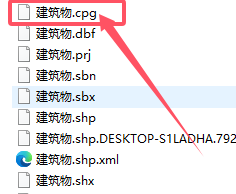
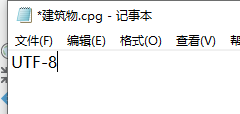
以记事本打开,显示为UTF-8。
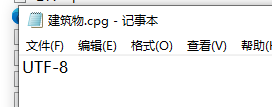
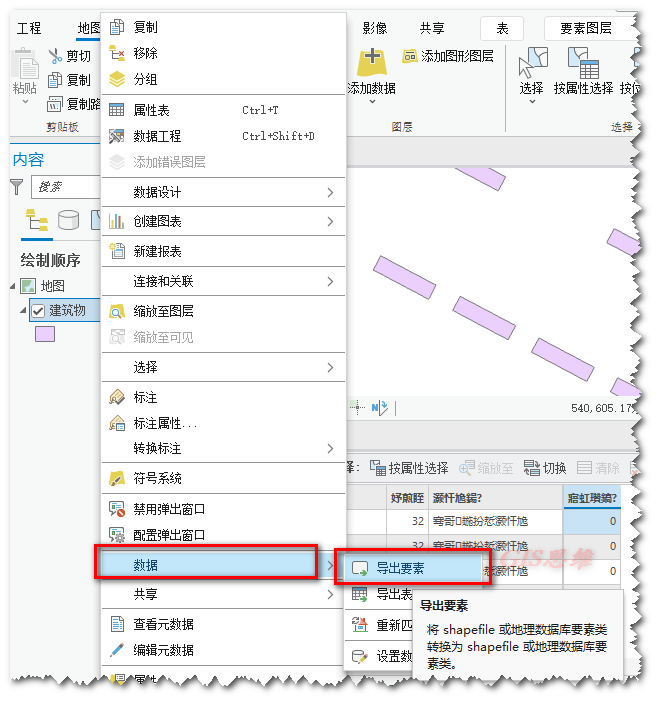
所以问题就出在这里,即使哦们将系统的字符编码改为了936(GBK),但是数据本身指定了UTF-8的数据编码,所以出现了问题,这个时候我们只需要将数据重新导出数据一份就可以,新生成的数据将不再带有CPG文件,默认GBK的字符编码了。
新导出的数据不再有CPG文件
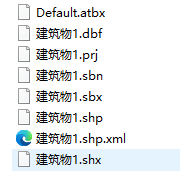
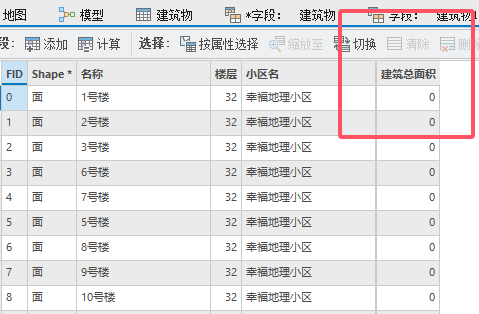
再去添加字段就可以了。
4 属性表乱码的解决
有时候我们在打开属性表后发现汉字显示乱码的情况。

第一步骤要做的就是如1、2步骤所述将系统的字符编码将UTF-8改为GBK,改完之后能解决最好,不能解决还是乱码,那会是什么原因引起的呢?这个时候大部分是由于先前的创建shp文件的时候是有cpg文件,在文件传输的过程中cpg文件丢失或者在cpg文件中指定了错误的编码。
如果是cpg缺失,你可以尝试新建一个和shp同名的txt记事本文件,然后输入编码:可以分别写入UTF-8、936、OEM等尝试,然后将文件的.txt后缀改为,cpg,这个时候只要指定了正确的字符编码,属性表就会恢复正常。
![]()
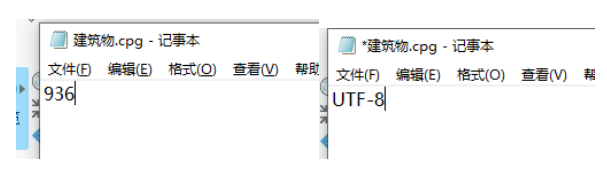
一般在我们修改了系统的默认字符为GBK后,属性表还是乱码的情况,且cpg文件丢失的情况那么一般原始shp的cpg的字符编码就是UTF-8 ,所以一般上上面写入编码时第一个就测试UTF-8的编码。
那如果是原来就存在cpg还是乱码的情况,一般就是cpg文件的编码指代错误,比如将编码指定为936,但是实际编码为UTF-8,这个时候打开cpg(记事本打开)直接将936改为UTF-8就好。
基本如上操作后属性表就恢复正常哦。

休息

一起来参加我们的系统学习吧
